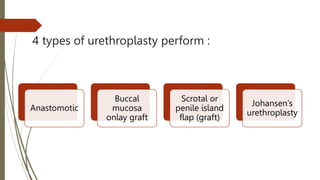
Urethroplasty is a surgical repair of the urethra to treat injuries or defects caused by trauma, medical procedures, or infections. There are several types of urethroplasty procedures that can be used depending on the location and severity of the damage. The surgery involves accessing and repairing the damaged part of the urethra by removing or rebuilding the strictured tissue. Grafts from the mouth, genitals, or rectum may be used to supplement the repair. After closing the incision, a catheter is placed to allow the urethra to heal while draining urine, and is usually kept in place for two weeks. Potential complications include bleeding, infection, erectile dysfunction,