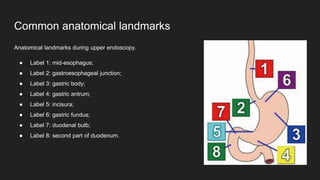
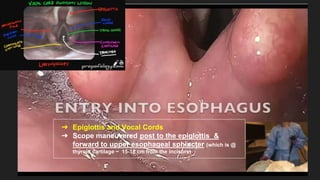
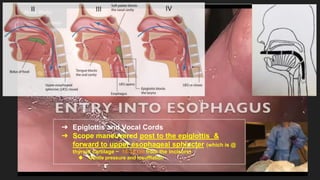
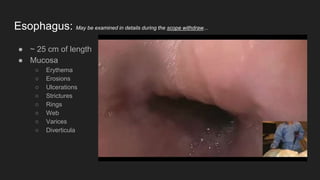
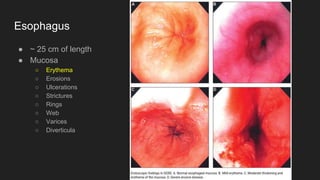
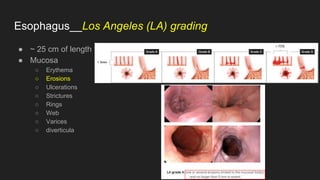
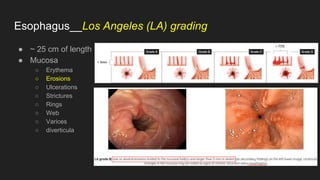
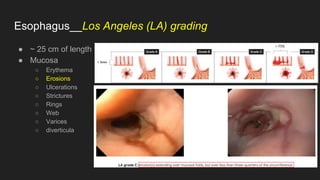
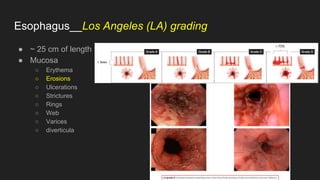
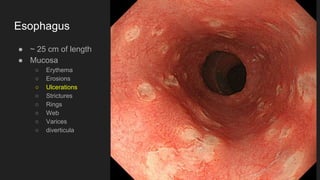
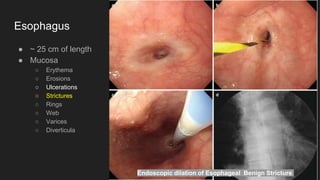
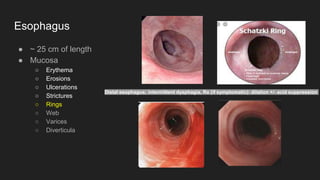
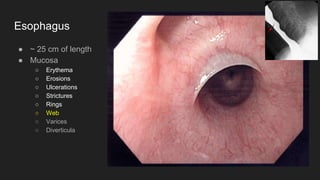
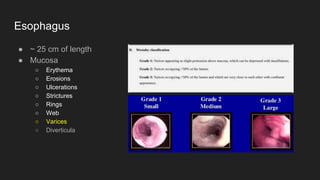
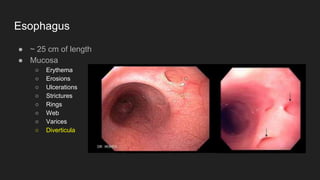
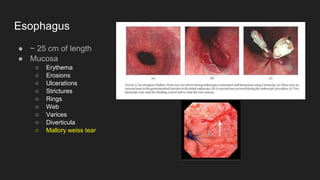
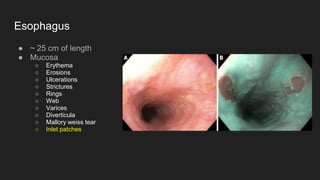
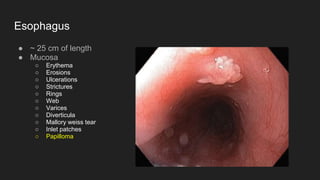
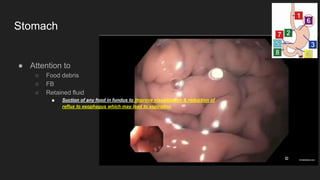
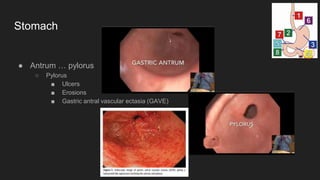
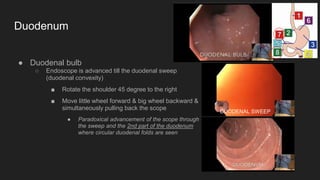
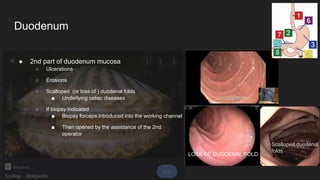
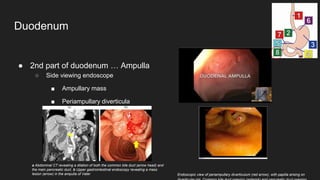
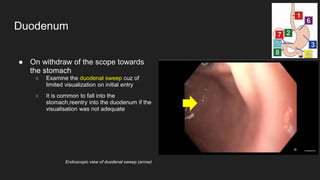
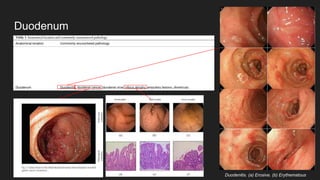
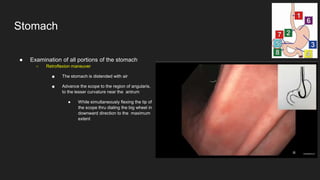
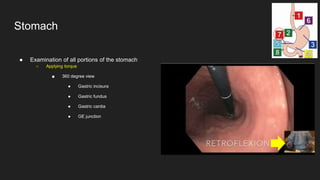
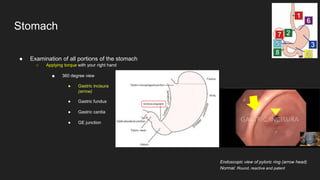
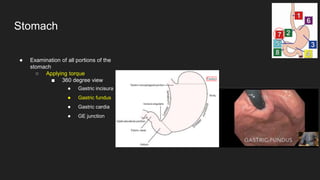
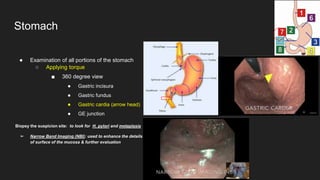
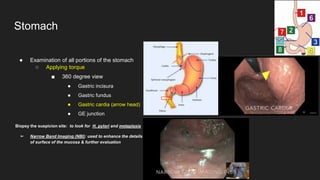
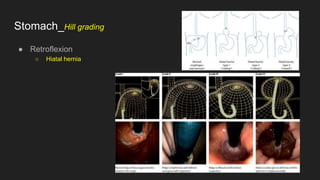
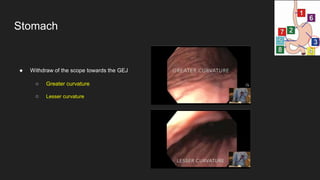
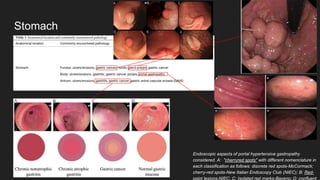
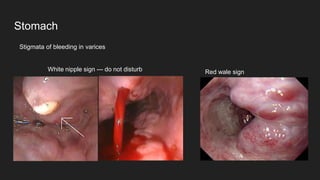
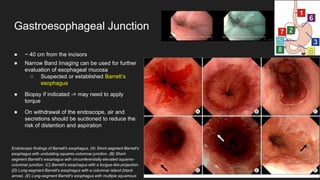
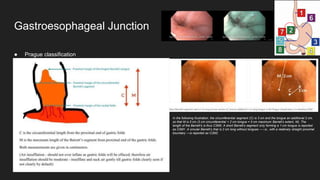
The document describes common anatomical landmarks seen during an upper endoscopy procedure. It lists the main areas examined, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Key landmarks are identified, such as the gastroesophageal junction and specific areas of the stomach and duodenum. Common findings and techniques for a thorough exam, such as retroflexion and applying torque, are also outlined.