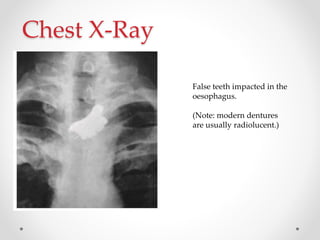
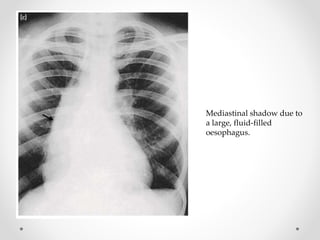
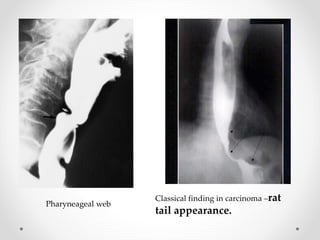
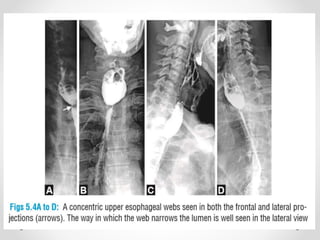
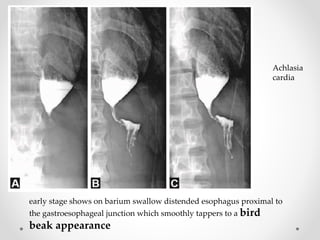
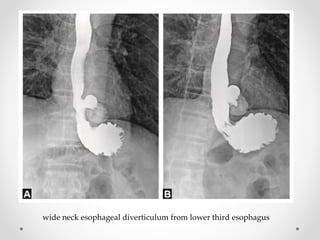
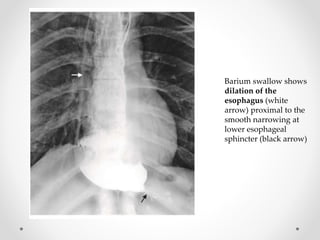
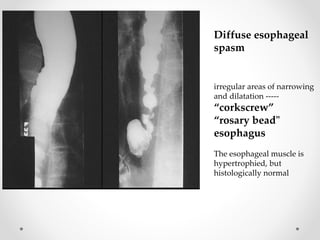
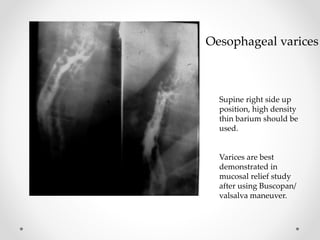
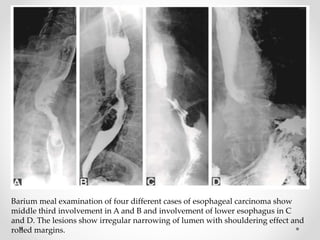
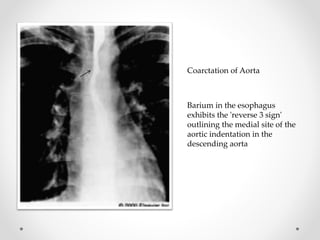
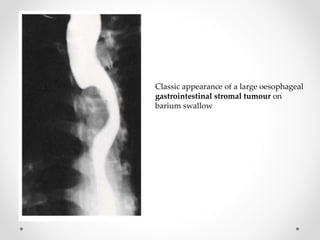
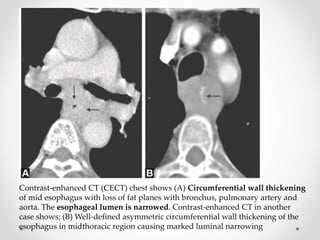
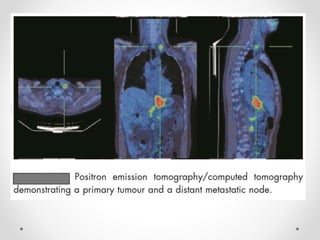
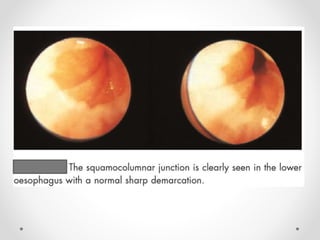
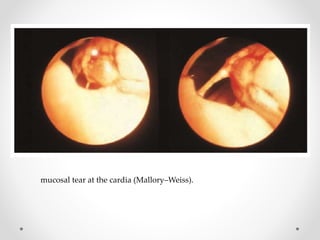
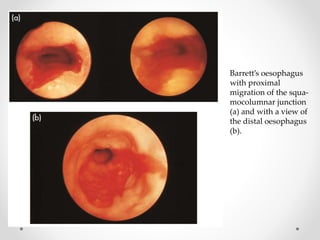
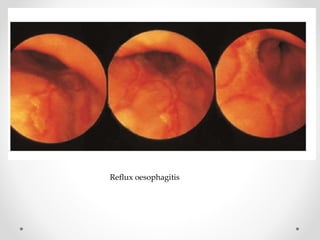
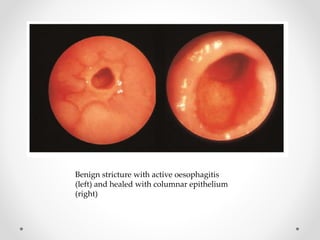
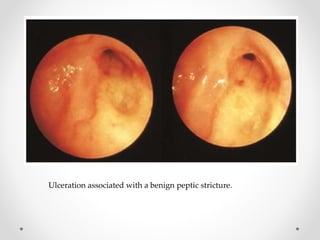
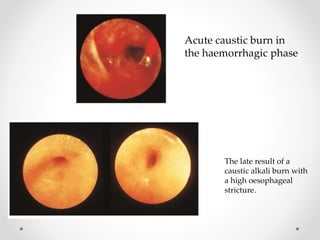
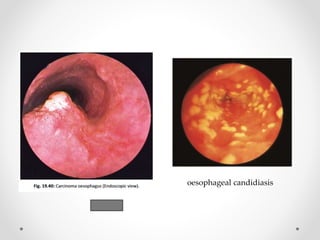
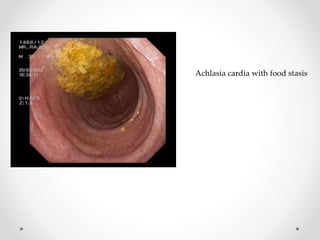
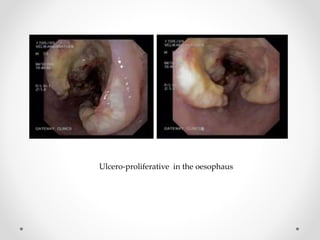
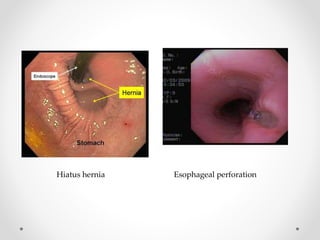
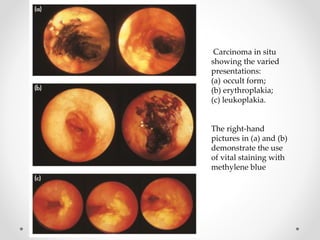
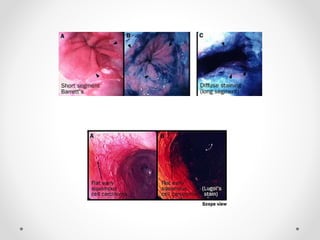
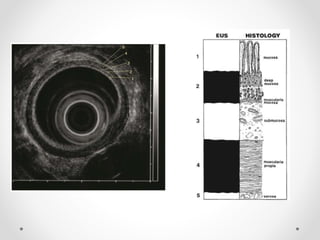
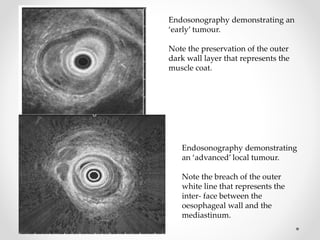
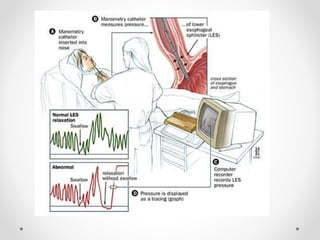
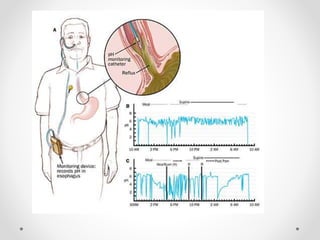
Barium swallow, endoscopy, endosonography, and manometry are key investigative tools for evaluating abnormalities of the esophagus. Barium swallow involves ingesting barium sulfate to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and surrounding structures on x-ray. Endoscopy allows direct visualization of the esophagus and biopsy of lesions. Endosonography uses high-frequency sound waves to image the esophageal walls and nearby structures. Manometry assesses esophageal motility and sphincter function by measuring pressure during swallowing. Together these investigations aid in diagnosing conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease, tumors, and motility disorders of the esophagus.