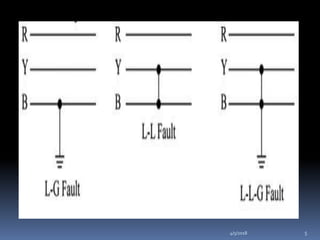
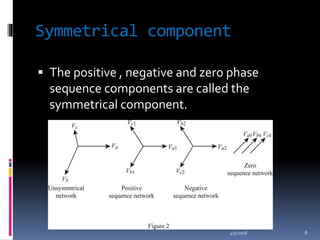
This document discusses unsymmetrical faults in power systems. It defines unsymmetrical faults as faults that lead to unequal currents with unequal phase shifts in a three-phase system. These faults can occur due to open circuits or short circuits in transmission or distribution lines caused by natural disturbances or human errors. The document describes the types of unsymmetrical faults and the problems they cause, such as changes in phase sequences and impedance values. It explains that symmetrical component analysis is the preferred method for removing unsymmetrical faults because it is a simple method that provides a useful tool for fault protection and tracking fault currents.