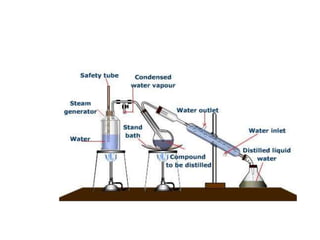
Bitumen is a naturally occurring semi-solid form of petroleum that is formed from the remains of ancient algae and other organisms. It is refined from crude oil through processes like vacuum steam distillation. Tar is a similar black, thermoplastic material produced from the destructive distillation of coal. Both were widely used in the early 20th century as binders for road construction, leading to the term "tarmac". Bitumen has properties that make it a strong adhesive and durable sealant for engineering projects like roads. Various tests are conducted to evaluate properties like viscosity and durability.