The document discusses factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions, including:
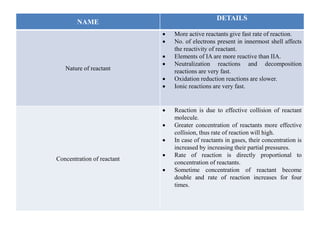
1) The nature and concentration of reactants - more active and concentrated reactants lead to faster reactions.
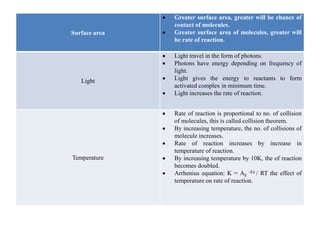
2) Surface area - greater surface area of reactants means more chances for molecular contact and a faster rate.
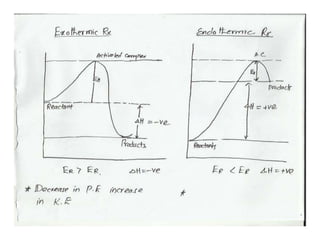
3) Temperature - higher temperatures increase molecular collisions and double the reaction rate with every 10K increase.
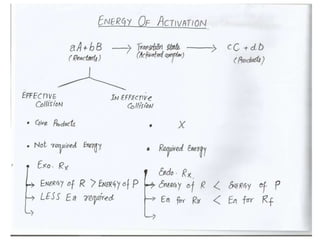
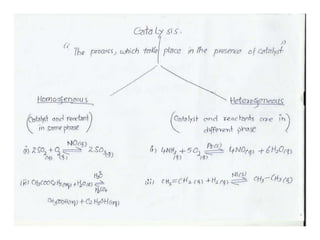
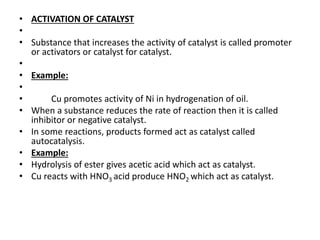
4) Catalysts - catalysts speed reactions by lowering activation energy without being used up in the reaction. Characteristics and types of catalysts are described.