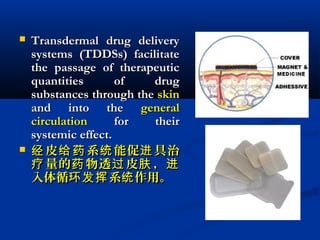
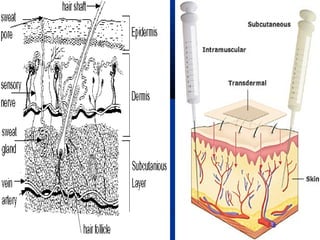
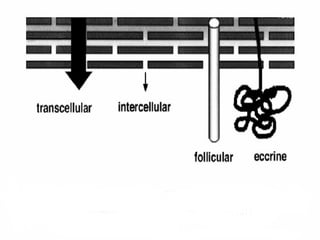
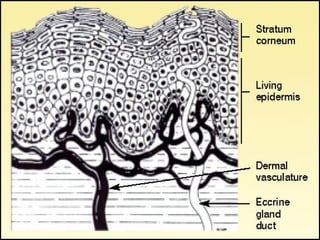
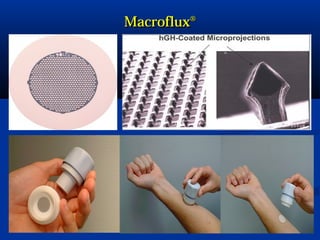
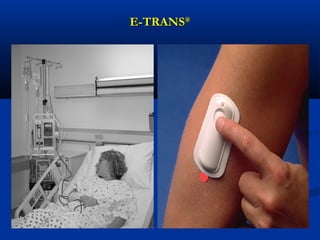
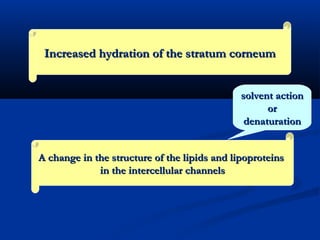
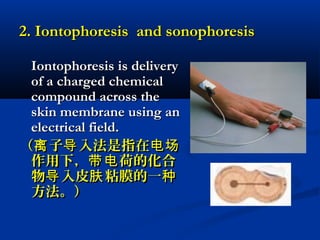
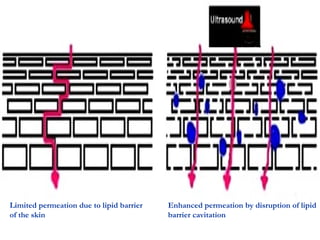
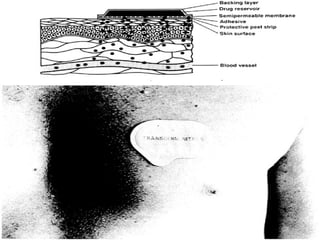
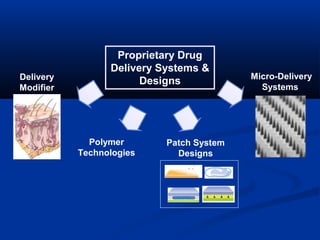
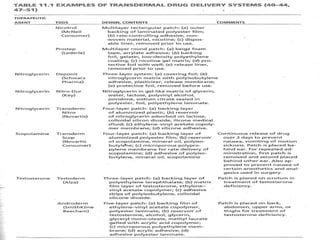
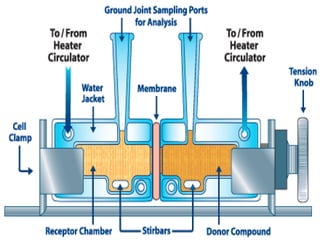
Transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDSs) facilitate the passage of therapeutic quantities of drug substances through the skin and into systemic circulation for their effect. Key factors that affect percutaneous absorption include drug properties like concentration, molecular weight, solubility as well as skin properties like hydration and thickness of stratum corneum. Chemical enhancers and physical methods like iontophoresis and sonophoresis can increase skin permeability. The selection of a permeation enhancer is based on its efficacy, dermal toxicity, and compatibility with other components. Drugs delivered through TDDSs provide benefits over other routes of administration like avoidance of first-pass metabolism and improved patient compliance.