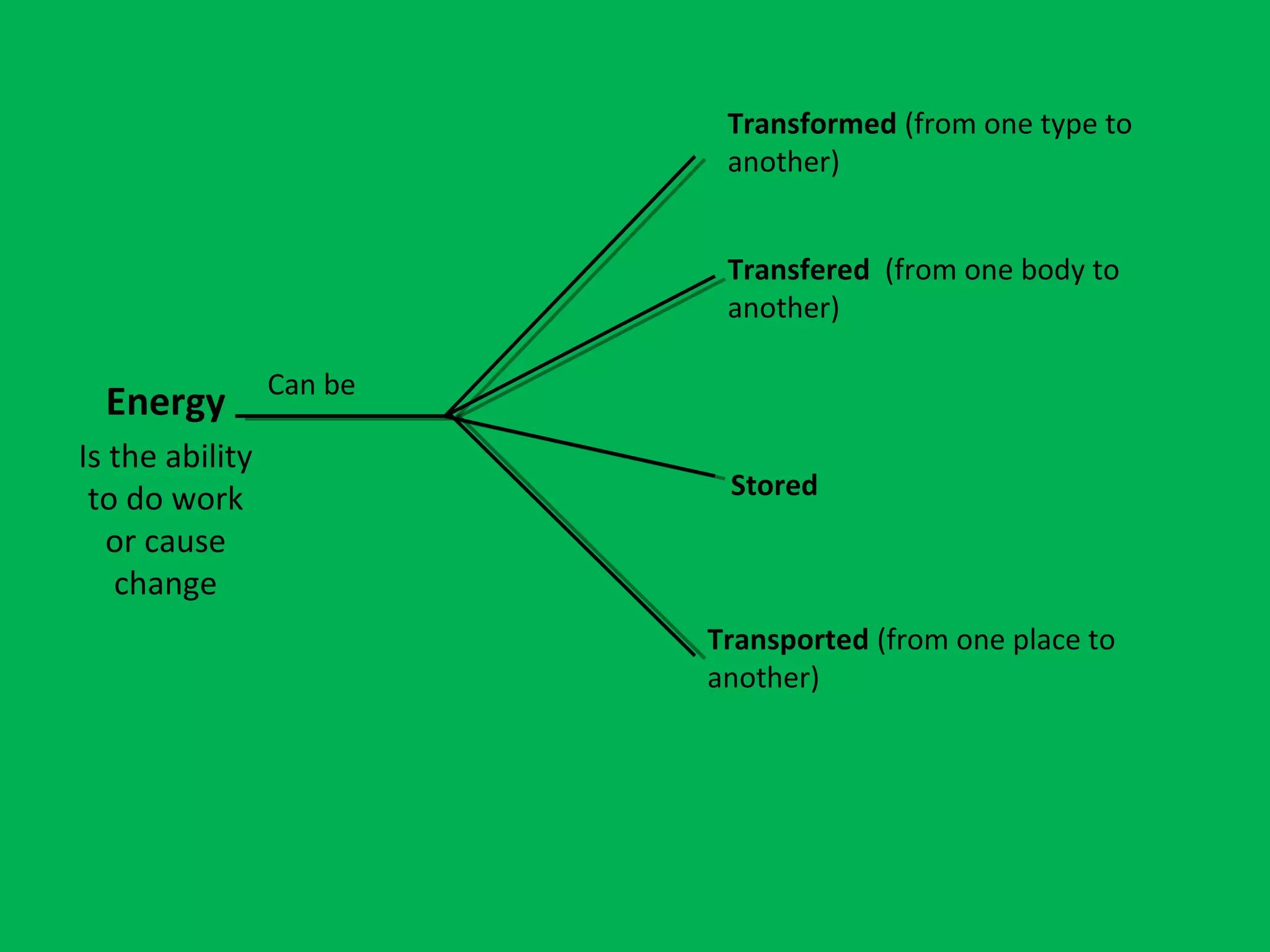
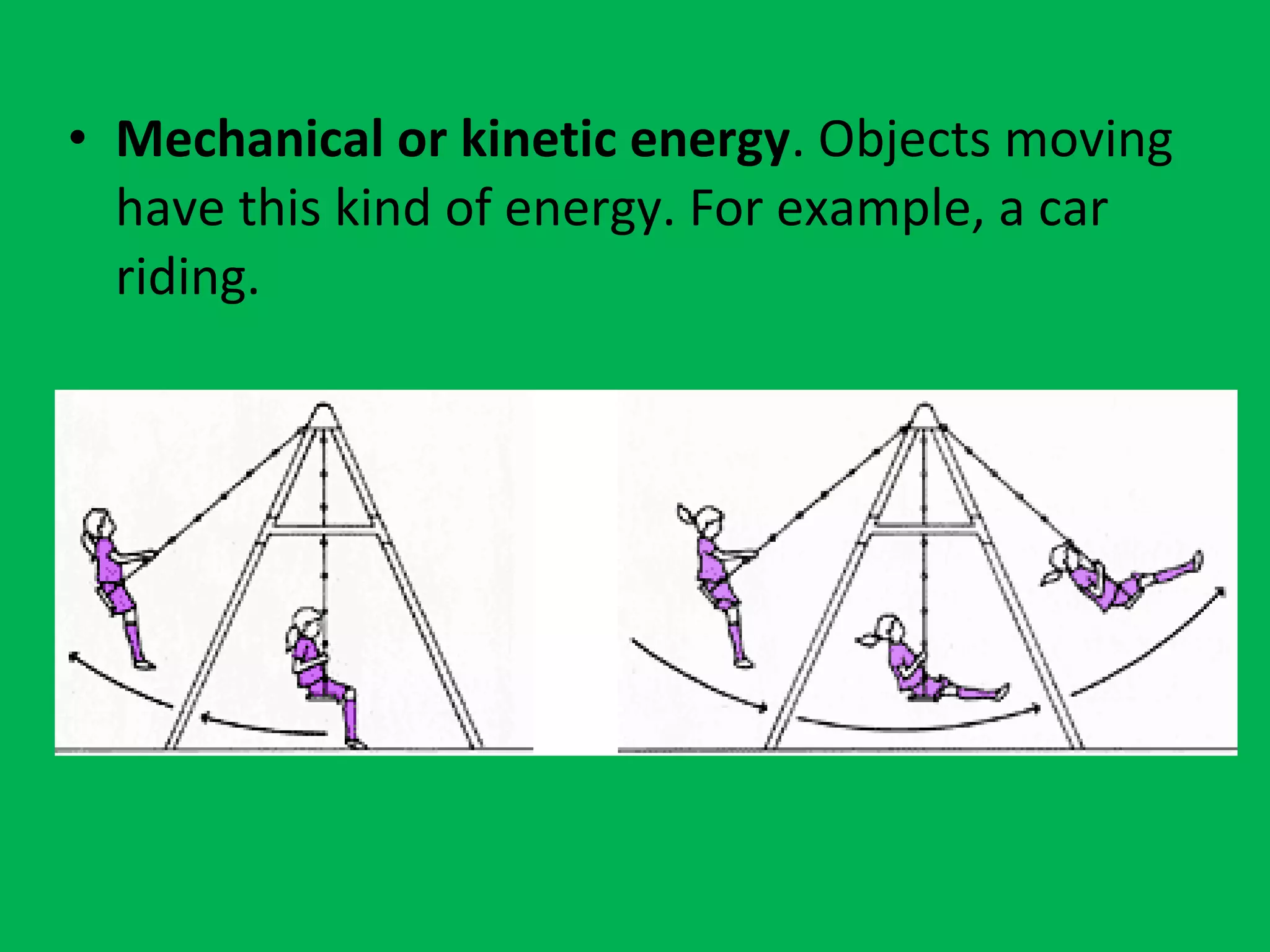
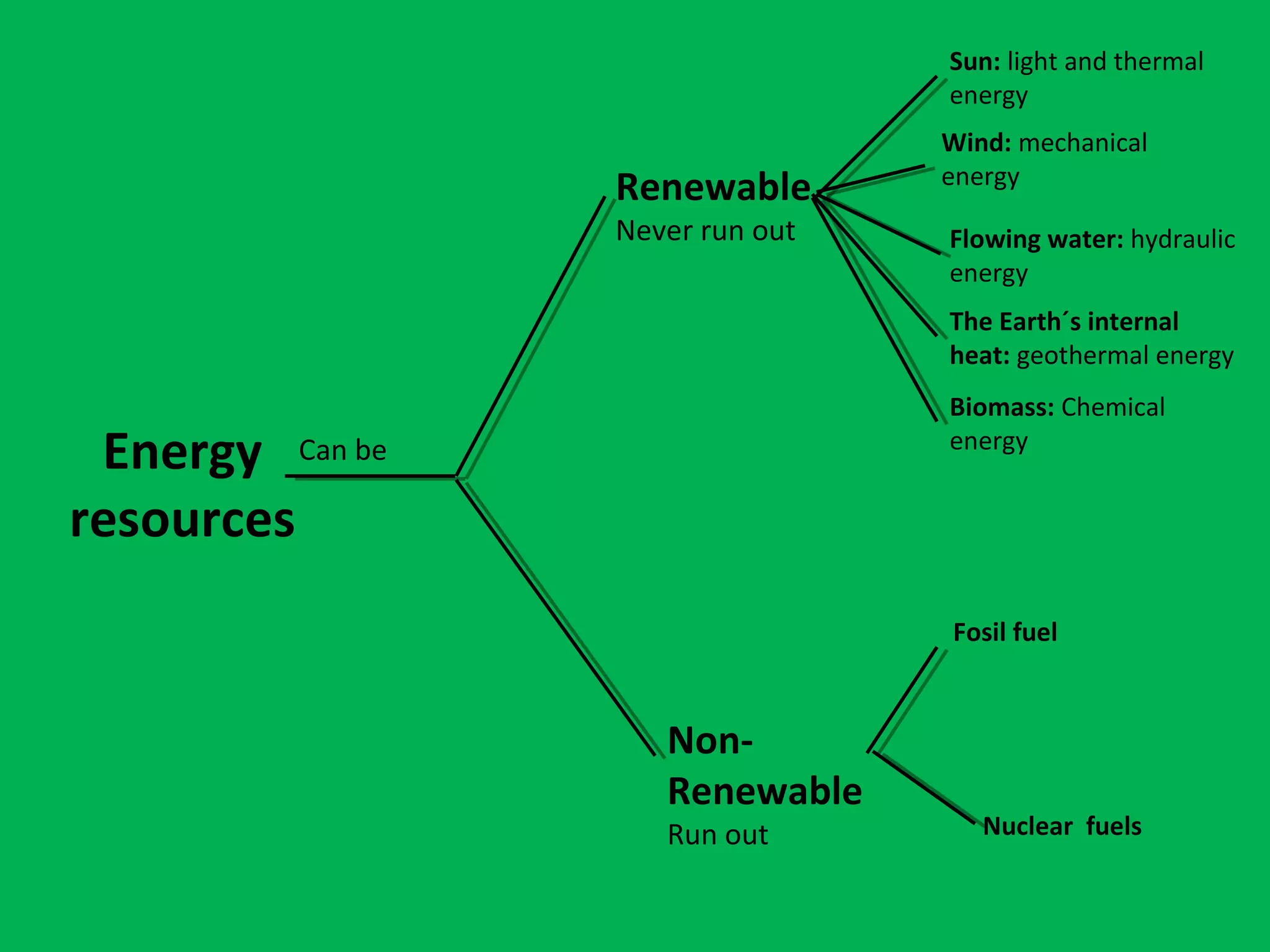
This document discusses energy, including its properties, types, sources, and consequences of use. It defines energy as the ability to do work or cause change, and explains that energy can be transformed, transferred, stored, and transported. The types of energy covered are chemical, light, nuclear, mechanical, thermal, and electrical. Energy sources are categorized as either renewable, including solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass, or non-renewable, such as fossil fuels and nuclear fuels. The document notes that non-renewable resources will run out over time.