This document provides notes on the key concepts of energy:
1. Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change.
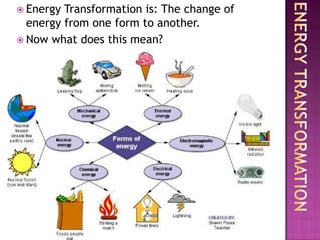
2. Energy transformation is the change of energy from one form to another.
3. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another.