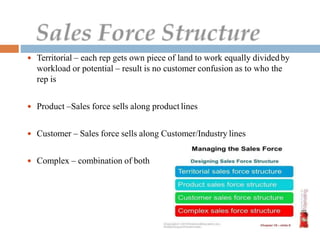
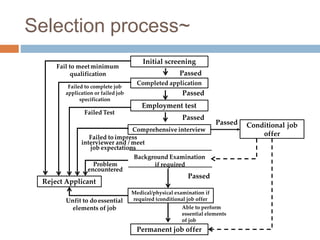
The document discusses key aspects of sales force management including:
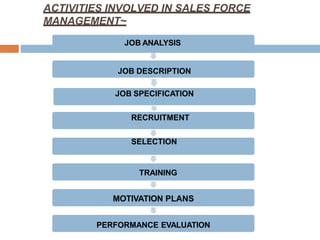
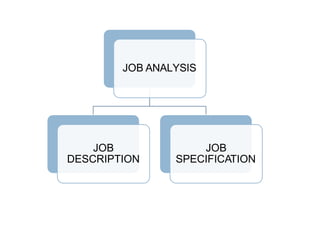
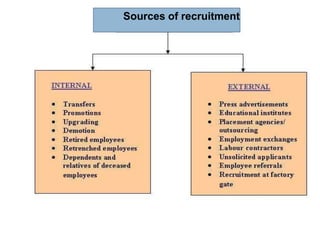
1. The activities involved in sales force management such as job analysis, recruitment, selection, training, motivation, and performance evaluation.
2. Different selling styles a company can use such as representative to buyer, sales team to buyer group, and conference selling.
3. Factors to consider when determining sales force size such as number of customers, call frequency, and representative workload.
4. The importance of training the sales force to adapt to changes in technology, structure, and diversity.
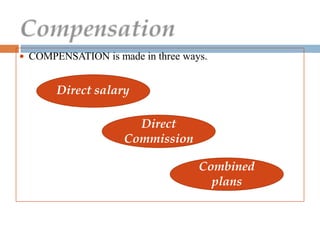
5. Methods of motivating the sales force including compensation plans involving salary, commission, or a combination.
6. The process of evaluating sales force performance against