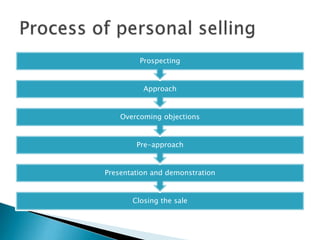
The document discusses several aspects of sales including:
1) Selling has a reputation for hard selling but most sales involve tasks to support the sale rather than direct selling.
2) Sales force organization determines the type and size of sales force which impacts control and profits.
3) Recruitment finds candidates while selection chooses among candidates. Sources can be internal promotion or external hiring.
4) Training prepares new salespeople for their jobs with knowledge and skills developed through organized learning programs.