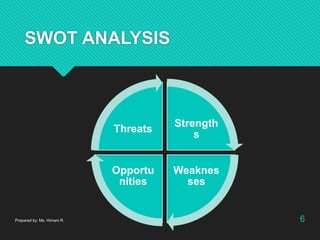
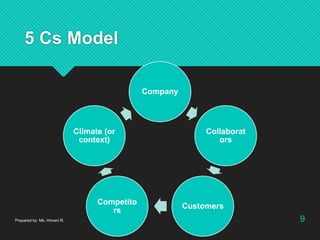
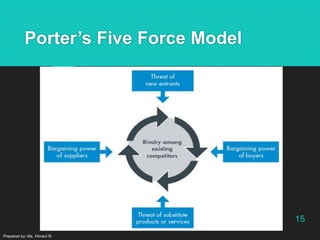
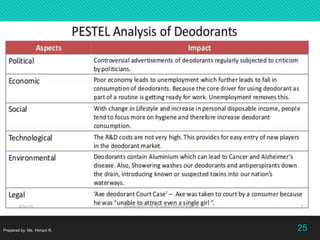
The document discusses advertising and campaign planning. It begins with an overview of components like situation analysis, objectives, and strategies. It then covers topics like the SWOT analysis, 5Cs model, Porter's Five Forces, and PEST analysis to evaluate opportunities and threats. The document also outlines developing an advertising plan, including targeting audiences, messaging, and media. It discusses objectives, the DAGMAR approach, and measuring advertising effectiveness. The overall summary is that the document provides an in-depth overview of analyzing a marketing situation and developing an advertising strategy and campaign.