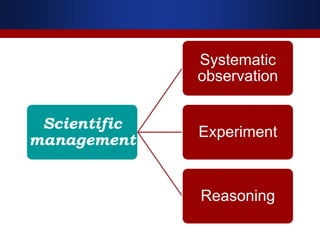
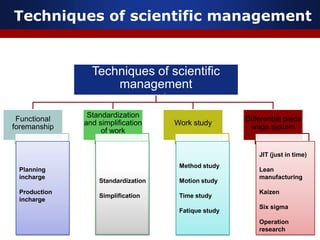
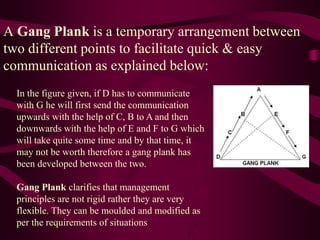
This document summarizes key concepts from principles of management theorists Frederick Taylor and Henri Fayol. It discusses Taylor's scientific management principles including finding the most efficient work methods and harmony between management and workers. Fayol's 14 principles of management are also outlined, such as division of work, authority, and unity of command. The document provides an overview of the foundational ideas developed by these early management thinkers.