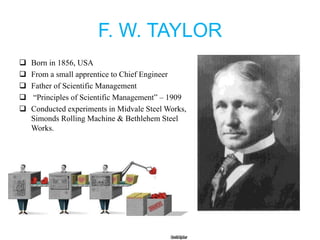
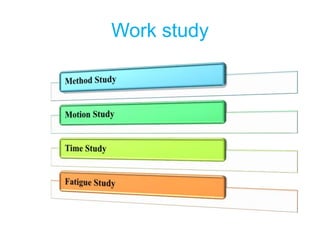
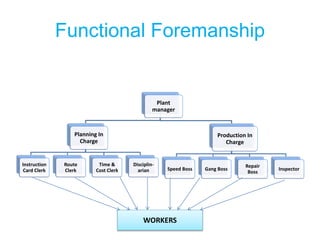
Scientific management is an approach to managing organizations that focuses on improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It analyzes workflows to improve efficiency and aims for cooperation between workers and management. The core principles include replacing old rule-of-thumb methods with scientific approaches, scientifically selecting and training workers, achieving maximum output through cooperation between workers and management, and equal division of responsibilities between planning and execution. F.W. Taylor is considered the father of scientific management and conducted experiments applying its principles in steel mills in the early 1900s.