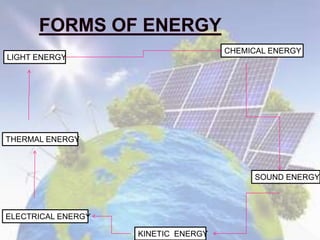
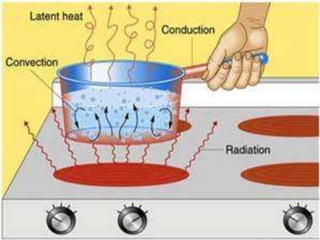
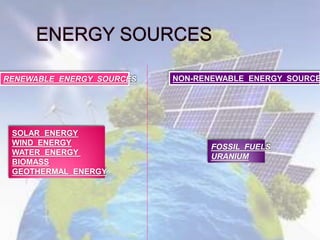
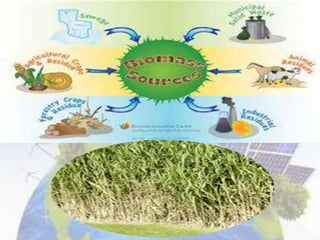
This document discusses different forms of energy: light energy, chemical energy, sound energy, kinetic energy, electrical energy, and thermal energy. It provides examples of different renewable and non-renewable energy sources, how they are used, and their environmental impacts. Key renewable sources mentioned include solar, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal, while non-renewable sources include fossil fuels and uranium. The document also covers electricity and magnetism.