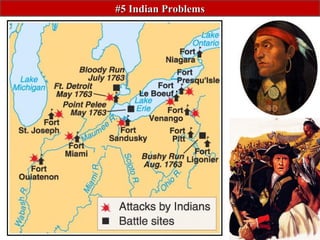
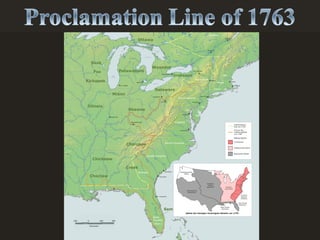
The document summarizes Britain's changing policies towards its American colonies from the mid-17th century to the 1770s. It begins with a policy of "salutary neglect", where Britain left the colonies alone as long as they were profitable. However, after the French and Indian War, Britain adopted a more controlling "hands on" approach to try to pay off war debts and manage its lands. This included passing new taxes like the Stamp Act to directly tax the colonies, leading to protests by colonists who argued they were being taxed without representation.