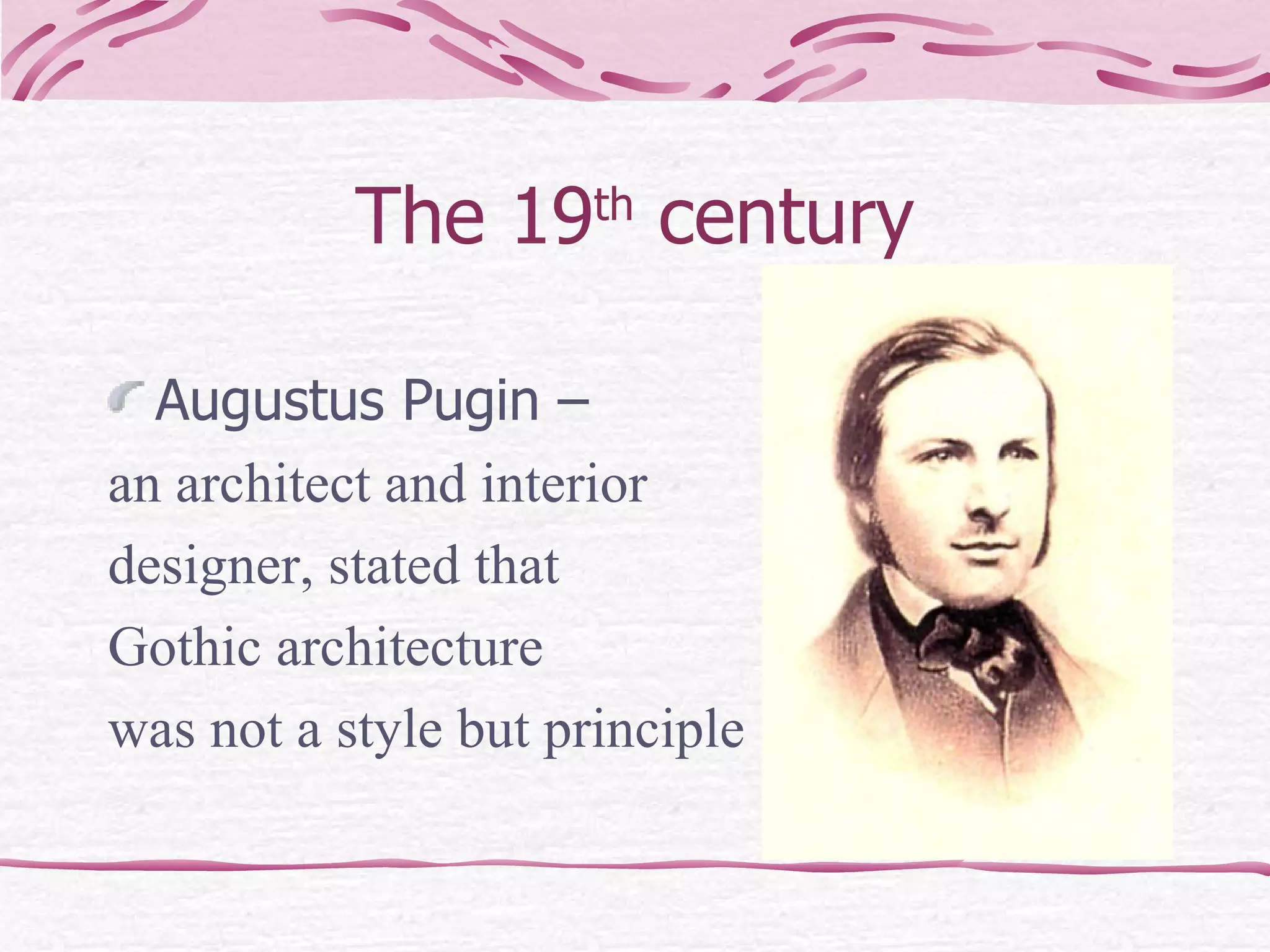
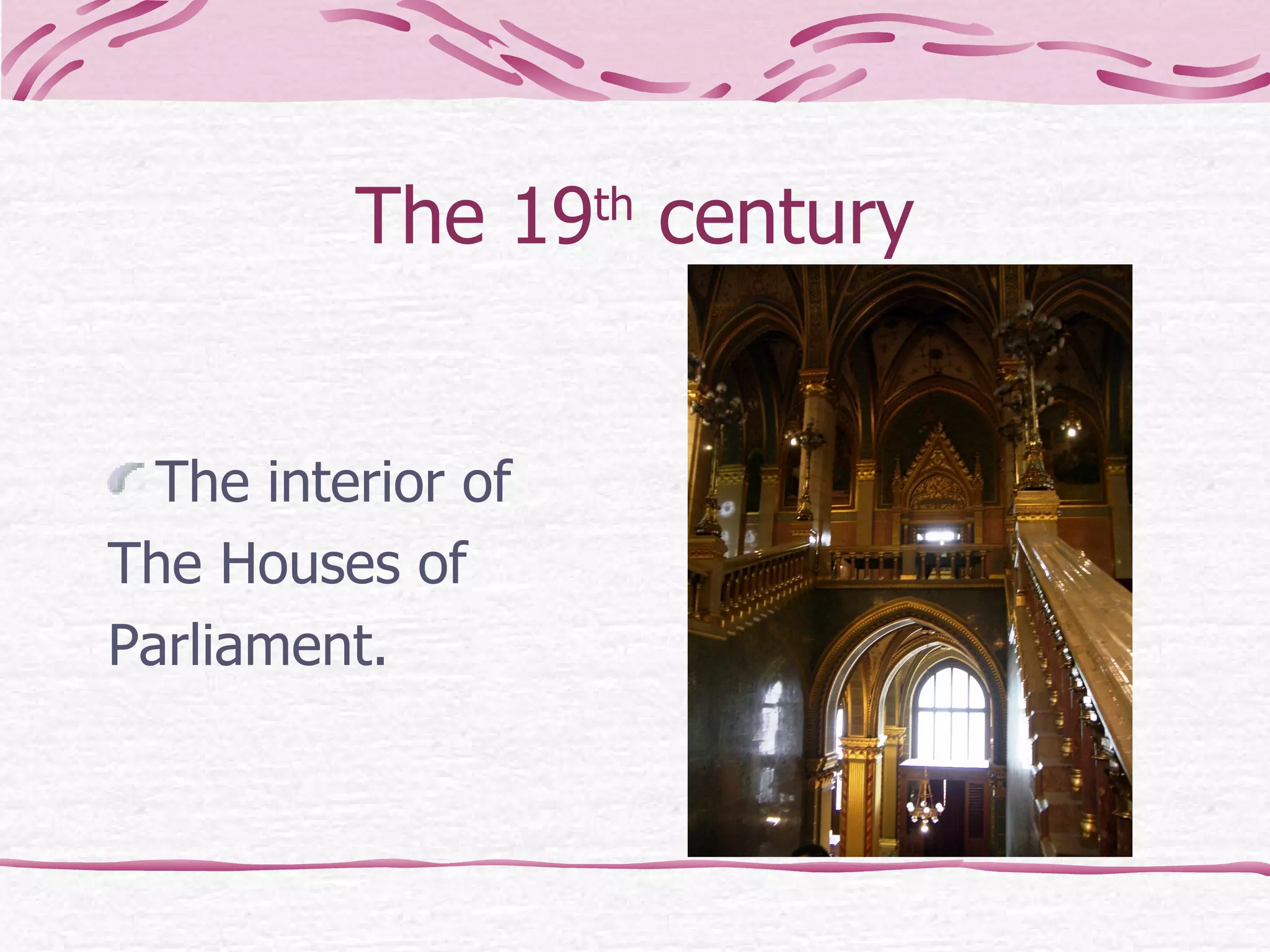
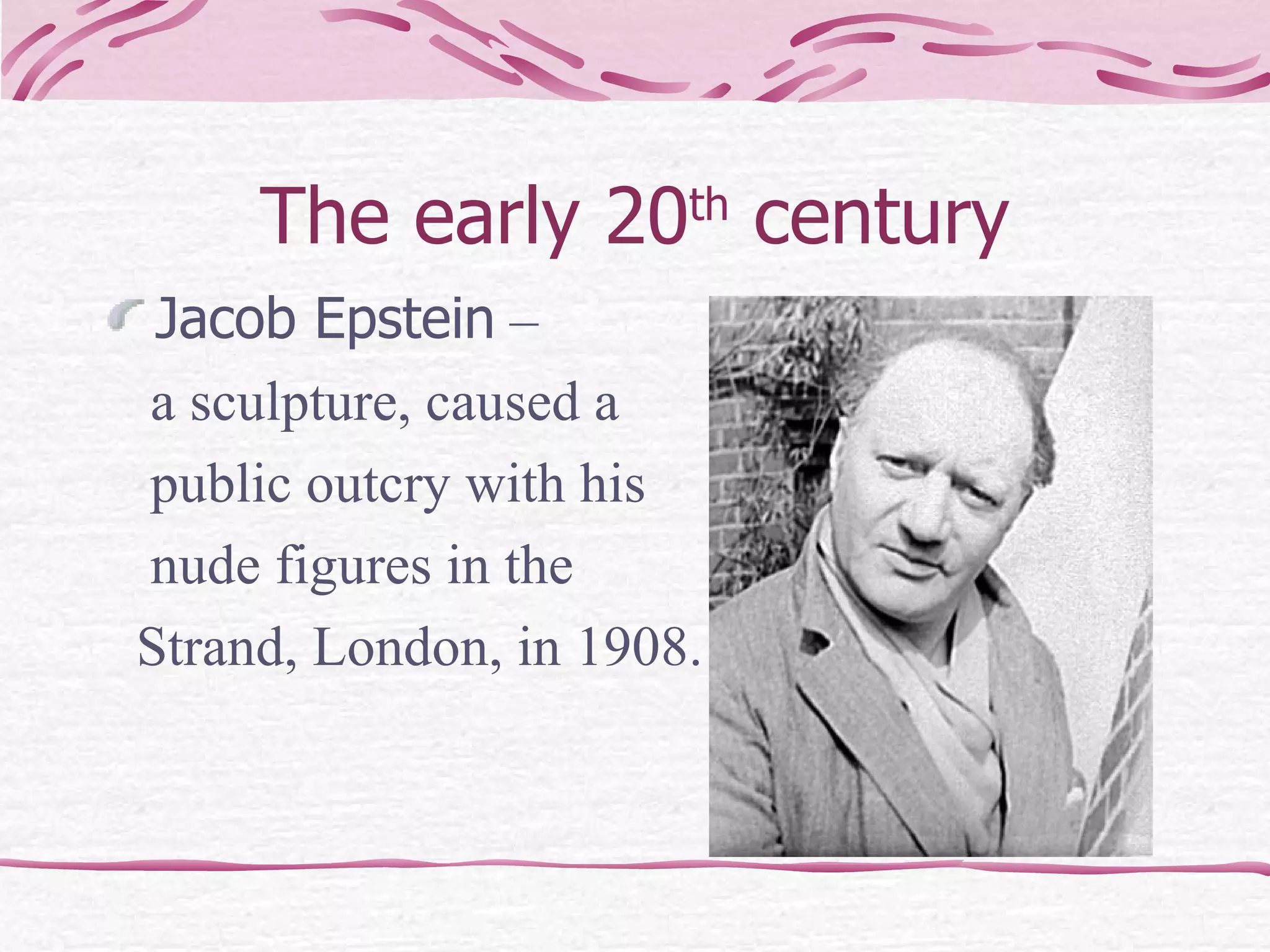
The document provides an overview of the history of art, architecture, and design in England from ancient times to the present day. It discusses important styles, movements, and notable figures that have influenced architecture, painting, sculpture, and other art forms throughout the centuries. Some of the key periods and developments mentioned include Stonehenge, medieval churches and castles, Gothic cathedrals, Palladian and Baroque styles in the 17th-18th centuries, landscape painting in the 19th century, and modern architecture in the 20th century.