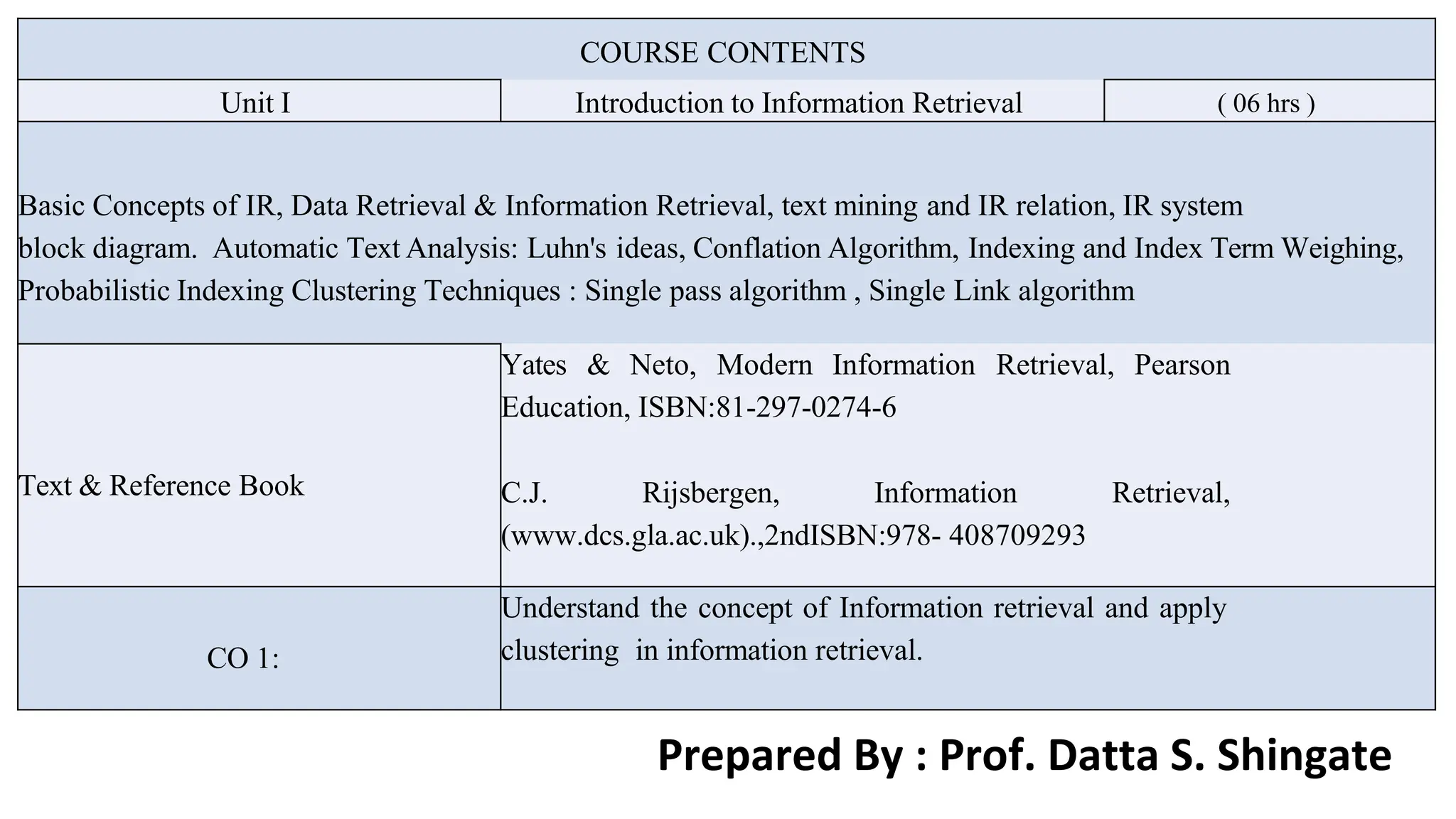
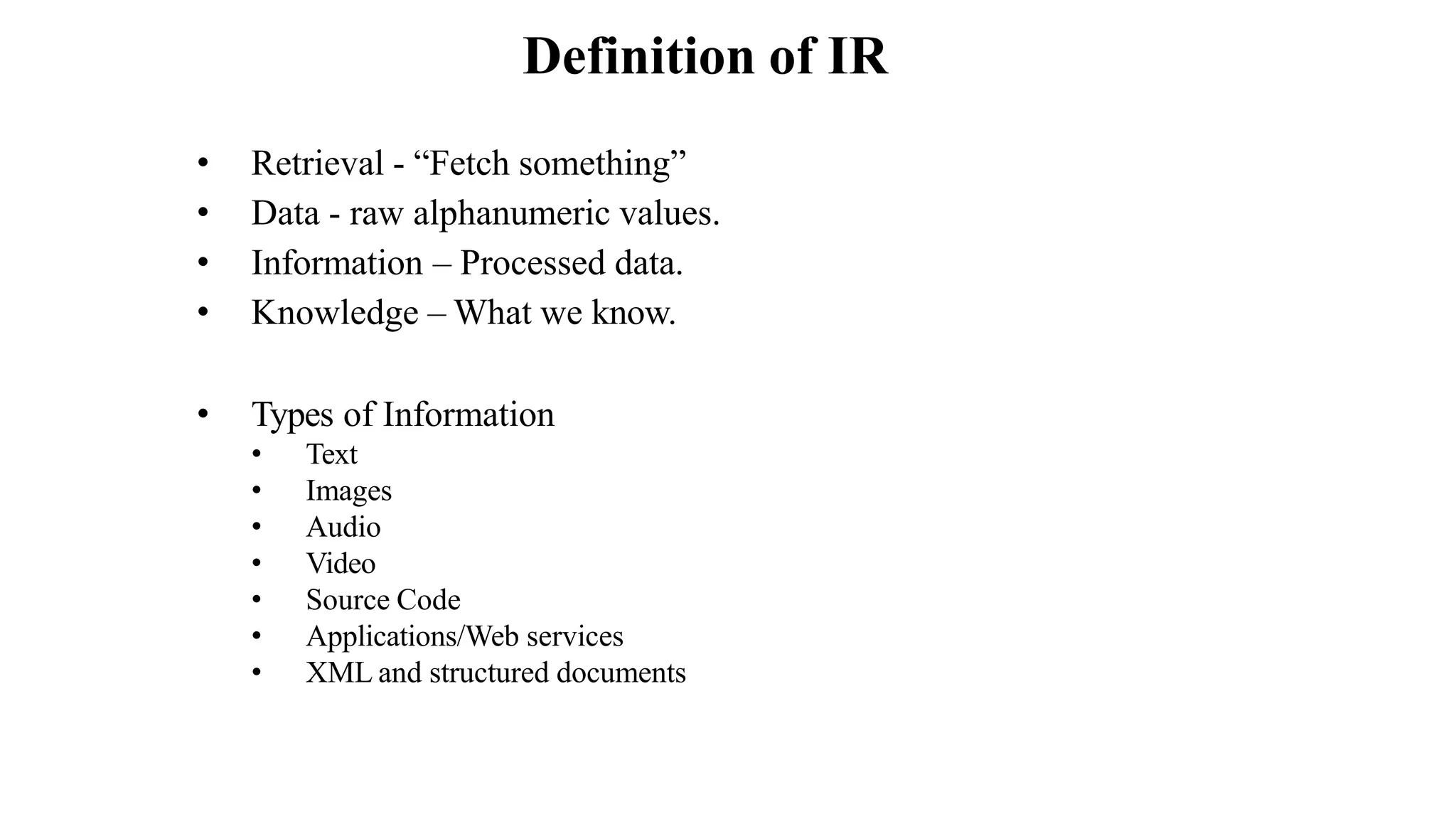
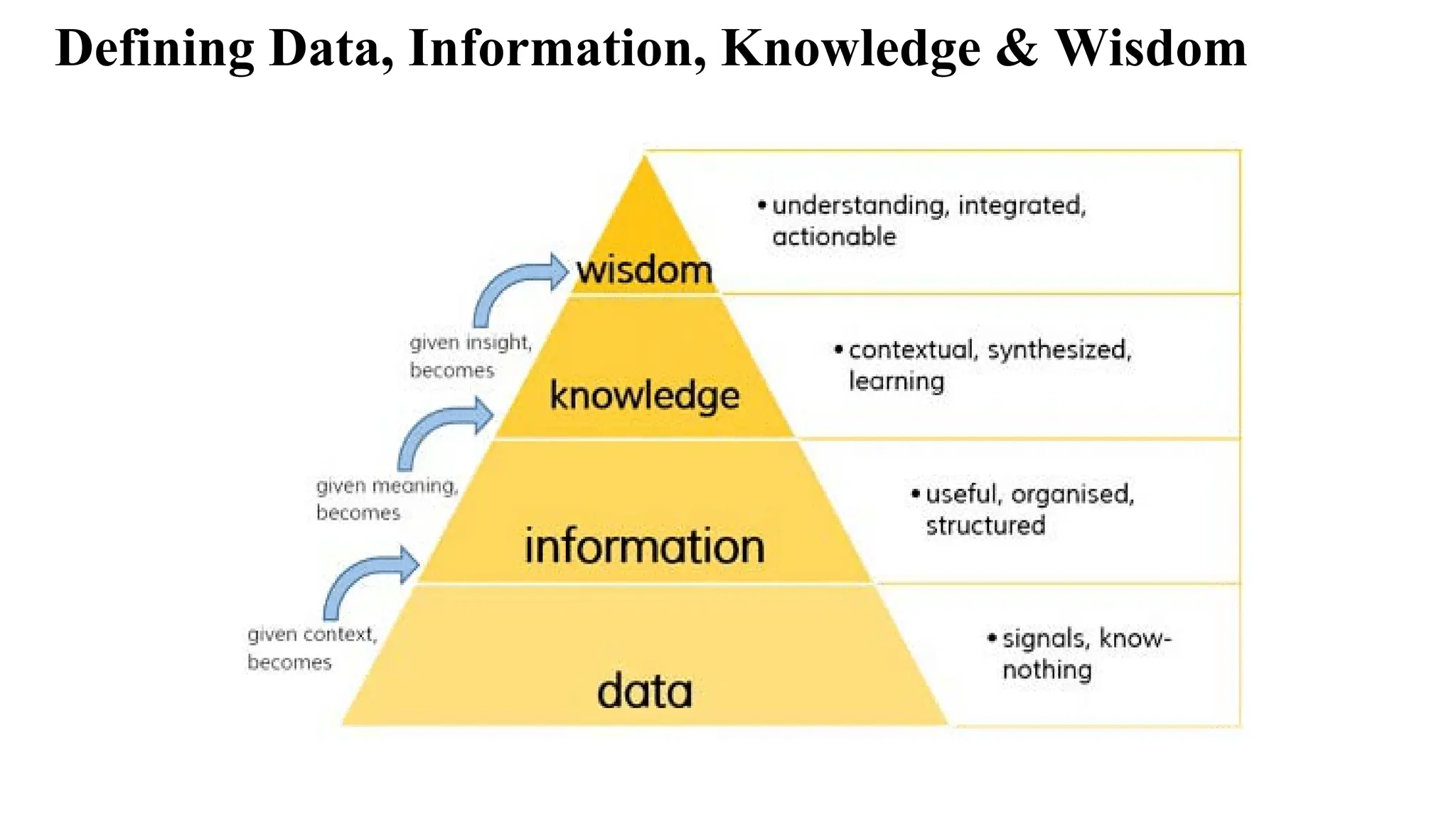
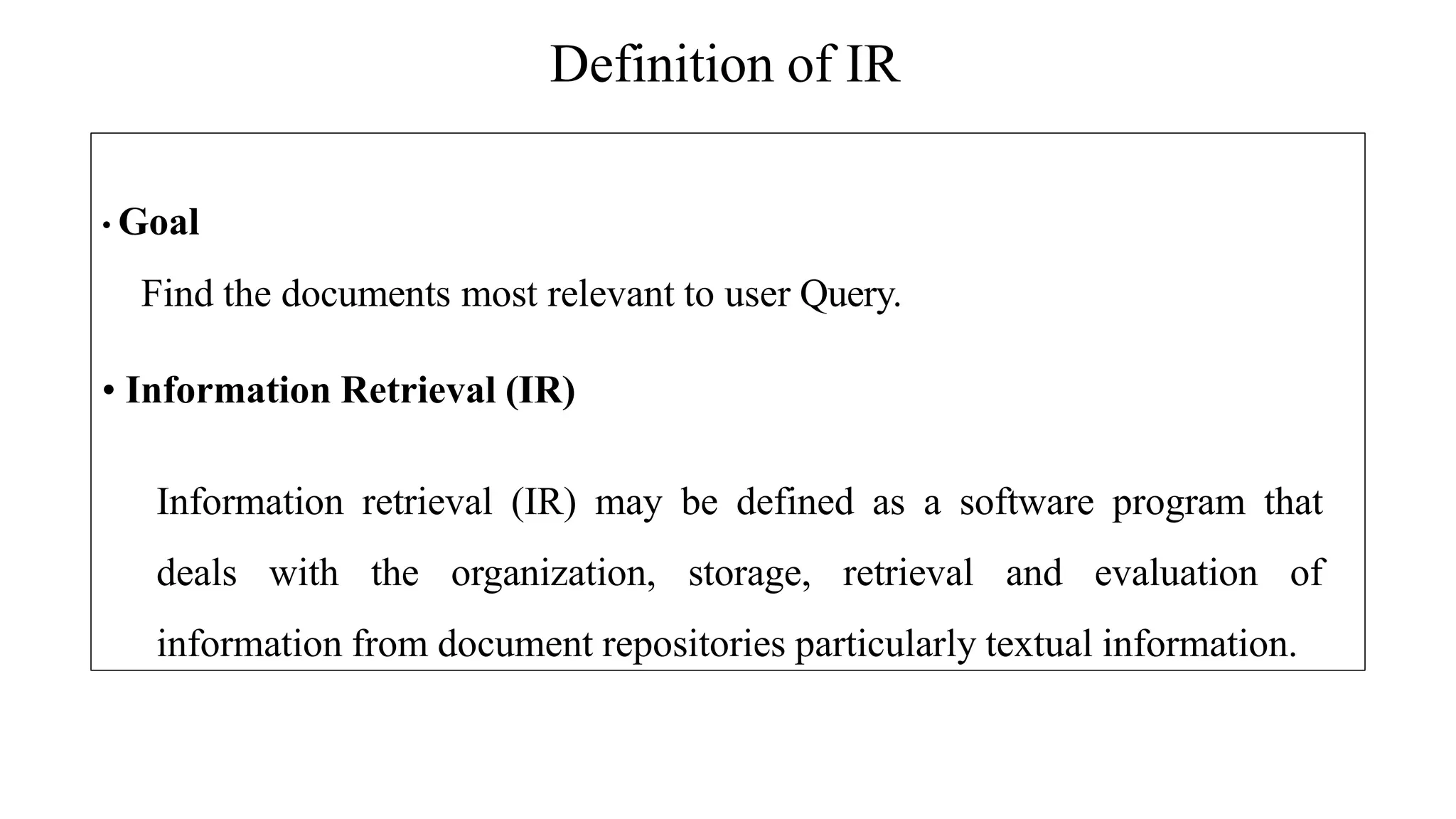
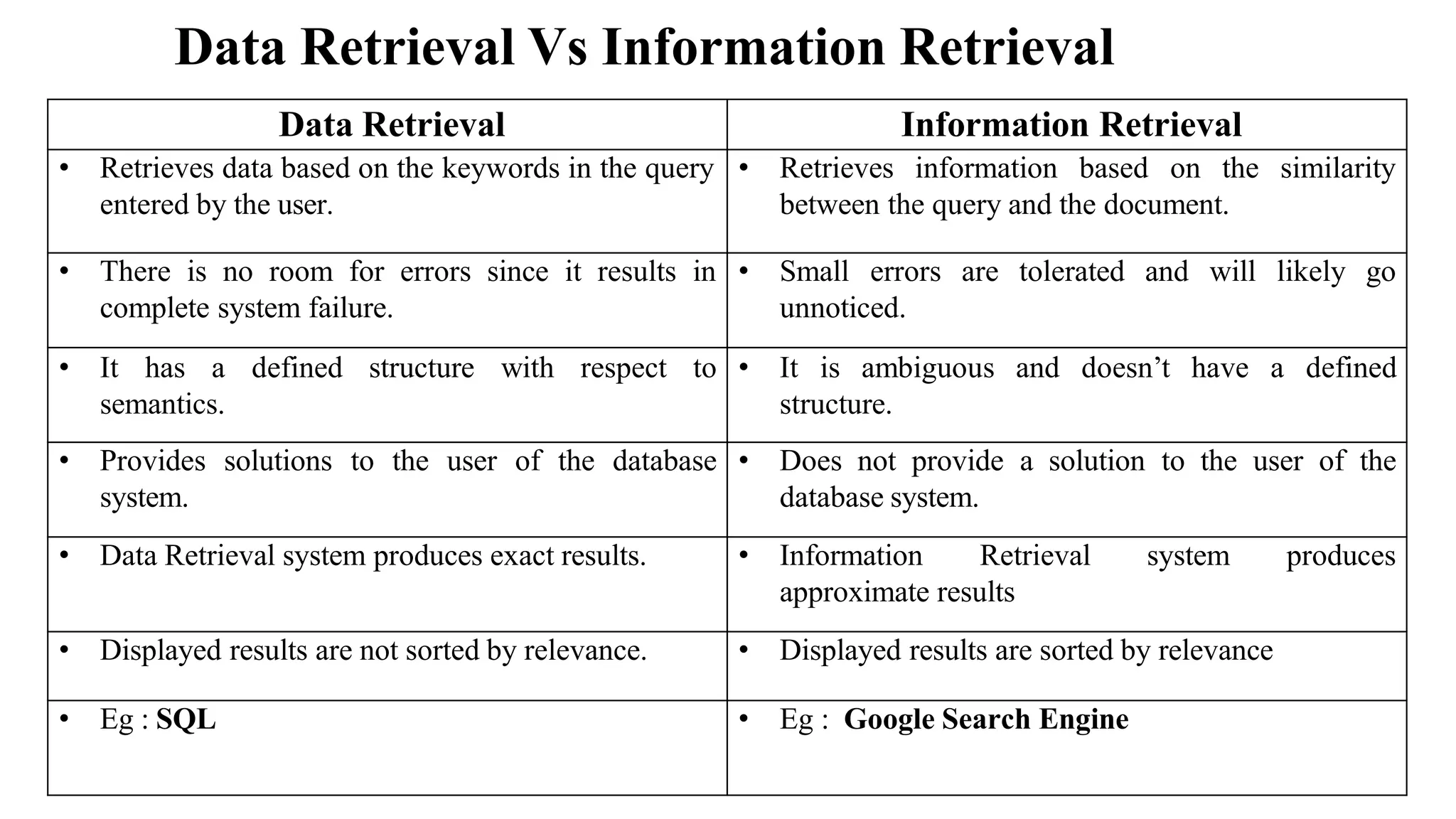
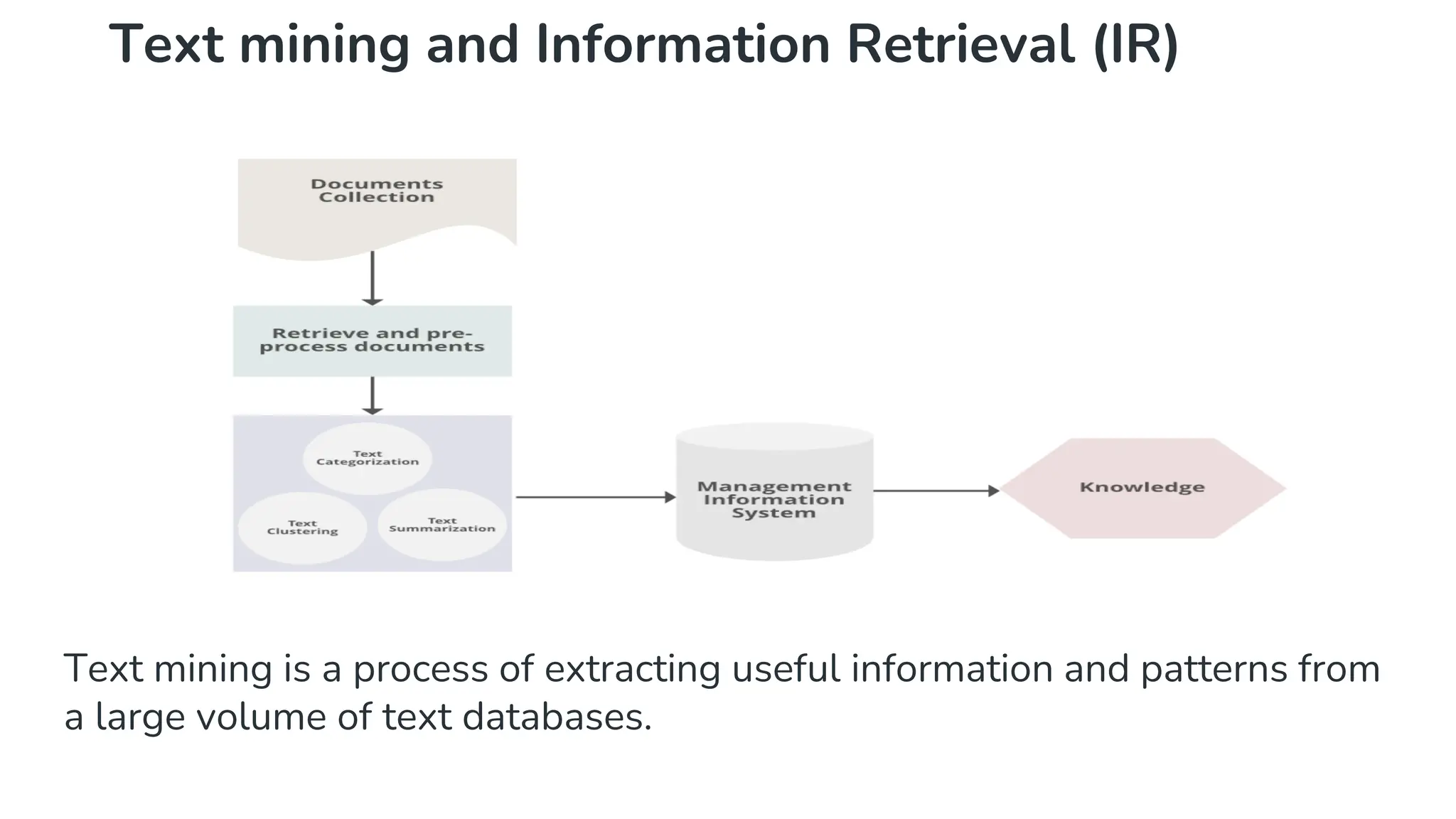
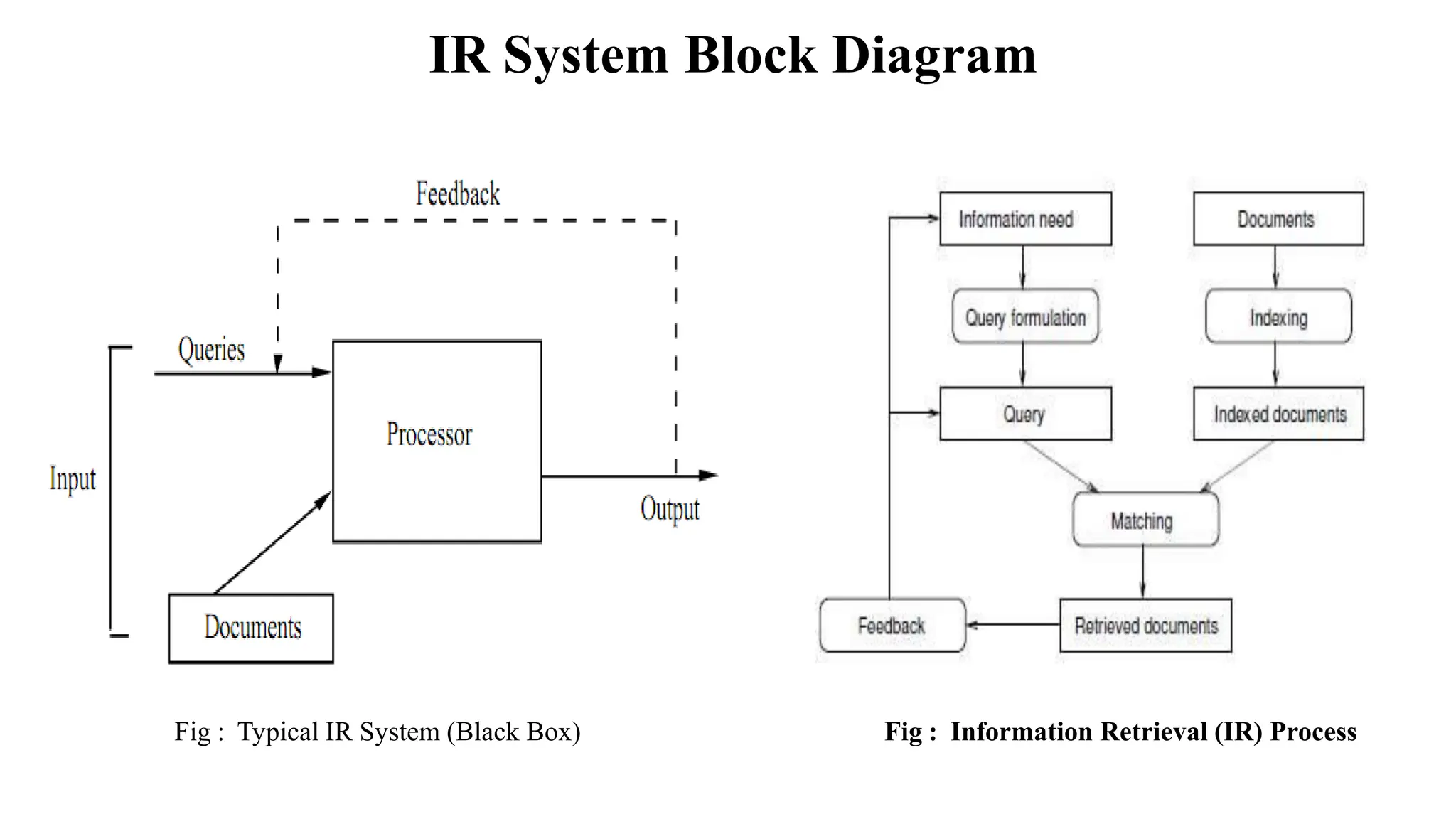
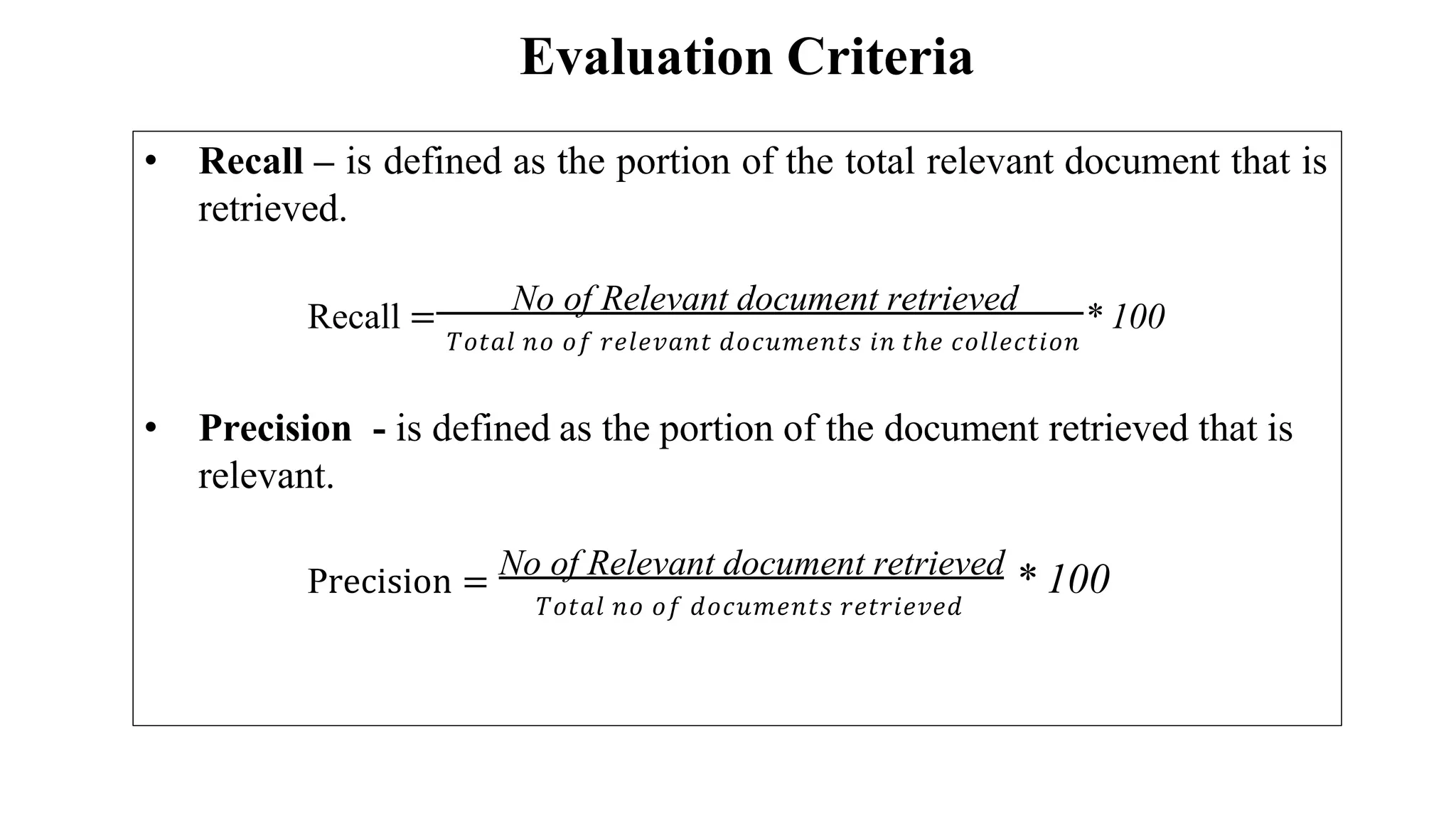
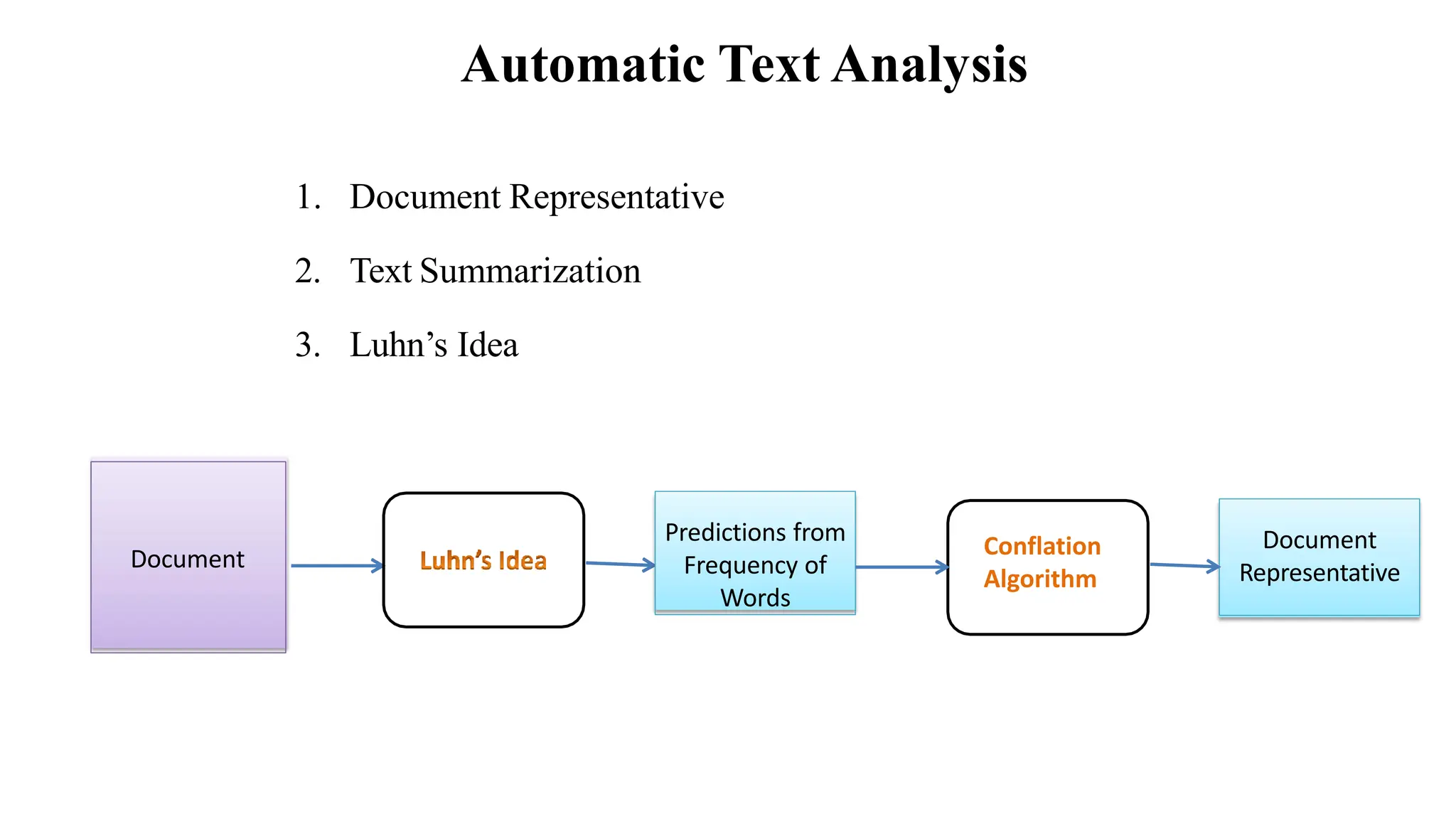
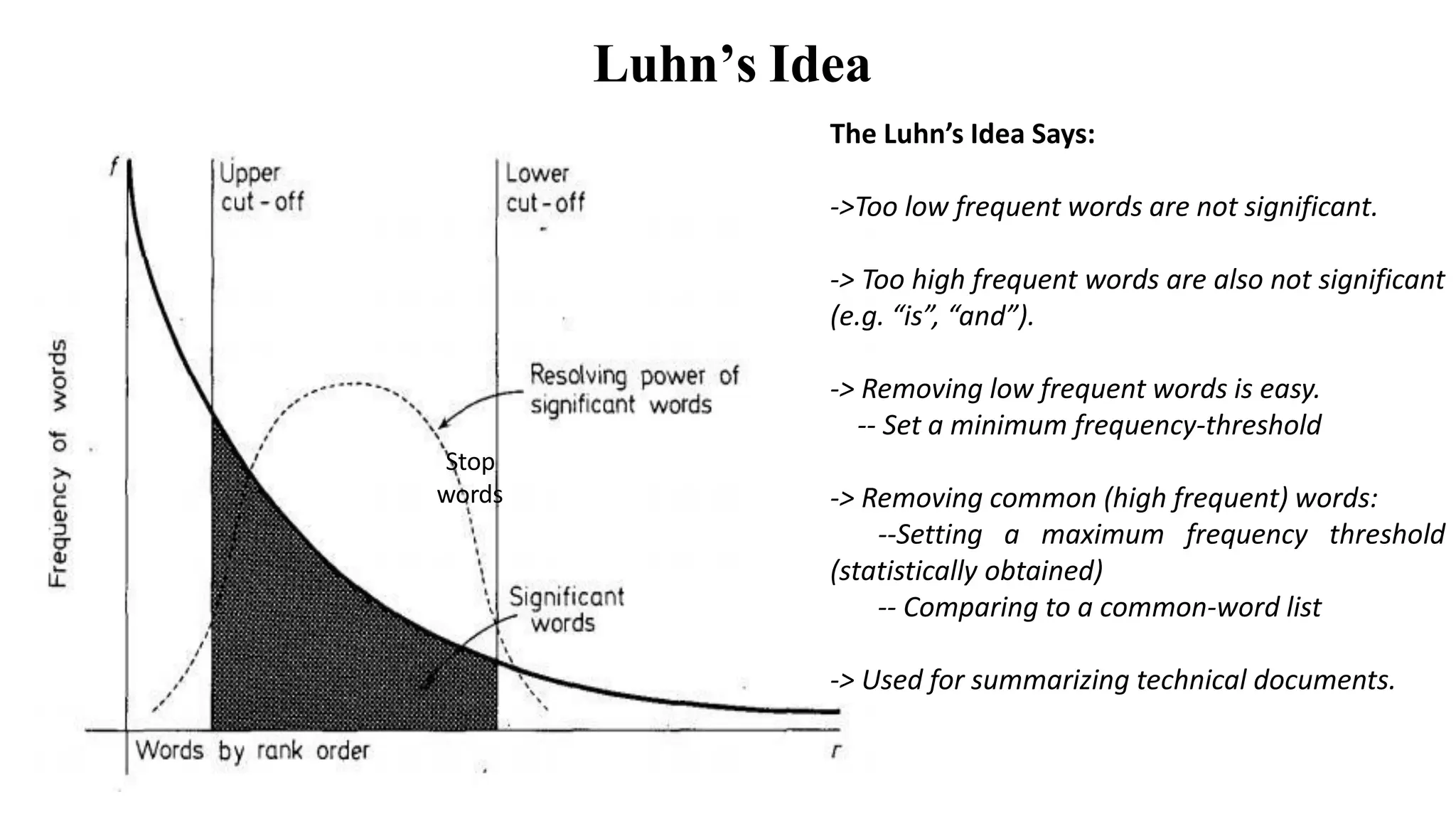
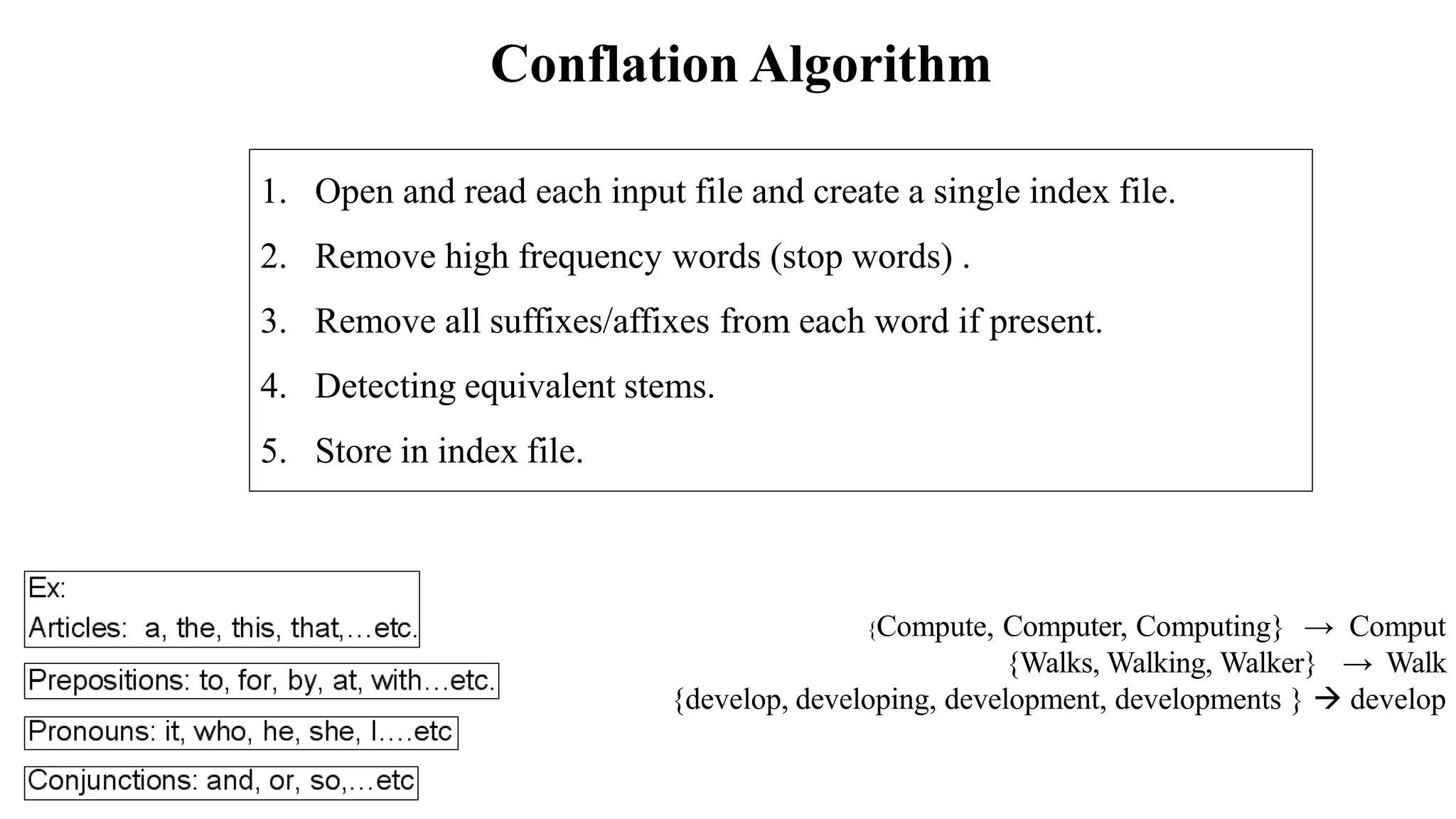
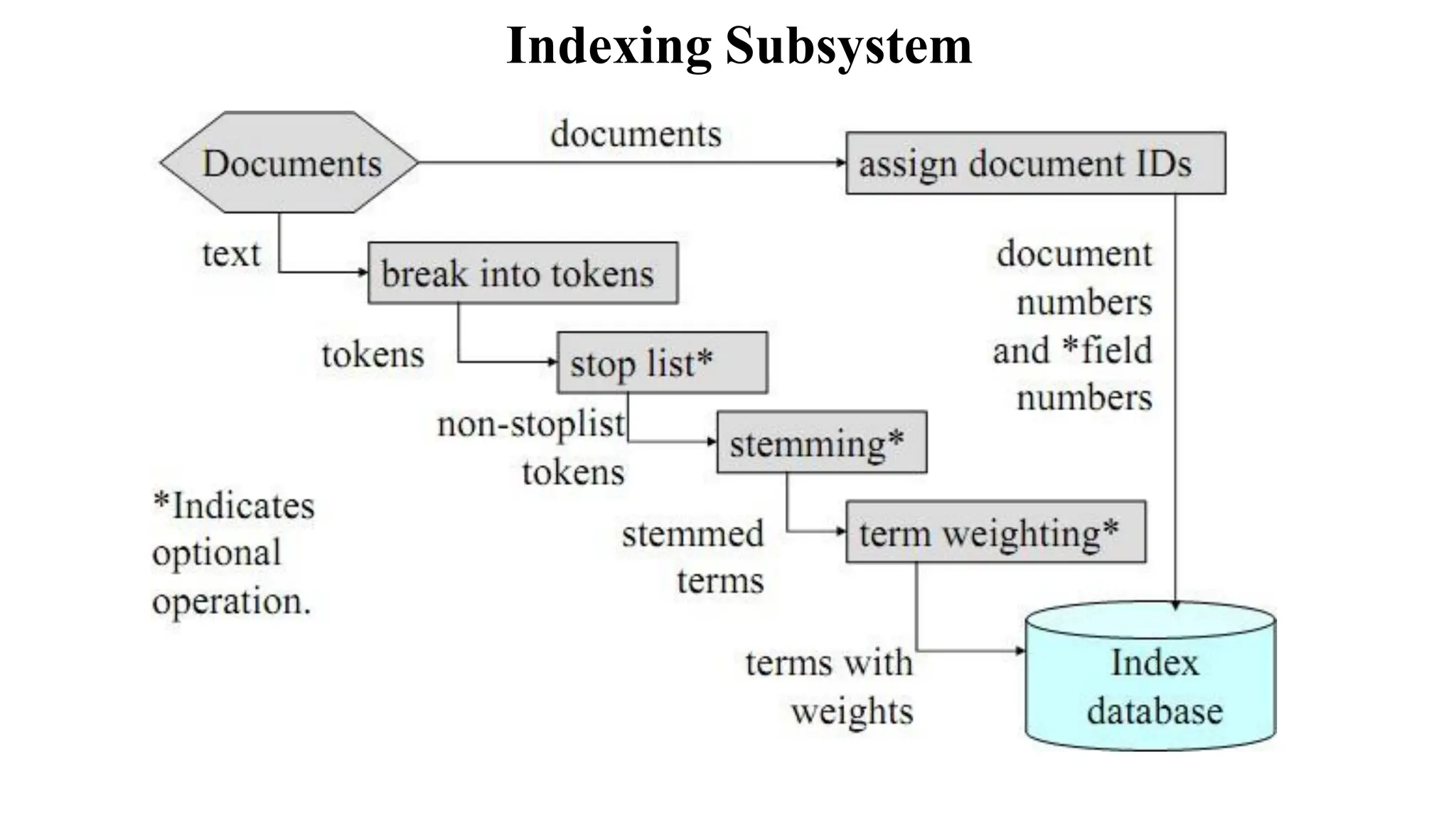
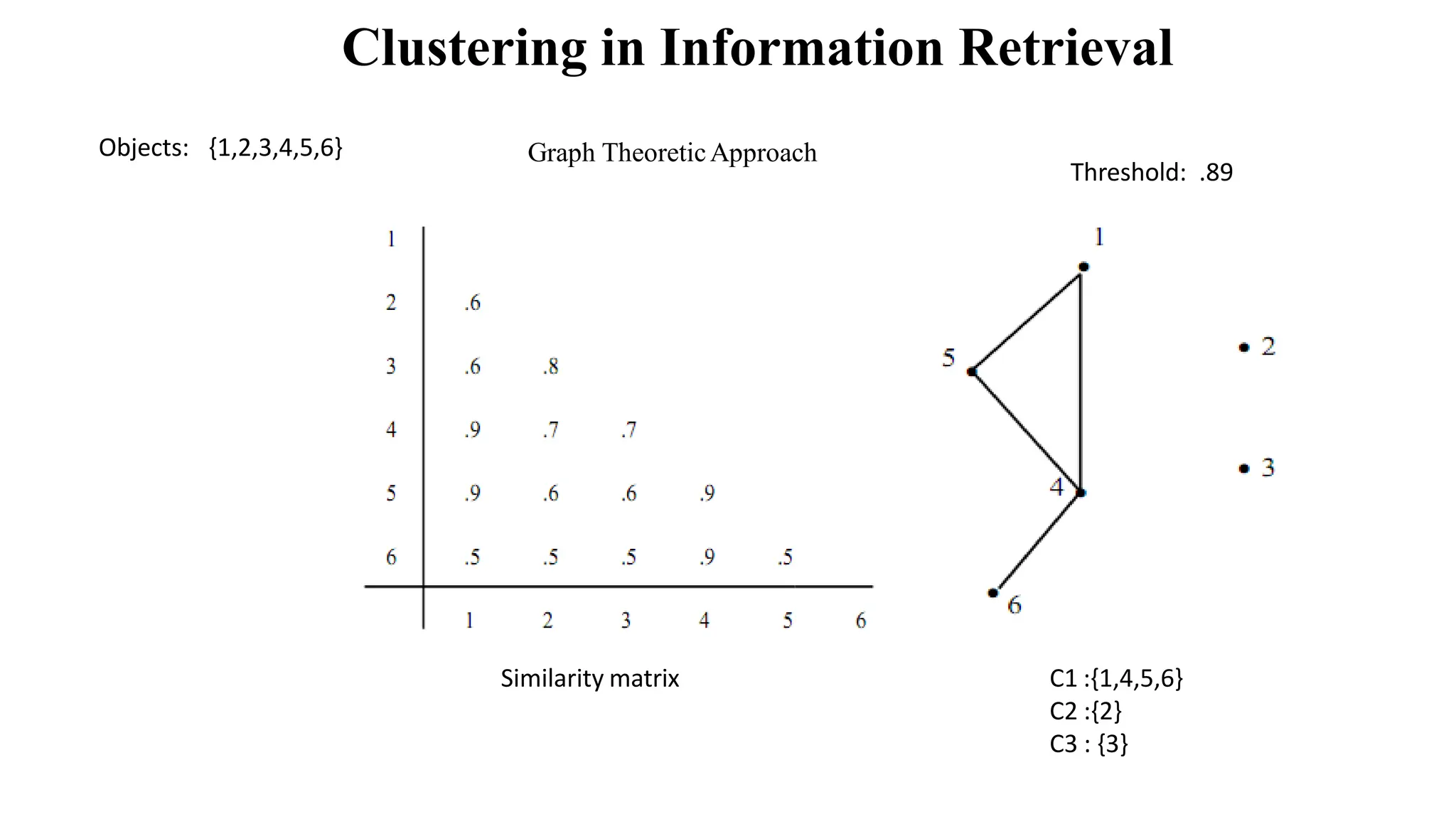
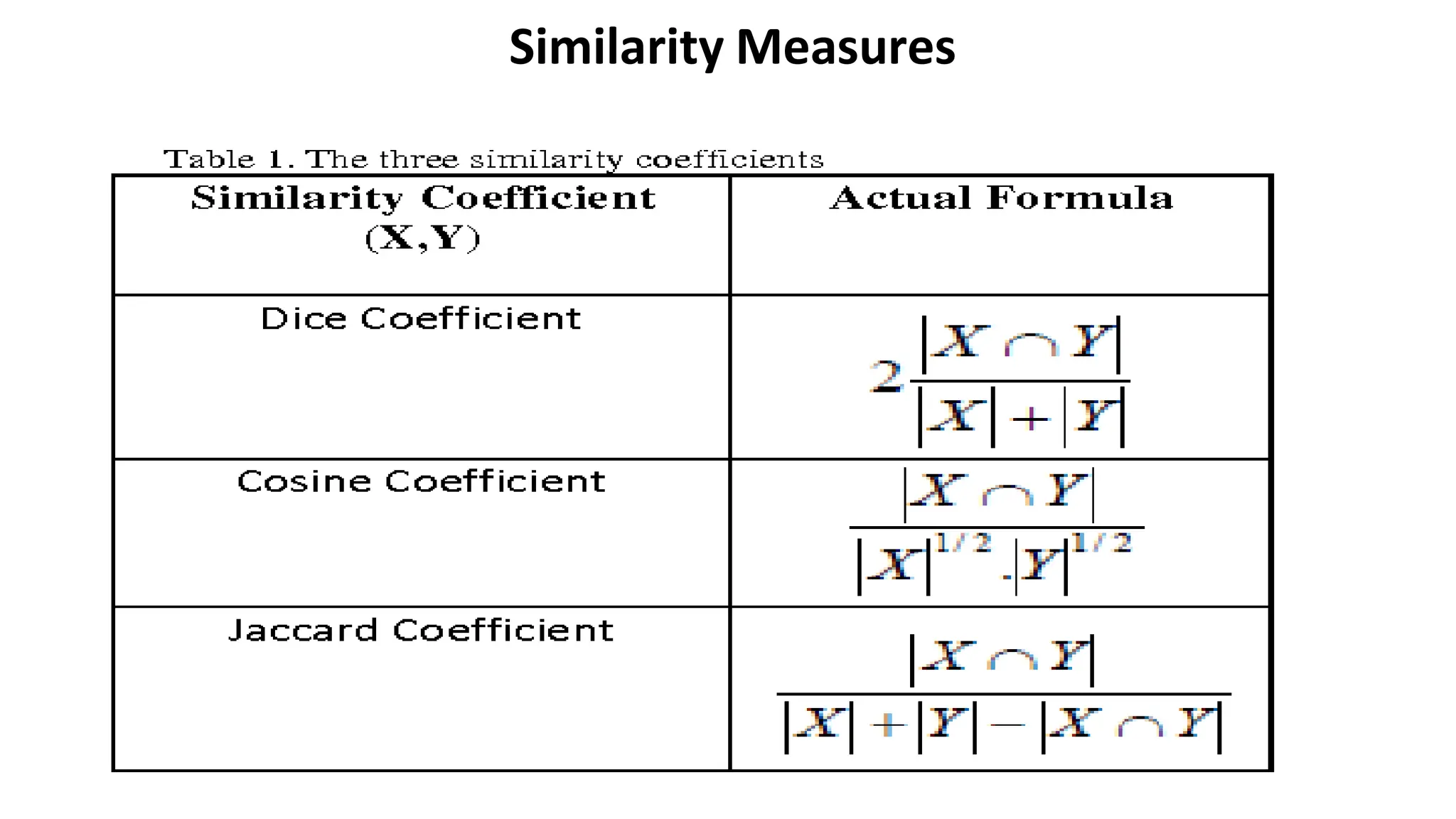
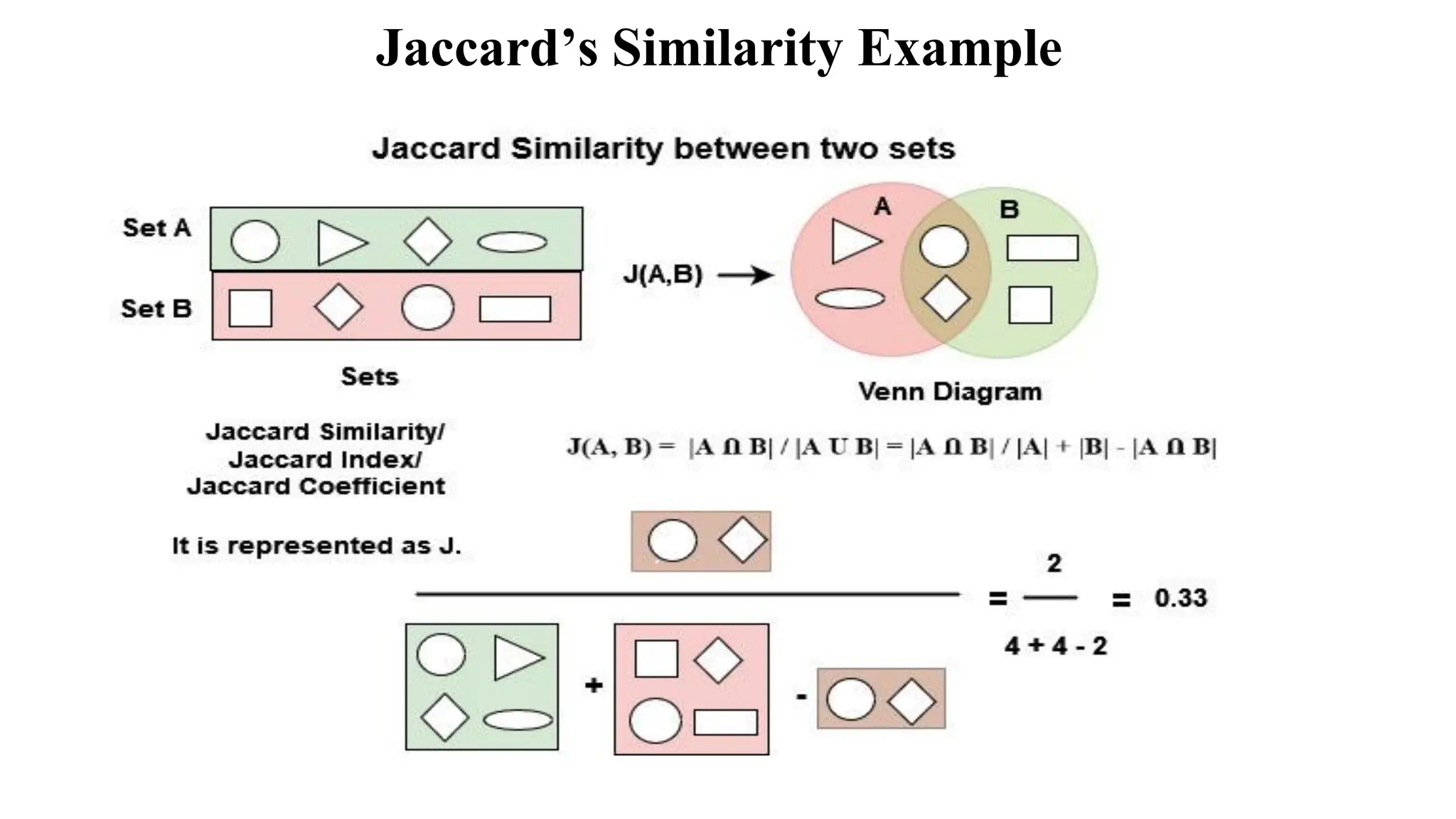
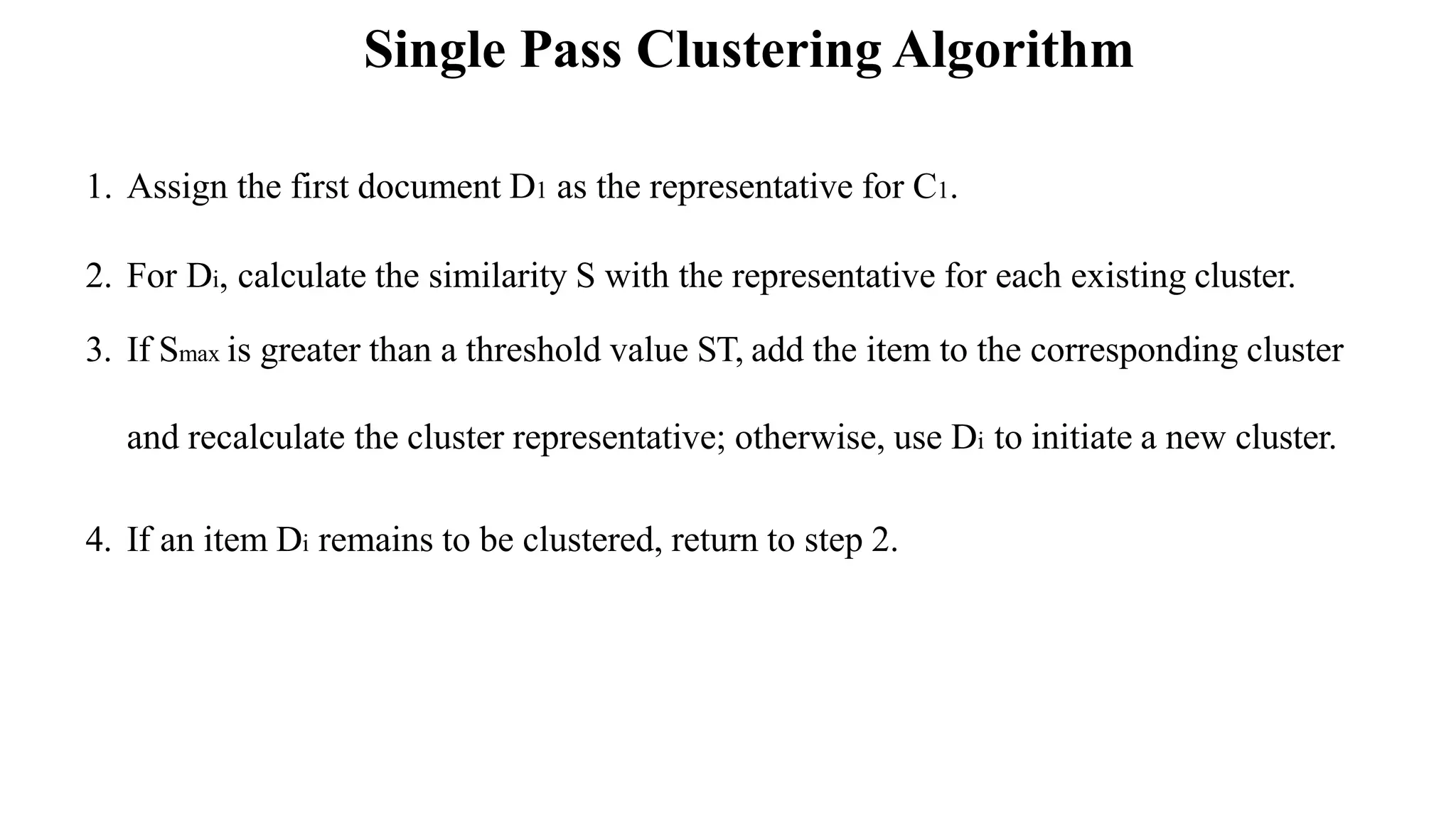
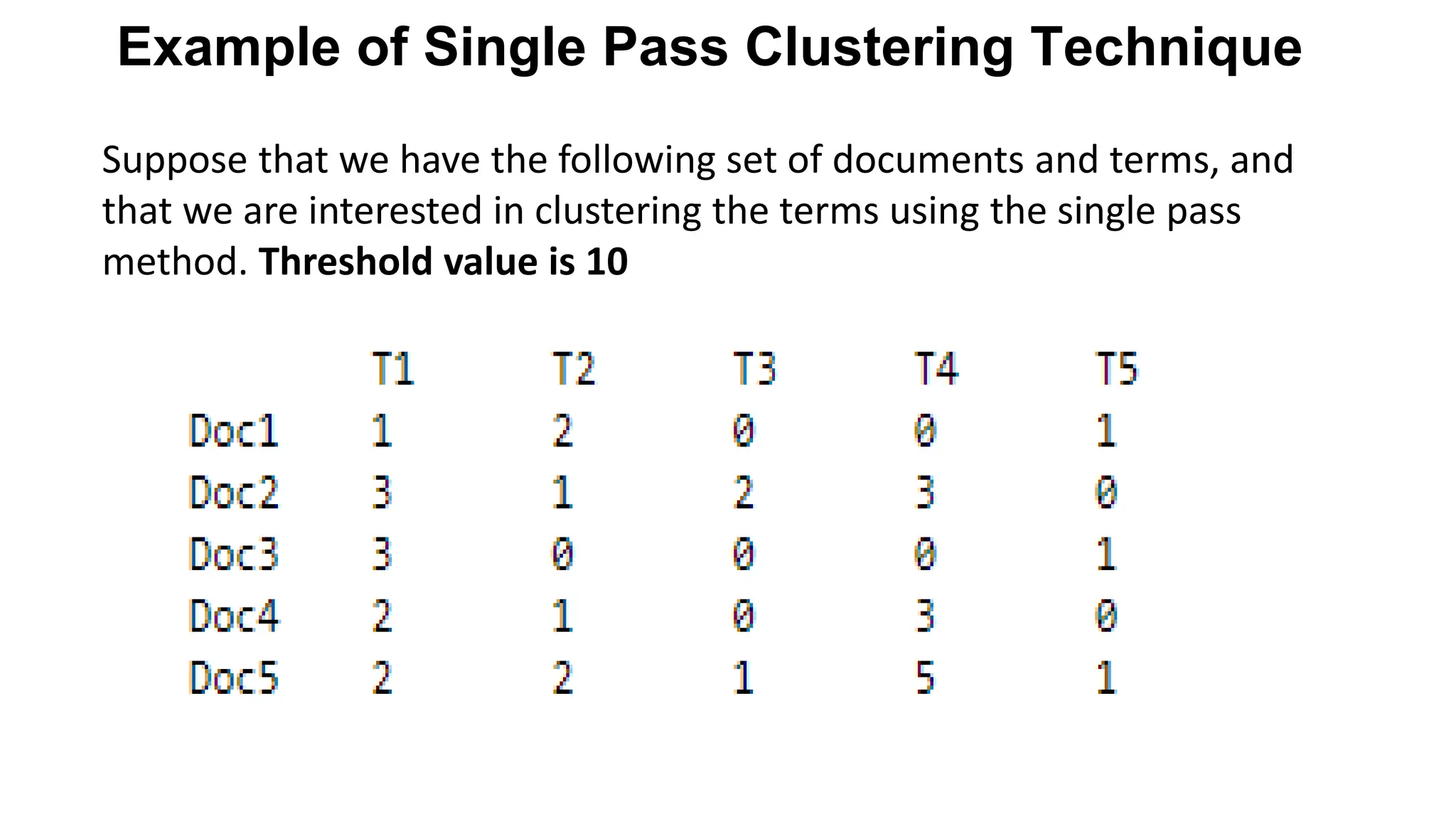
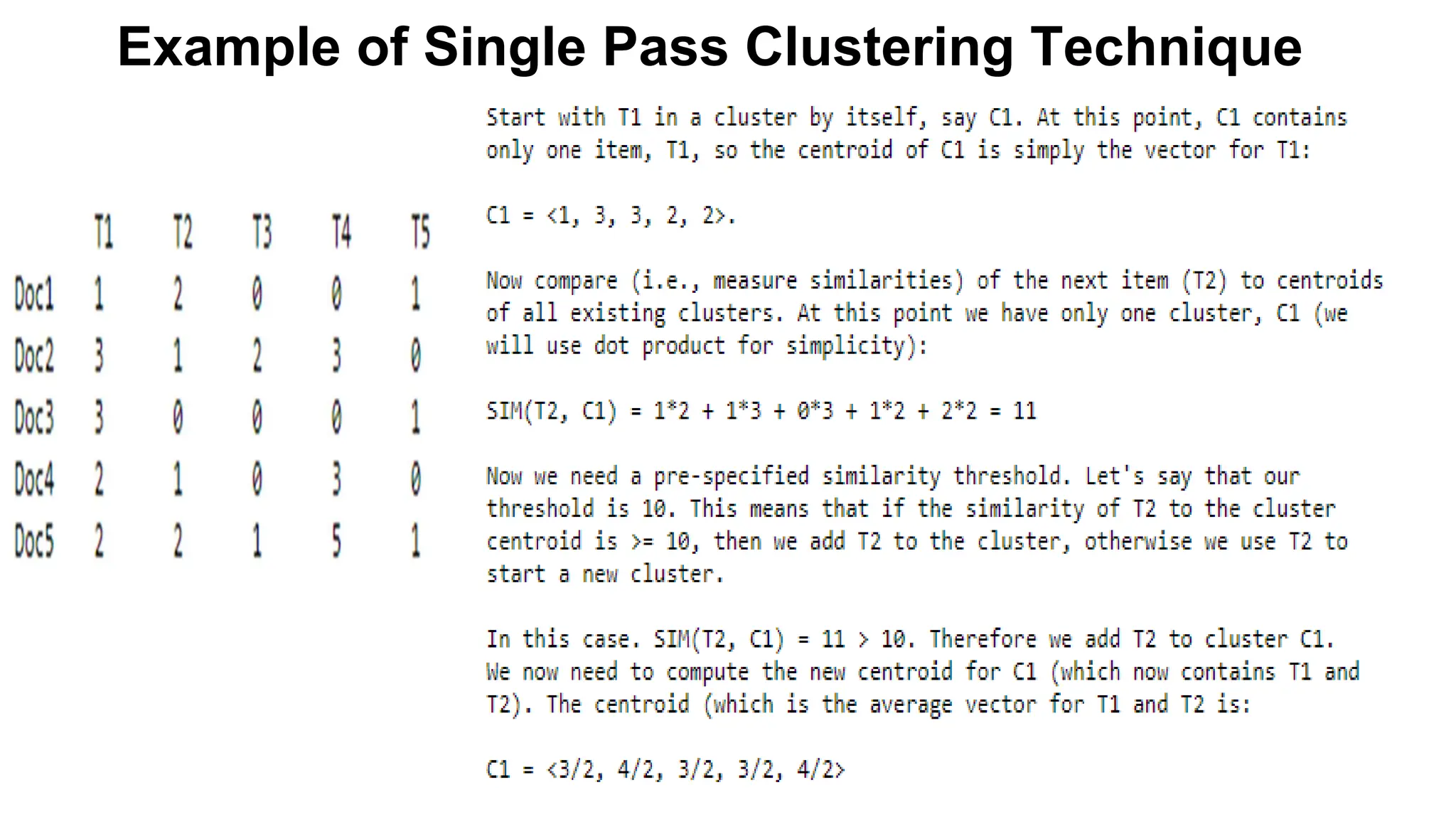
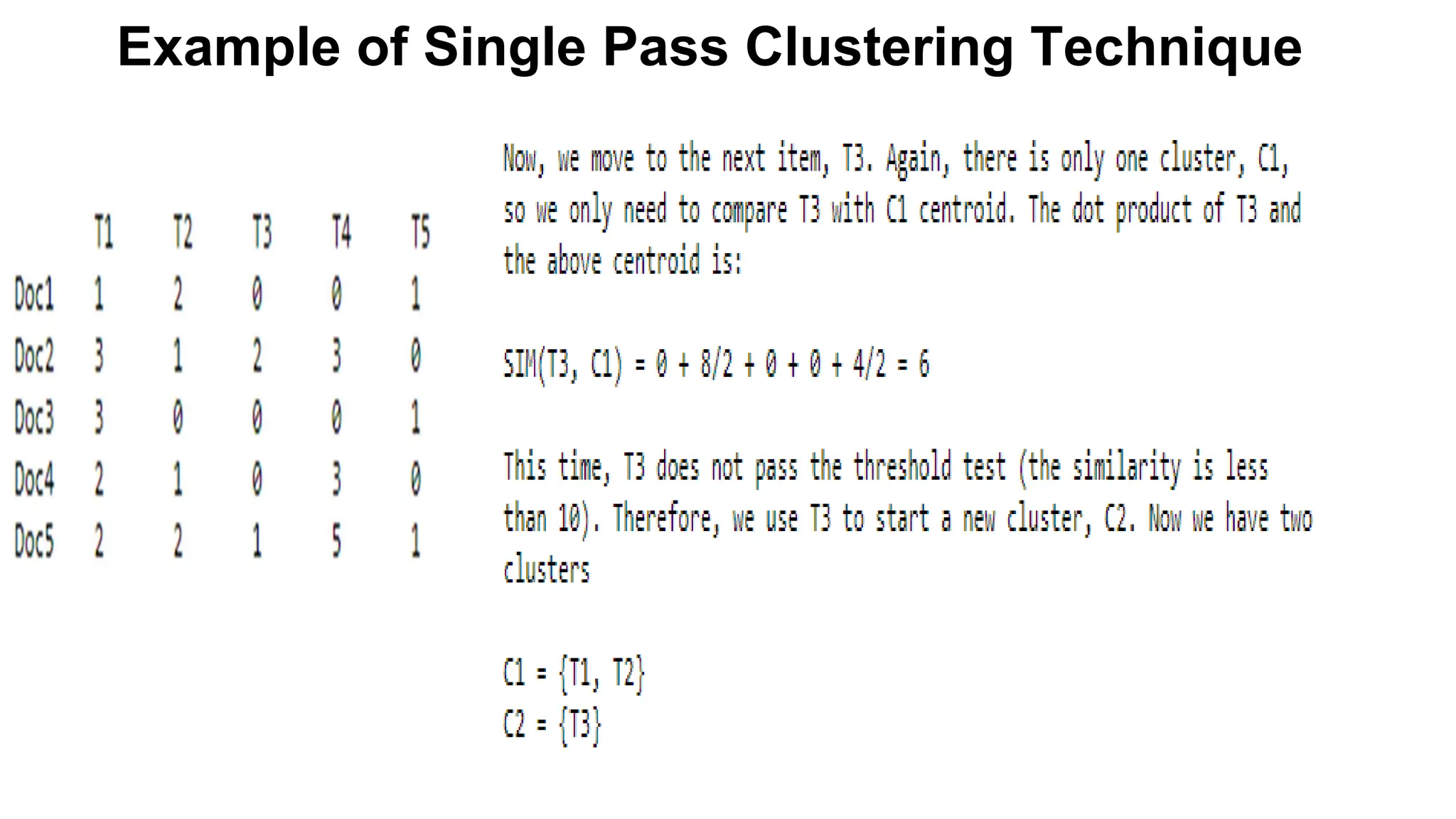
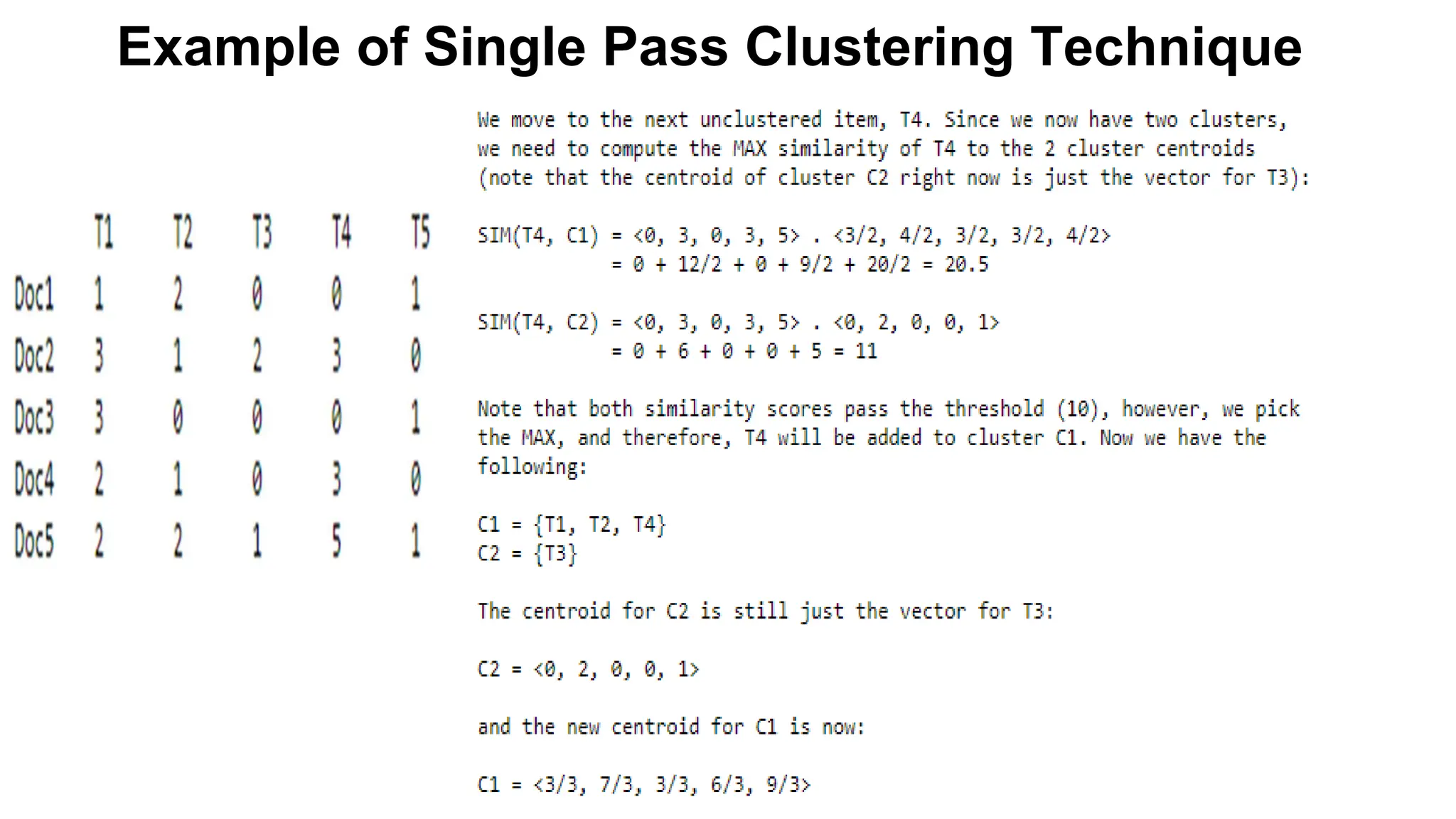
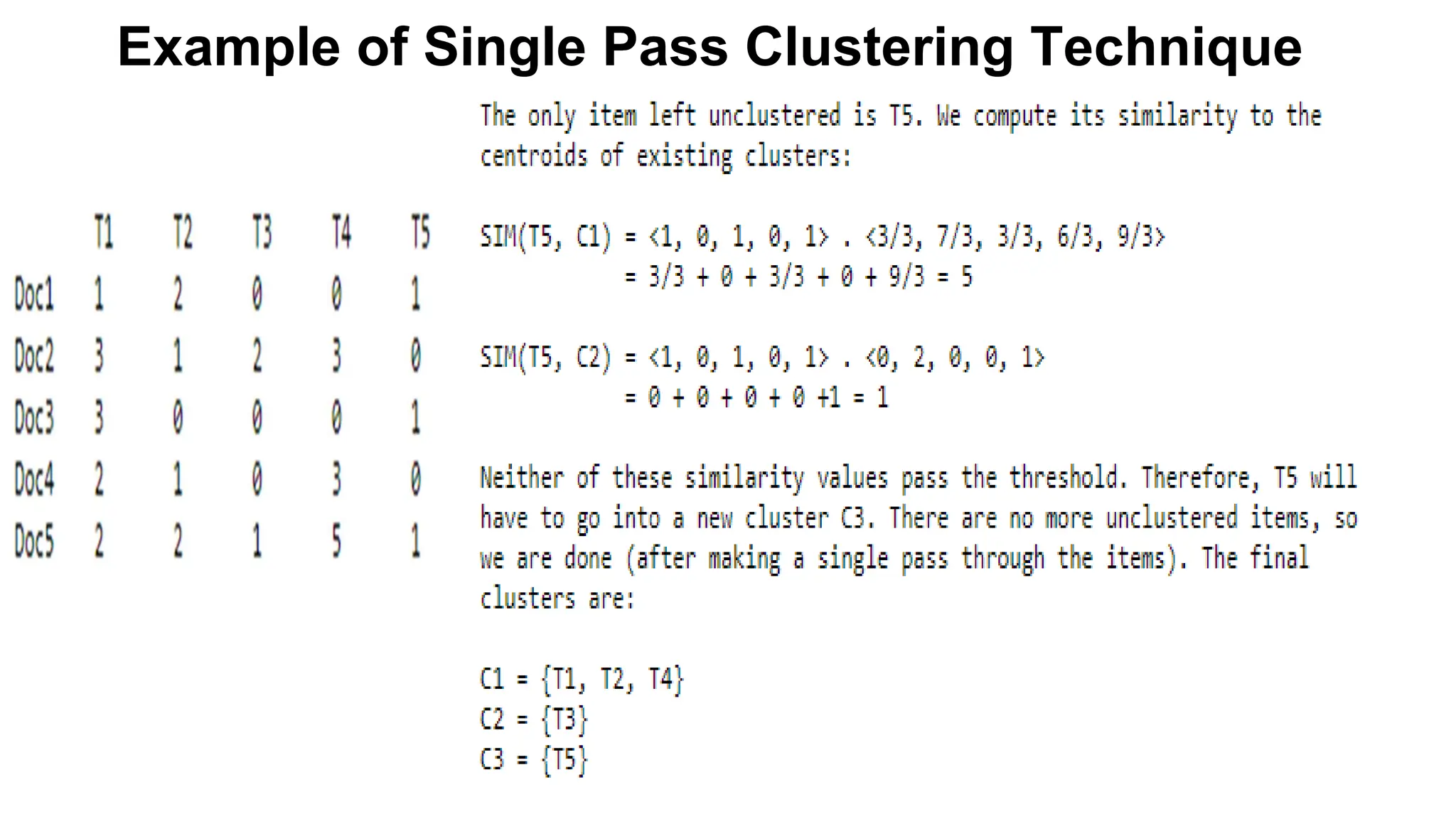
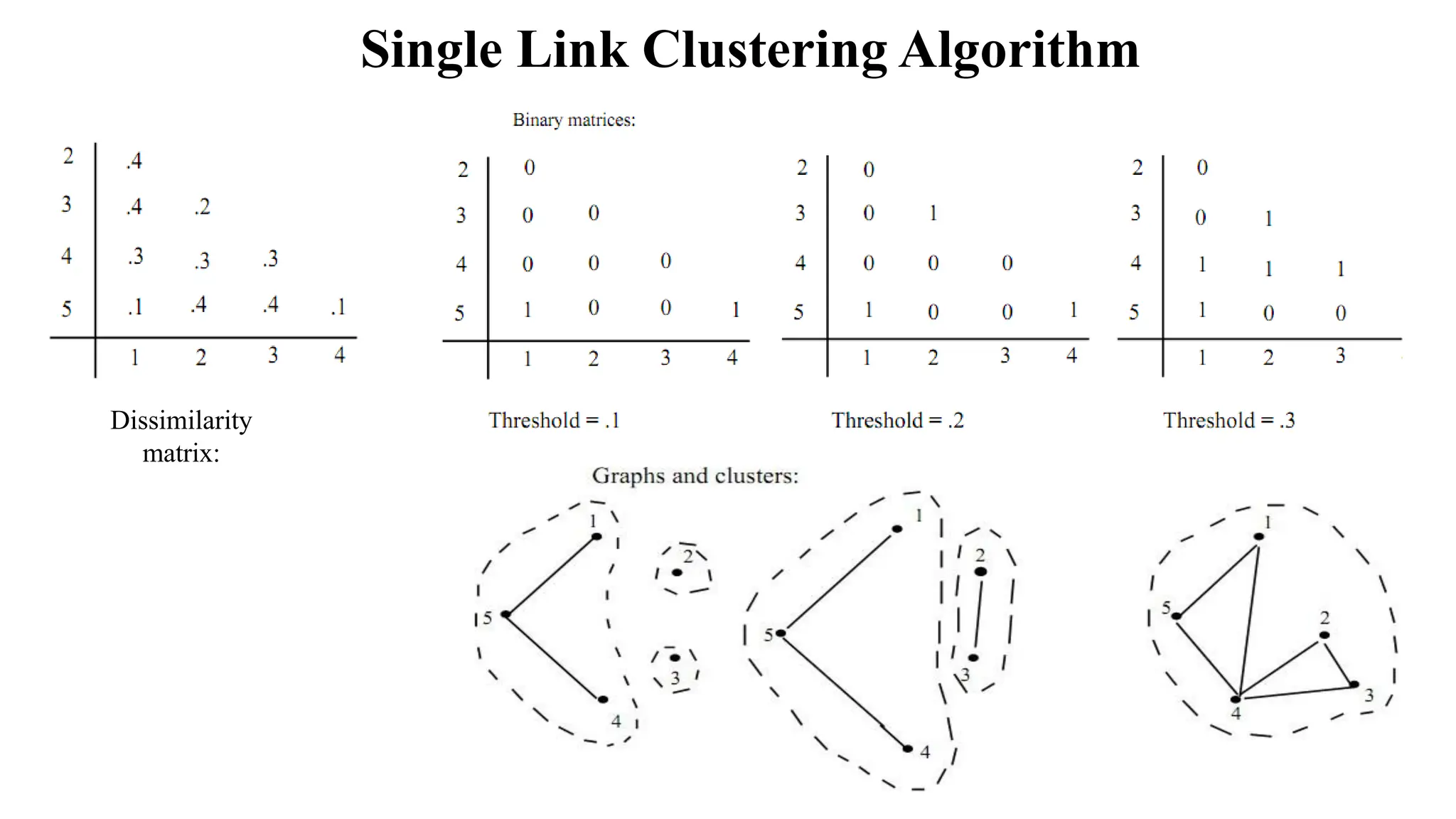
The document outlines the fundamentals of Information Retrieval (IR) including concepts, processes, and algorithms related to data and text mining. It distinguishes between data retrieval and information retrieval, detailing their operational differences, and presents various automatic text analysis techniques such as Luhn's ideas and clustering algorithms. Additionally, it covers evaluation criteria like recall and precision, along with frameworks for clustering in IR applications.