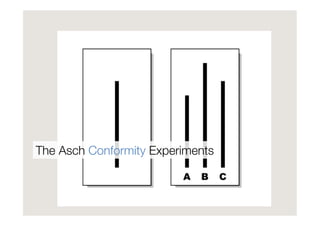
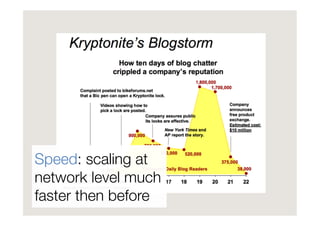
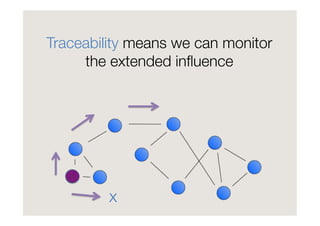
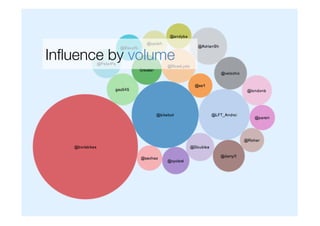
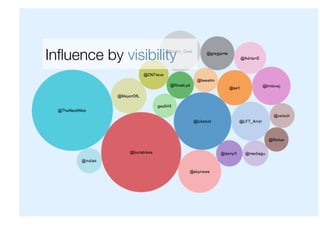
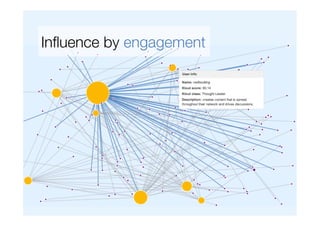
Francesco D'Orazio discusses the evolution of social influence in the context of social media, referencing Herbert Kelman's theories and Asch's conformity experiments. The document explores how social media alters the dynamics of influence, transitioning from a structure focused on individual compliance to one where individuals can influence many, highlighting concepts such as domain-specific influencers and the role of credibility, trust, and engagement. It emphasizes the importance of understanding audiences through shared passions rather than demographics.