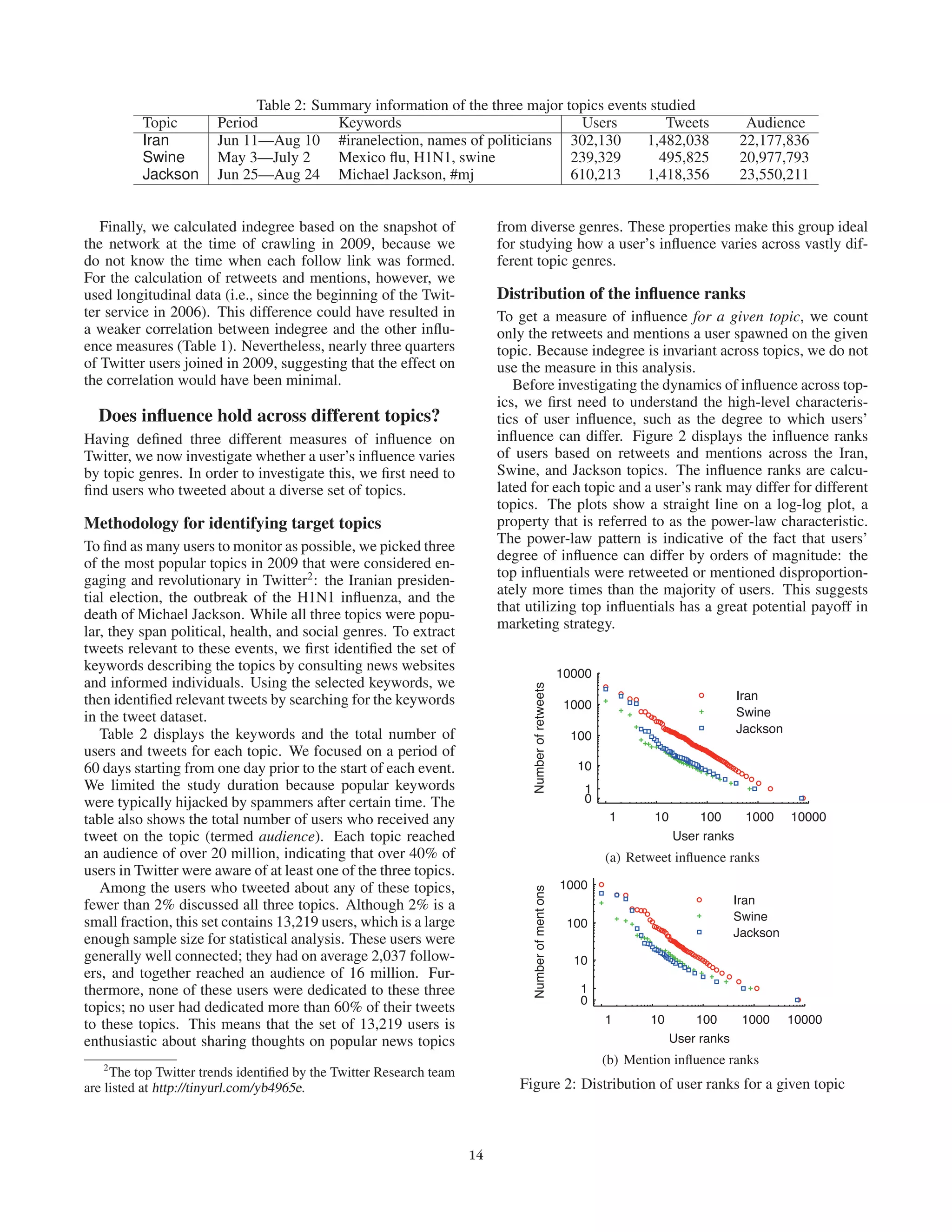
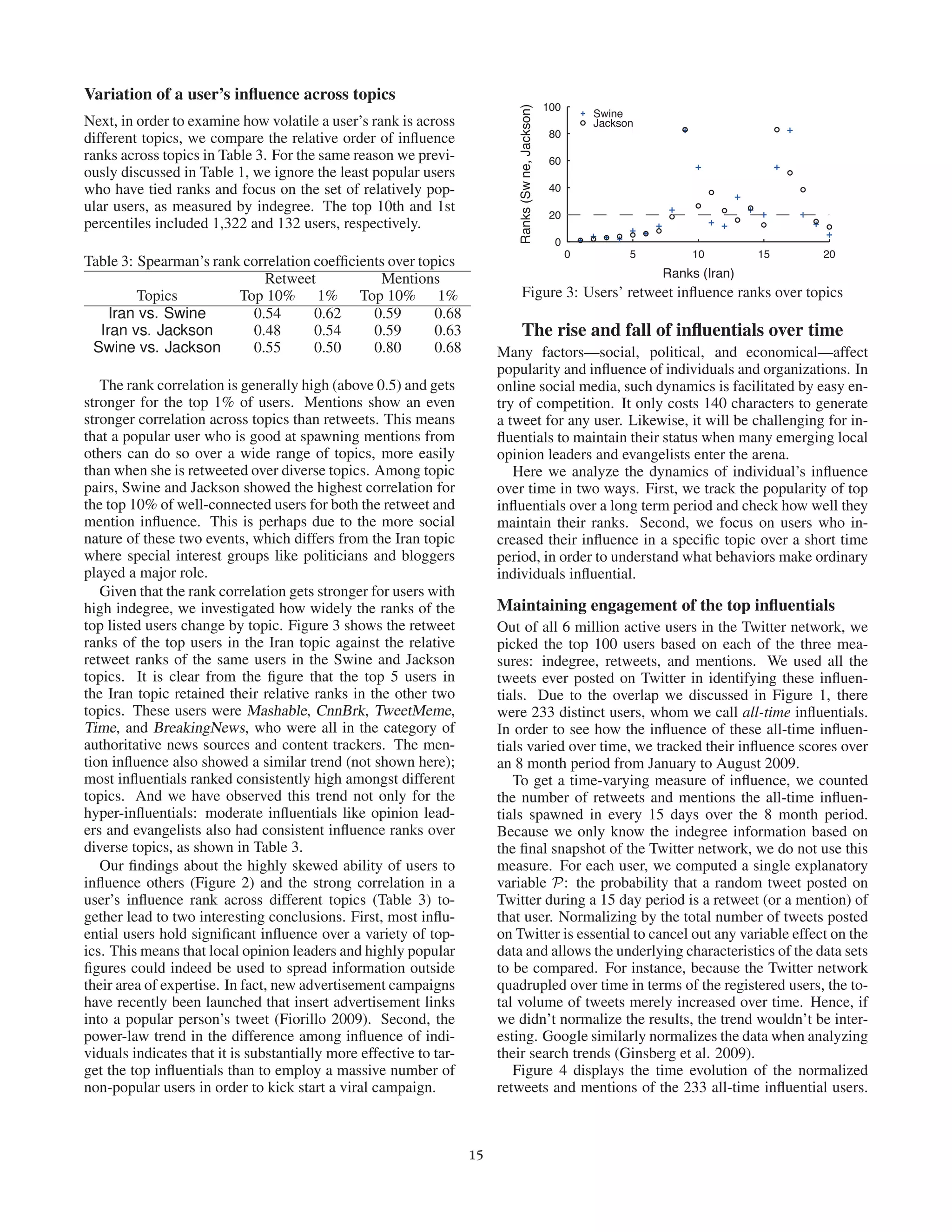
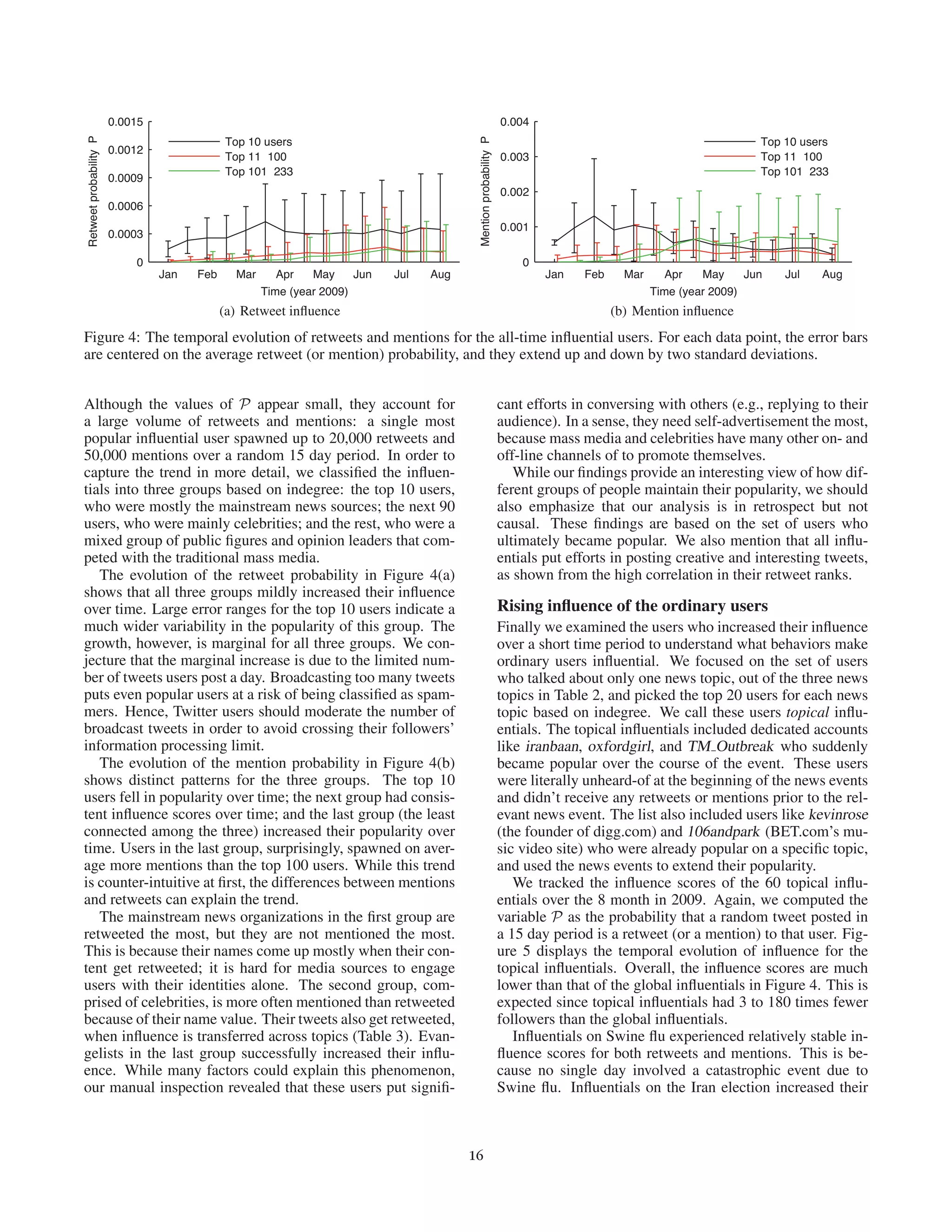
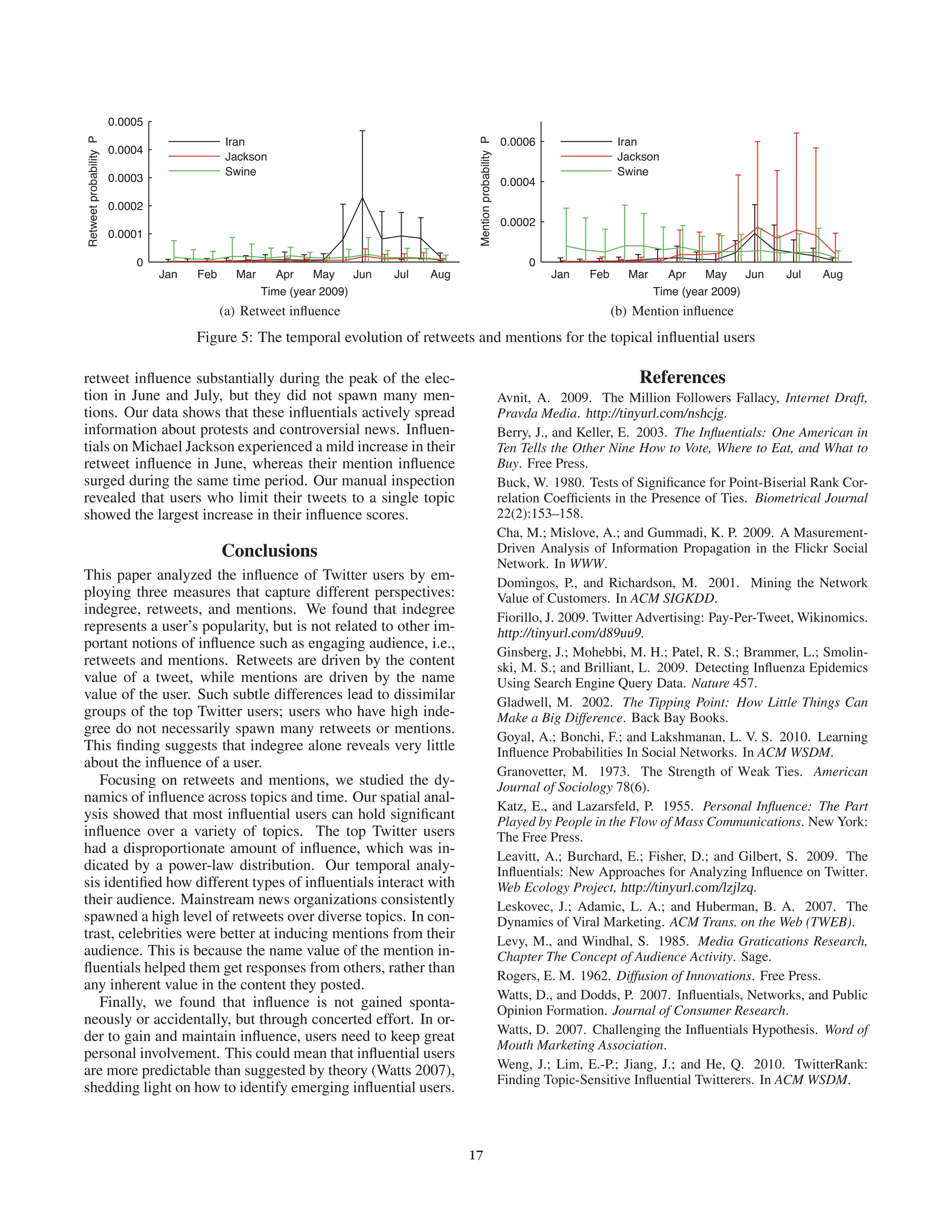
This document presents an empirical analysis of user influence on Twitter, evaluating three measures: indegree, retweets, and mentions. It challenges traditional theories of influence, suggesting that popular users do not always correlate with actual influence, and highlights that influence can vary across different topics and is often achieved through targeted efforts. The study underscores the importance of understanding user dynamics and the social context of Twitter to optimize marketing strategies.