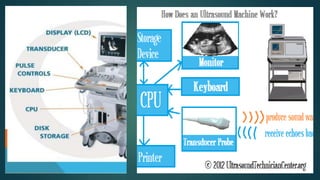
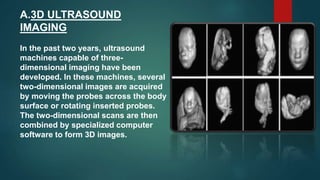
Ultrasound machines use high frequency sound waves to produce medical images of the body. They work by sending sound waves from a transducer probe into the body and receiving the echoes to produce images. There are two main types - 2D which shows a 2D image of 3D structures, and Doppler which measures blood flow. Ultrasound is widely used in obstetrics, cardiology, and urology due to its ability to image without radiation and its speed compared to other techniques. While ultrasound has advantages of being radiation-free and fast, it can cause local tissue heating and bubble formation from absorbed ultrasound energy.