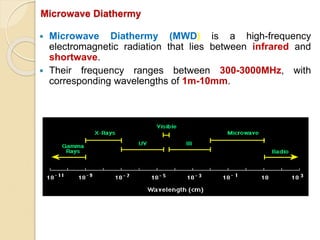
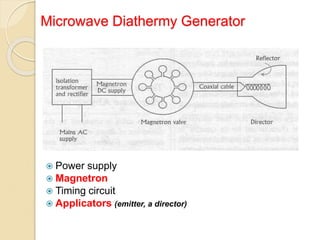
Microwave diathermy (MWD) is a therapeutic modality that uses electromagnetic radiation between 300-3000MHz to induce deep heating of tissues. MWD generates an electrical field that is strongly absorbed by fluid-rich tissues, causing ionic movement and heat. It can effectively penetrate tissues to a depth of 4.5cm. MWD is used to relieve pain, promote healing, and increase tissue extensibility through its physiological effects on metabolism, blood supply, and nerves. Proper application of MWD requires screening for contraindications, monitoring for safety, and documentation of treatment parameters.