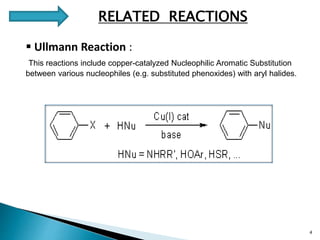
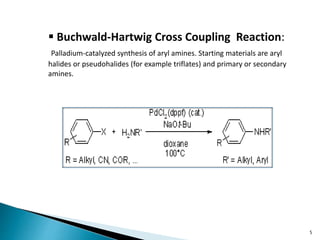
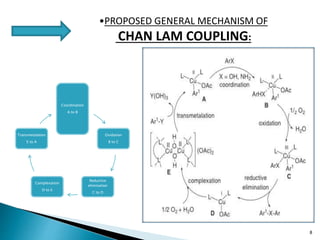
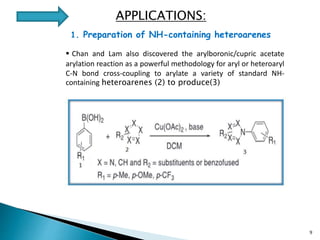
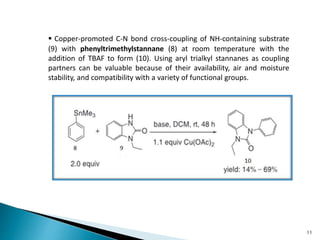
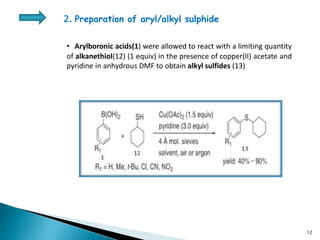
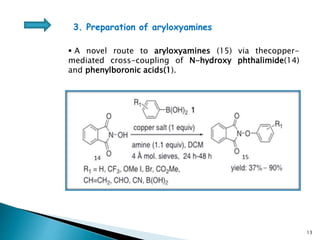
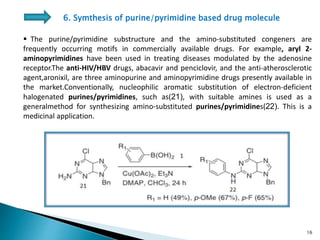
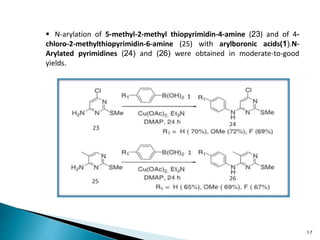
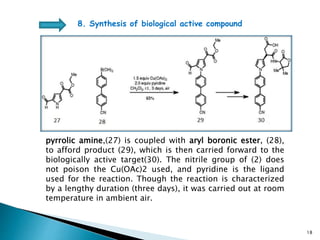
The document summarizes the Chan-Lam coupling reaction, which is a copper-catalyzed coupling between an aryl boronic acid and an alcohol or amine to form secondary aryl ethers or aryl amines. It provides the history of the reaction and compares it to related palladium-catalyzed reactions. The document then discusses the proposed mechanism and provides several applications of the Chan-Lam coupling reaction in synthesizing drug molecules, heteroarenes, aminoesters, and other compounds. In conclusion, the author discusses developing an improved Chan-Lam protocol using a novel copper catalyst that is simple, rapid, and produces products at room temperature in a short time.