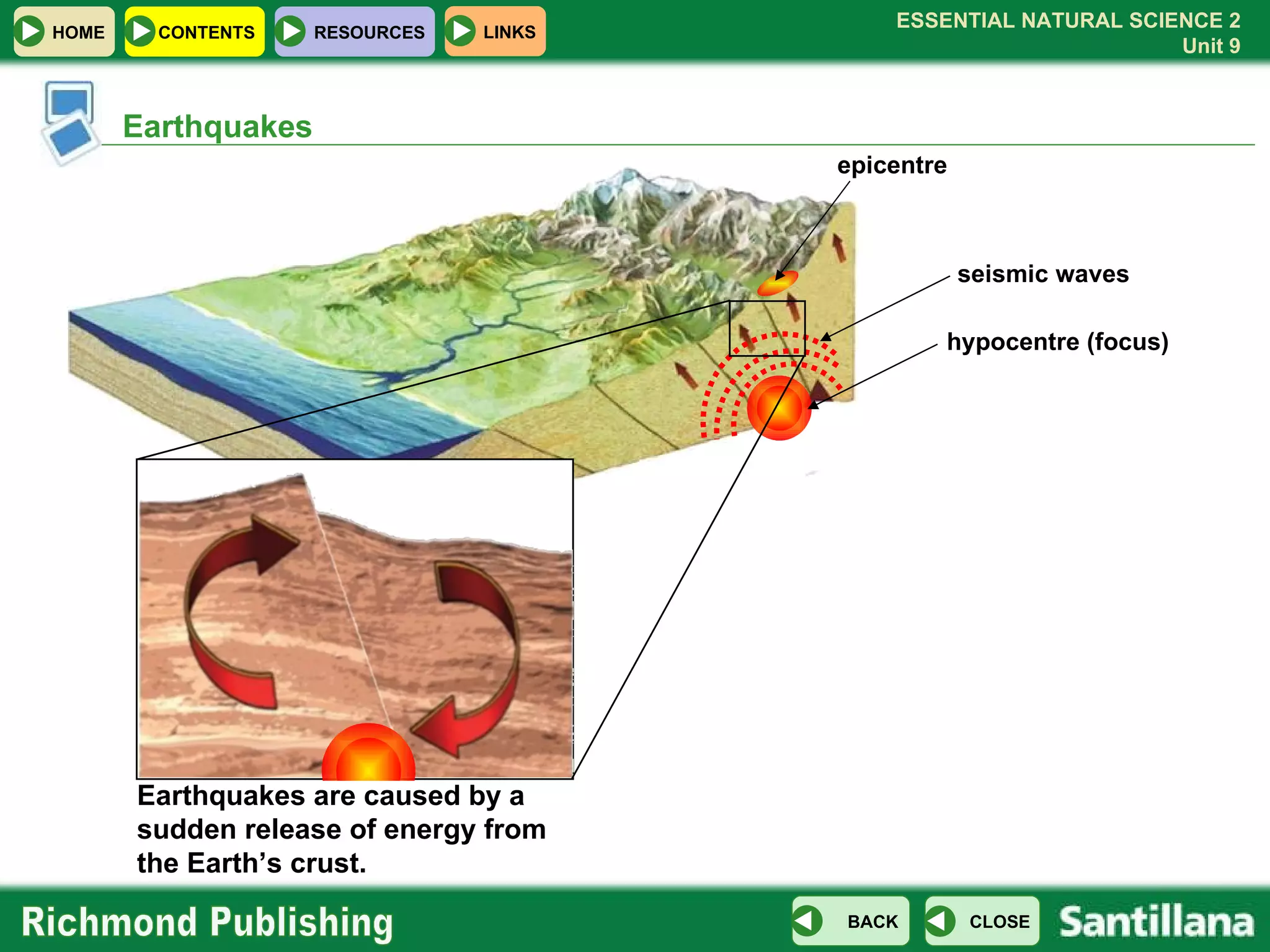
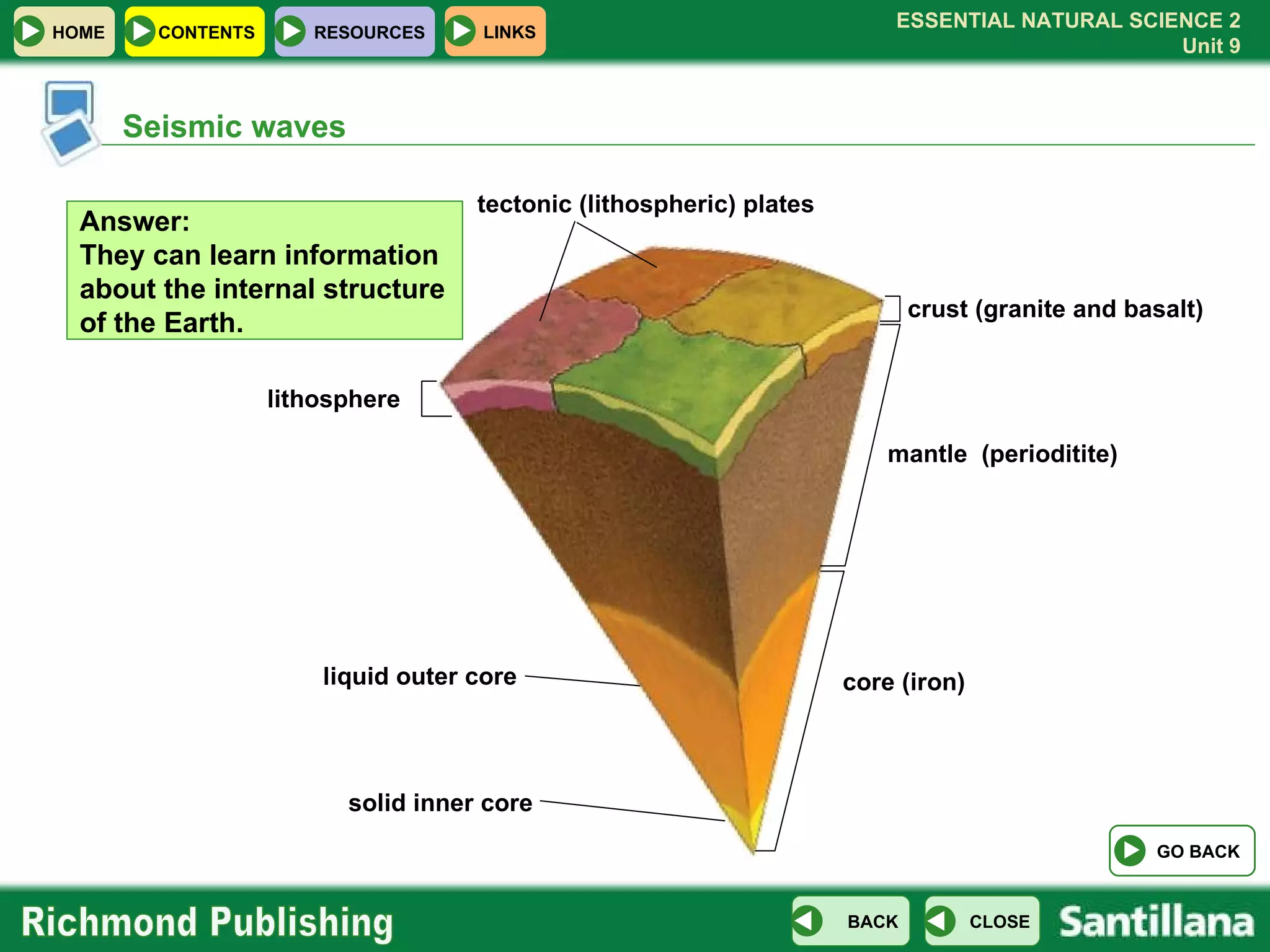
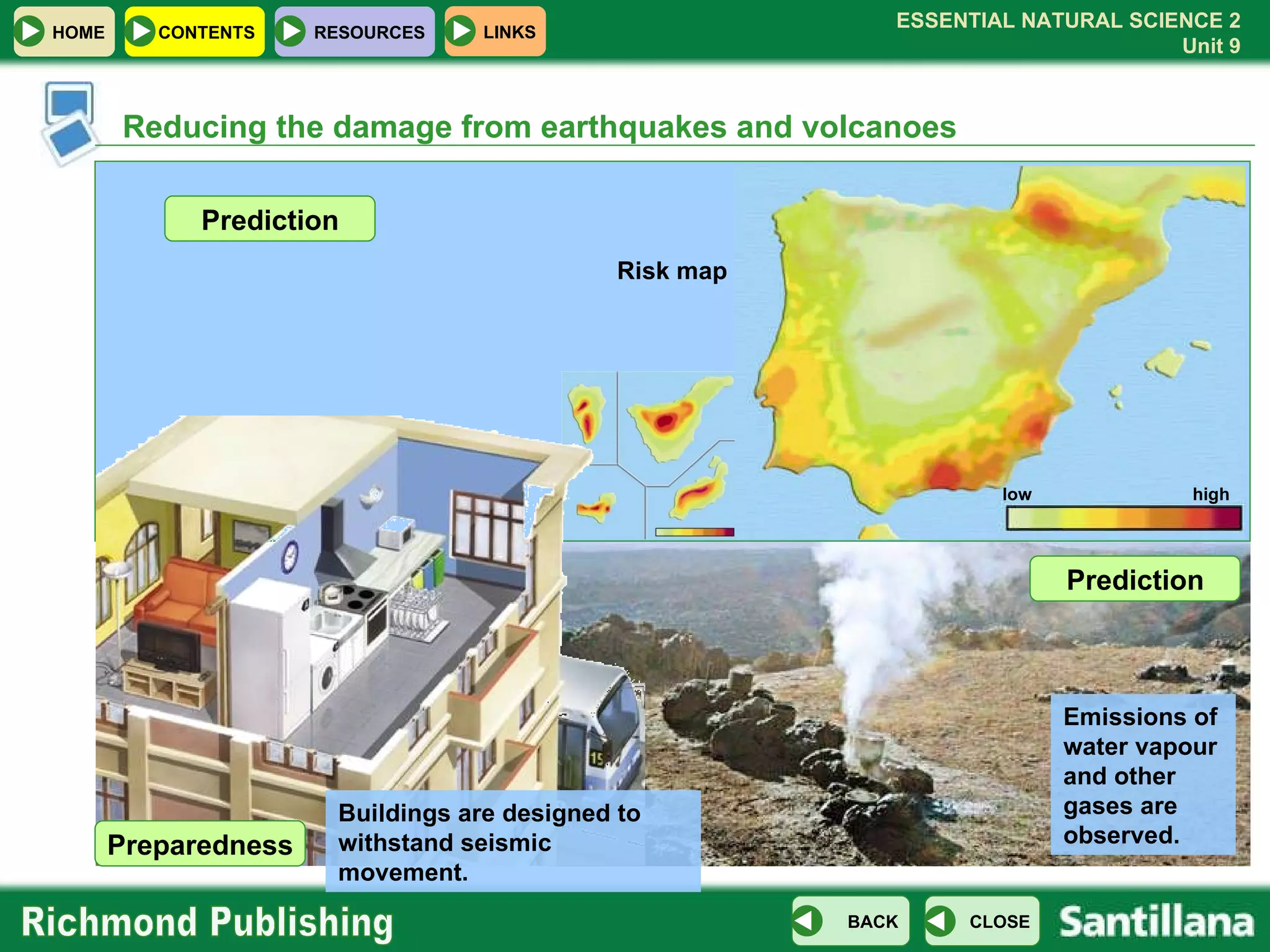
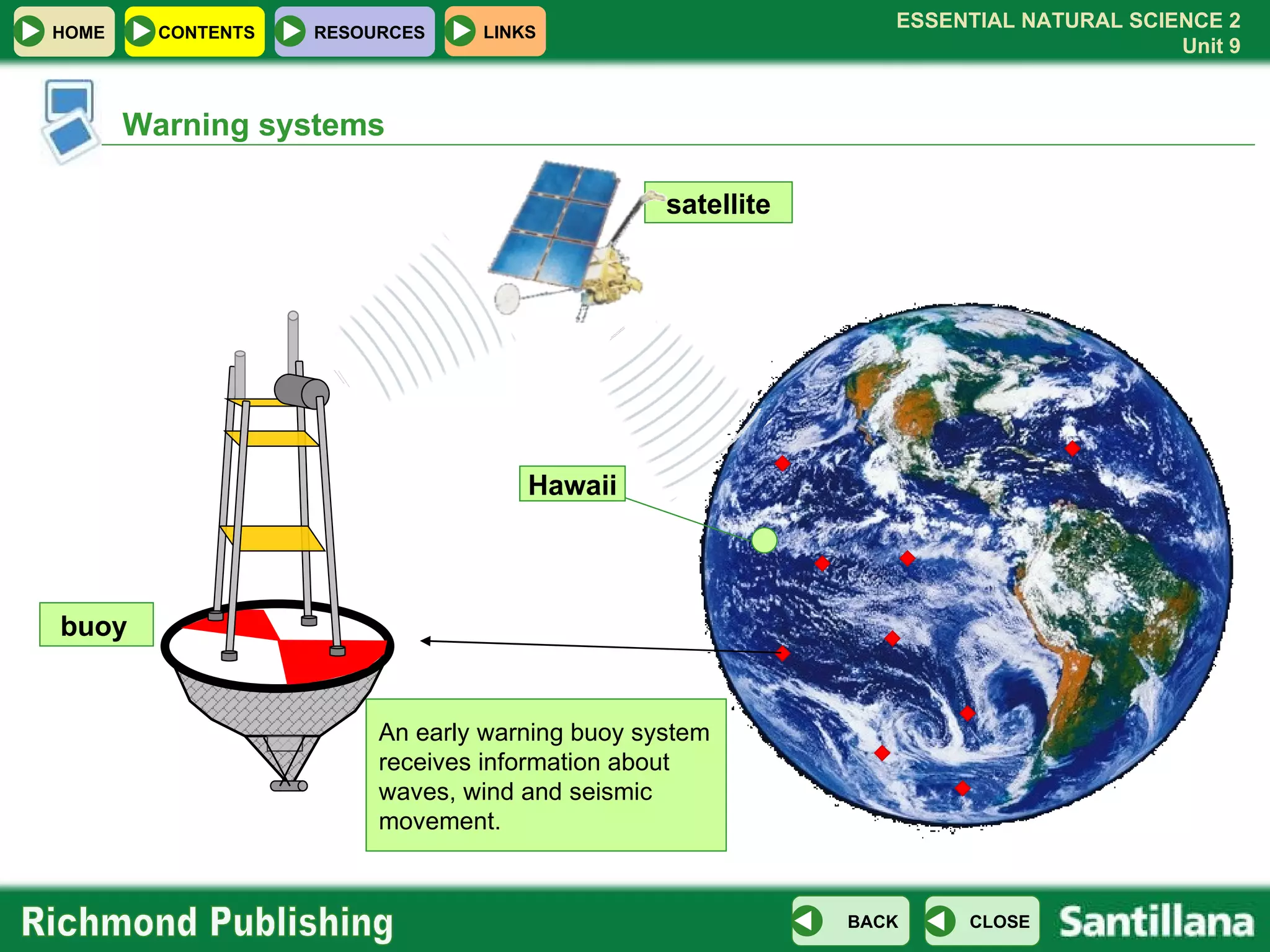
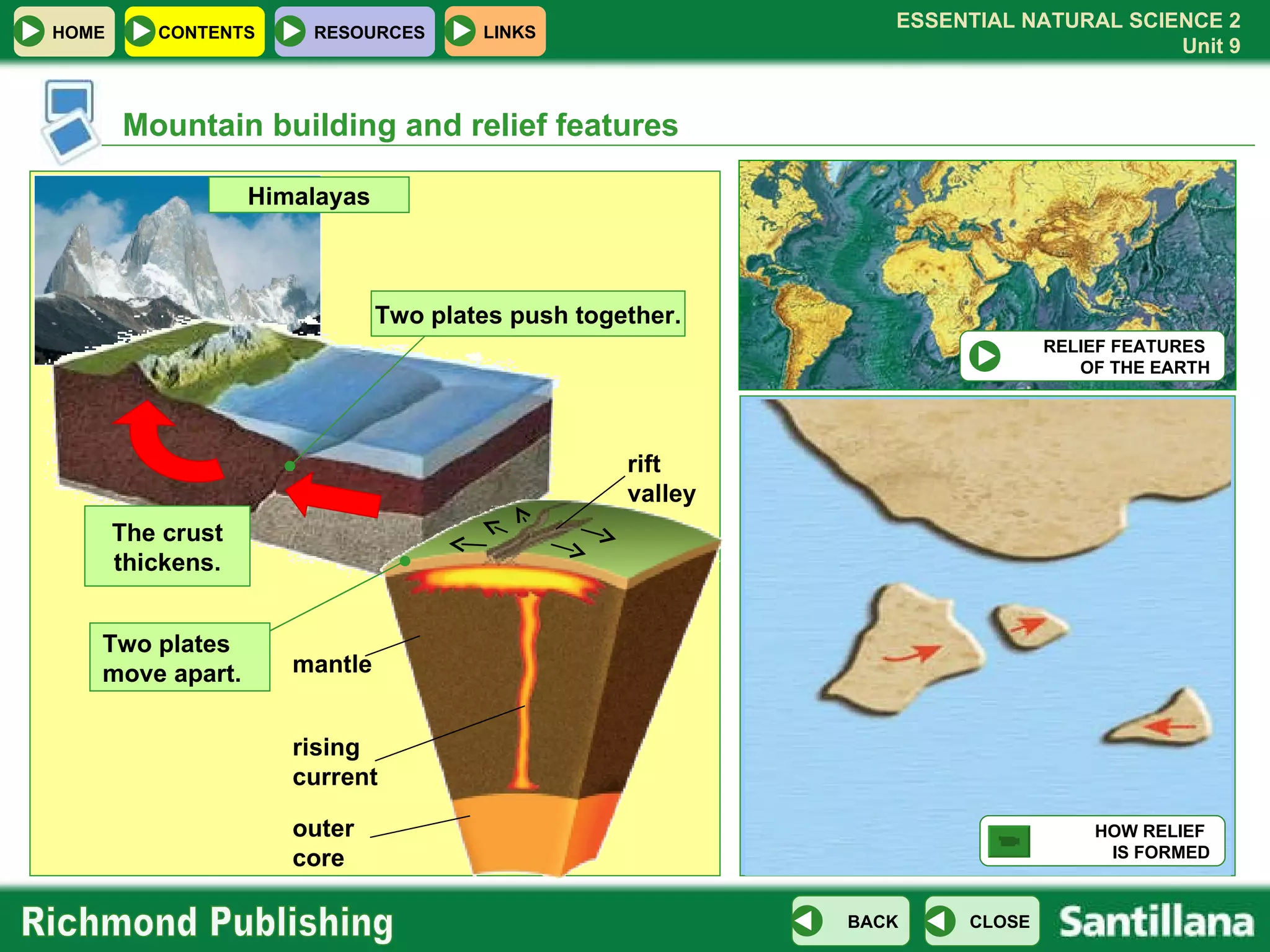
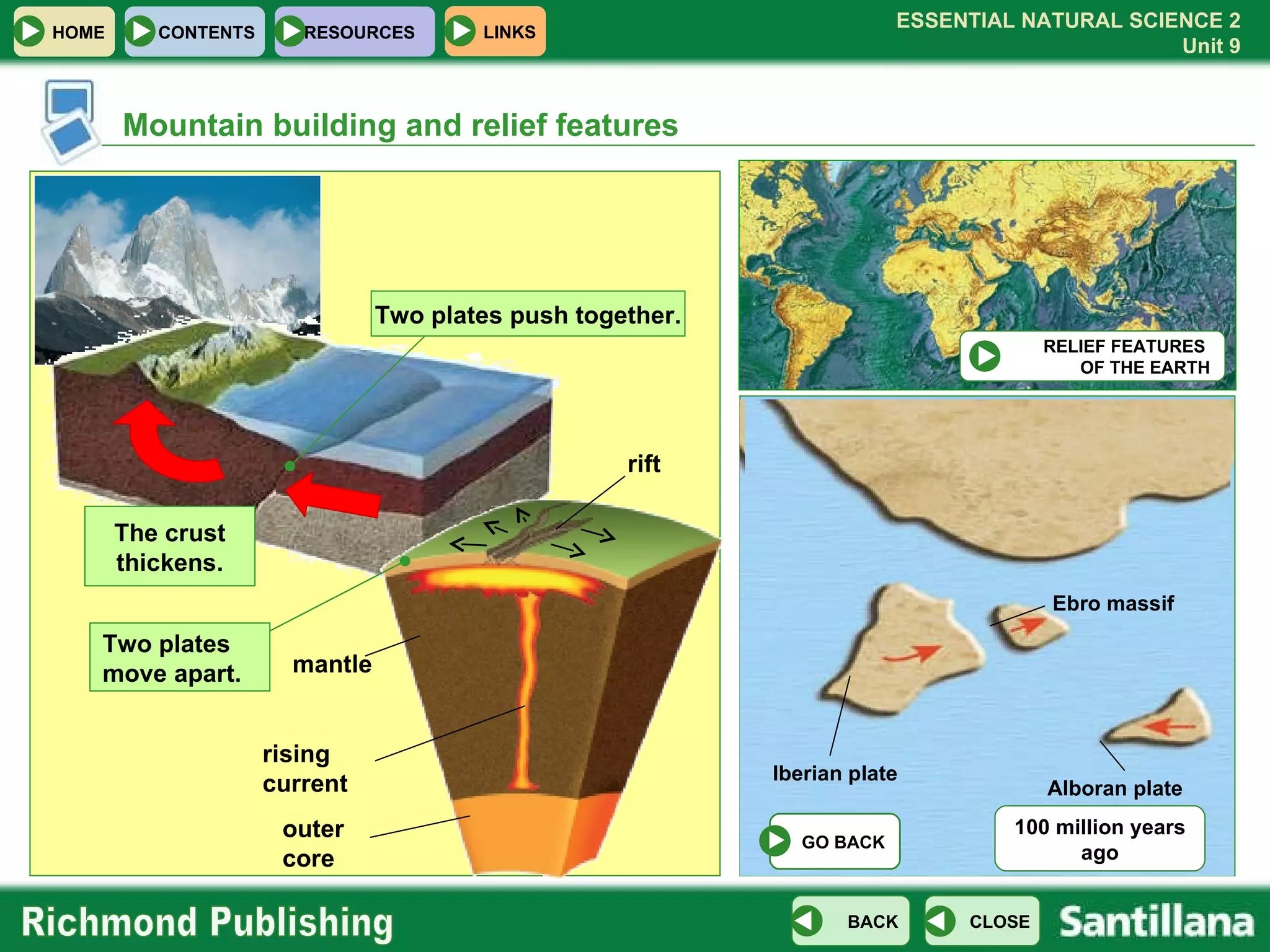
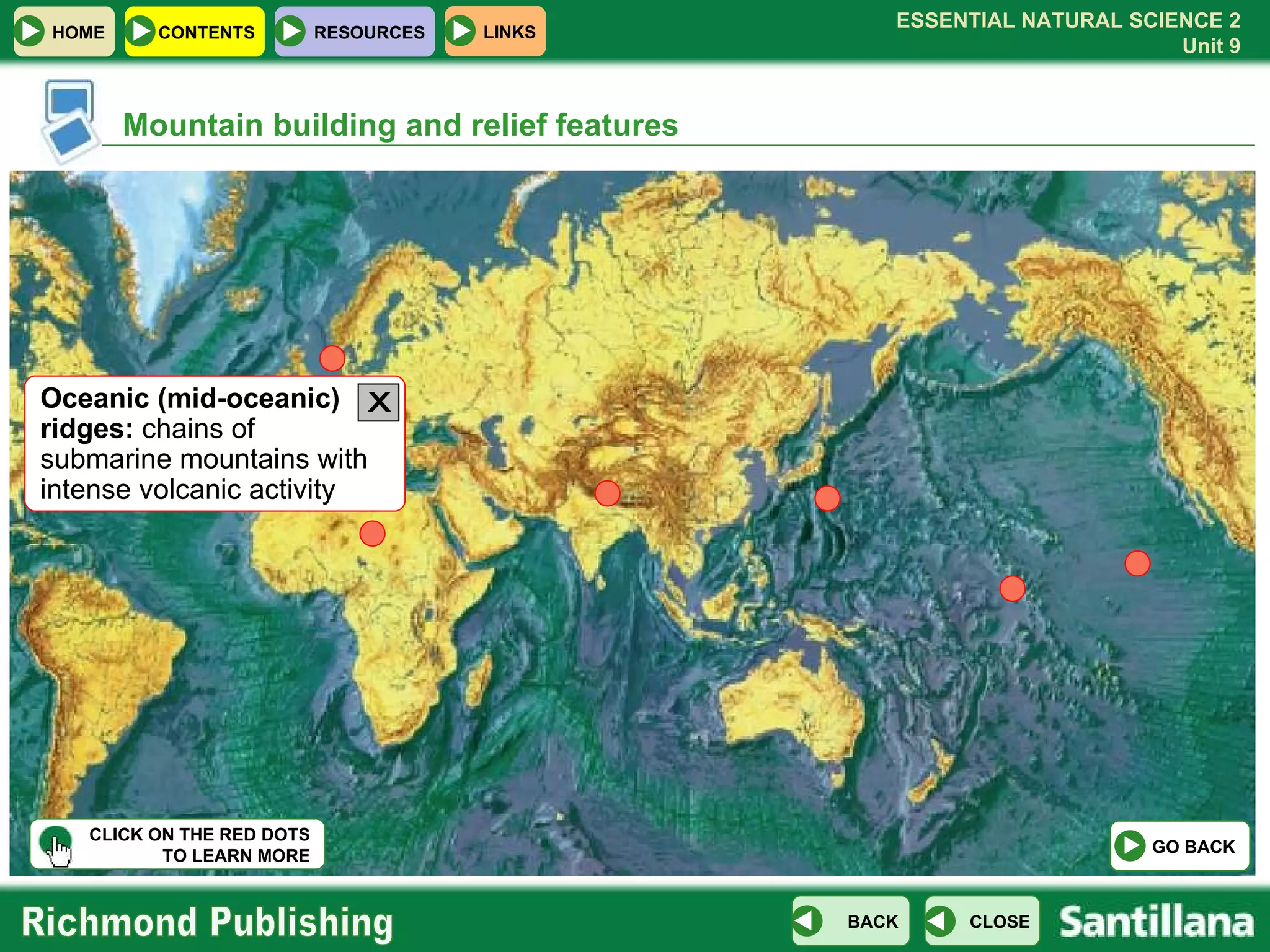
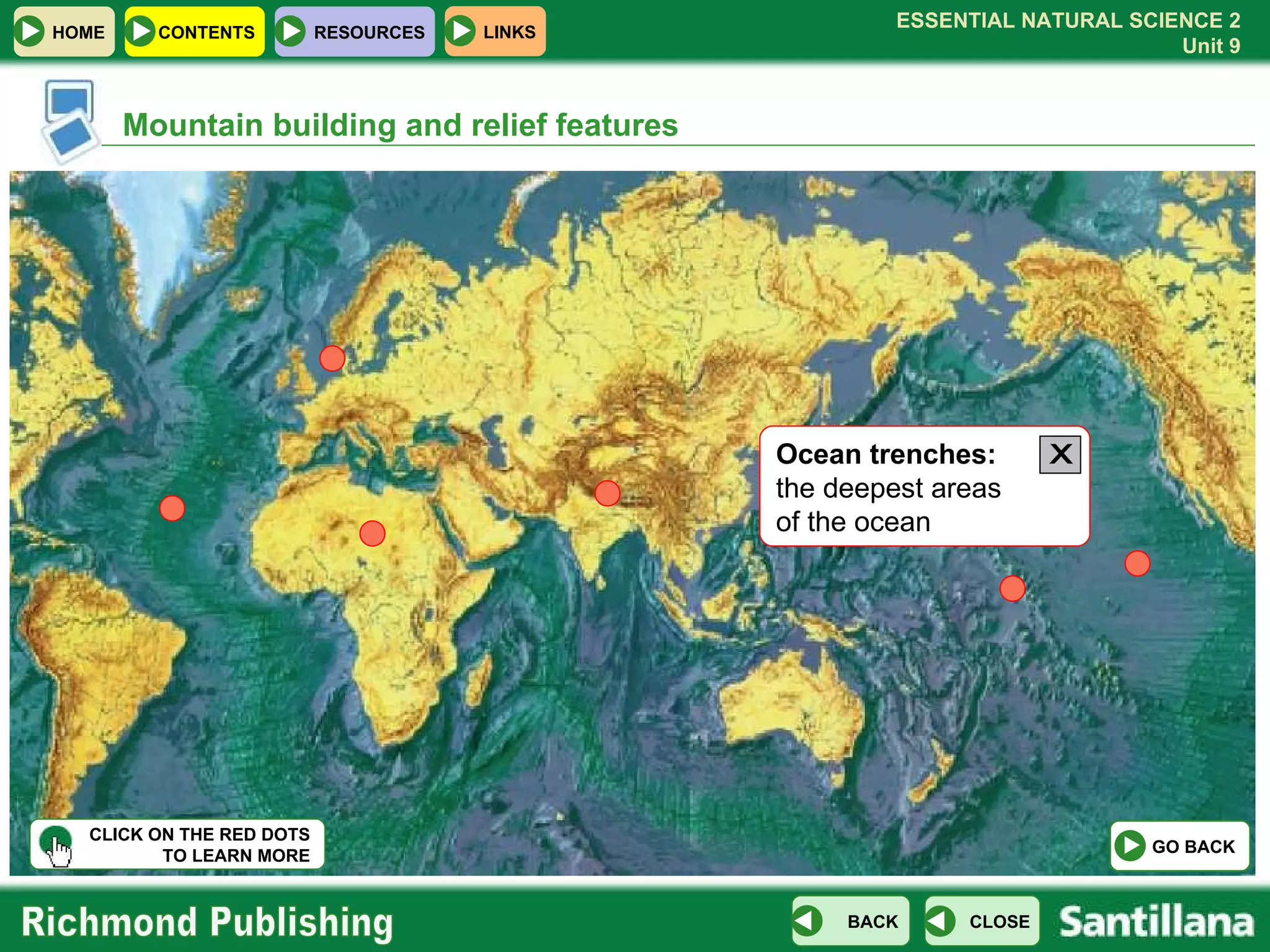
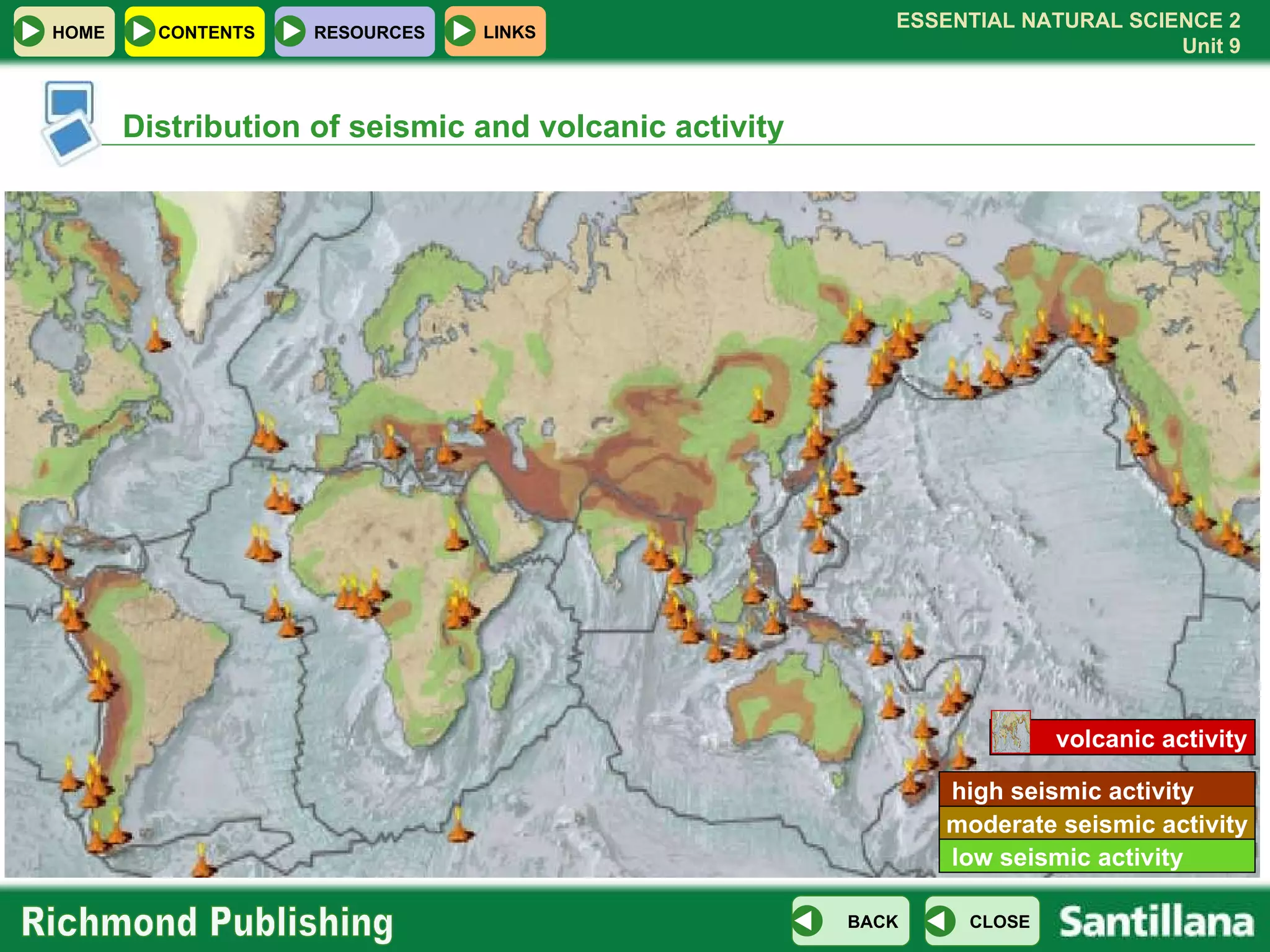
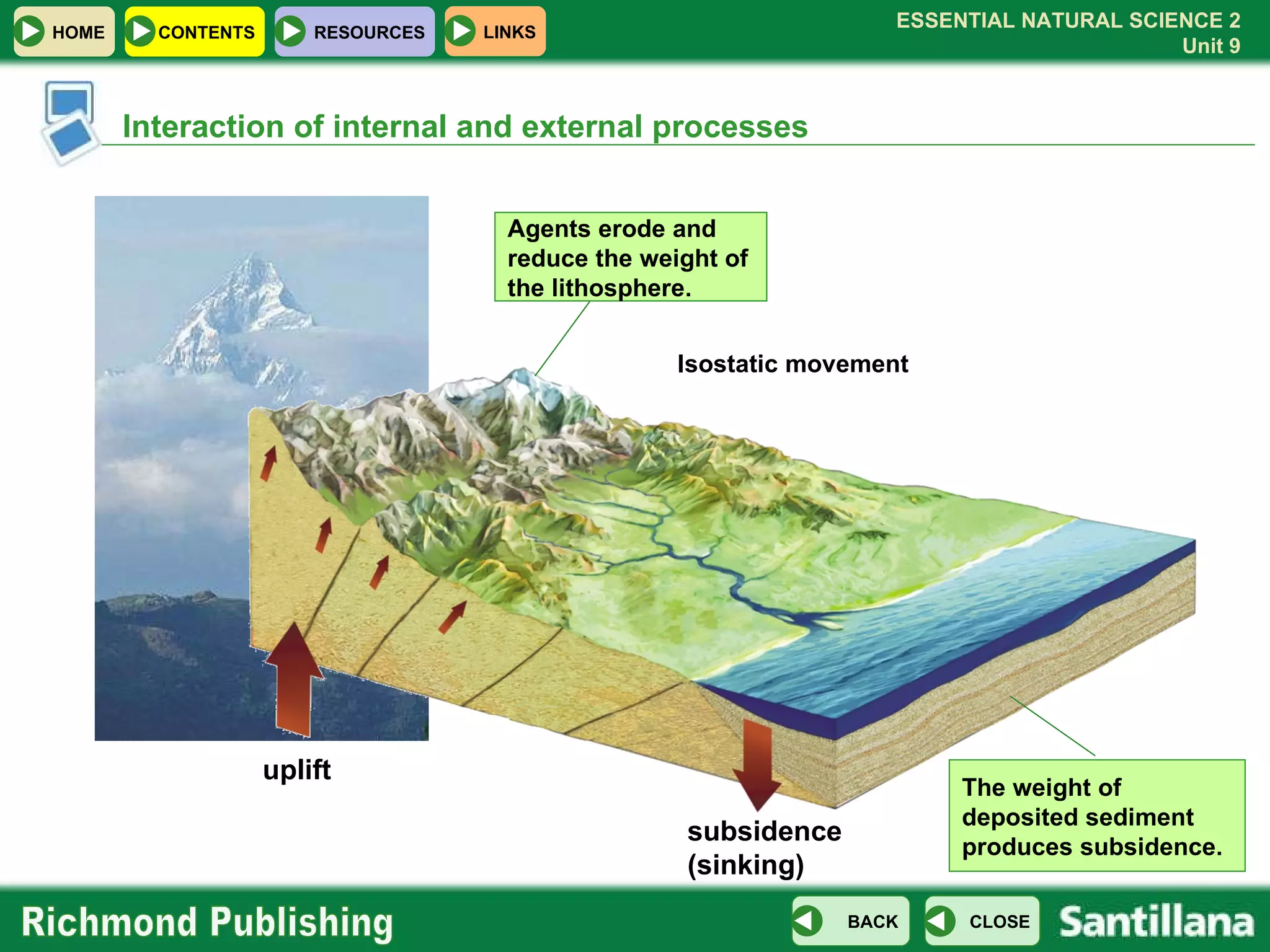
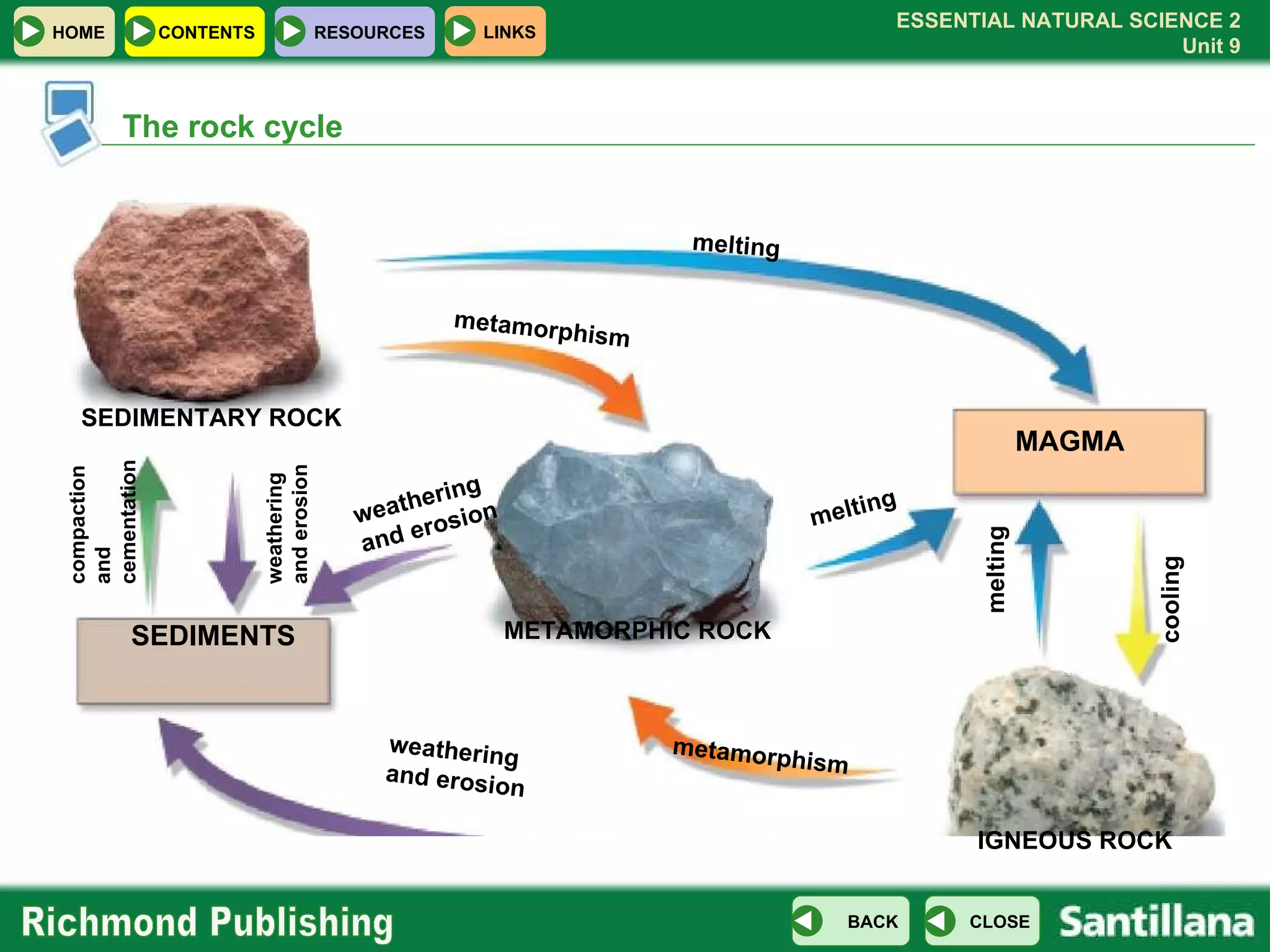
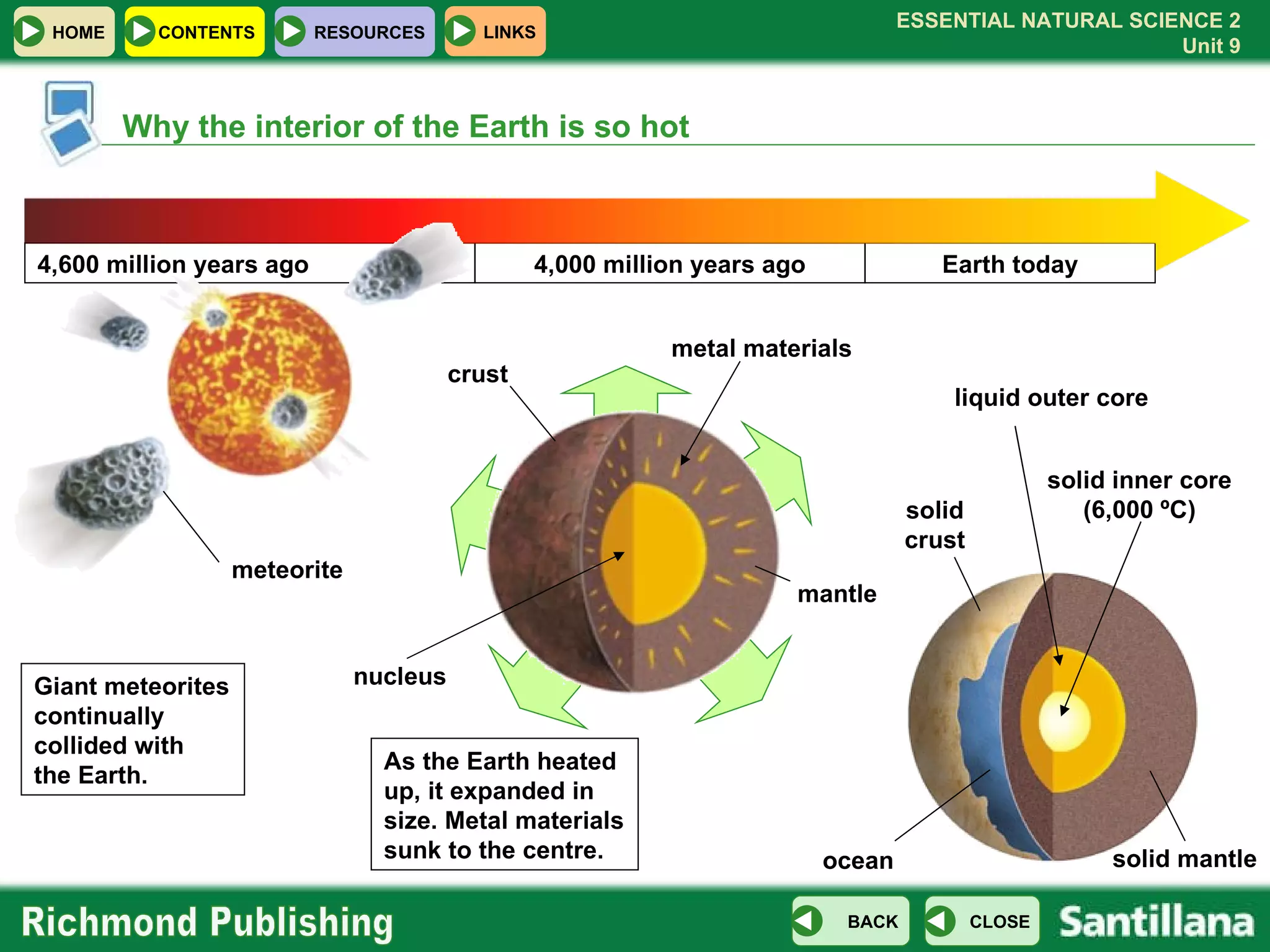
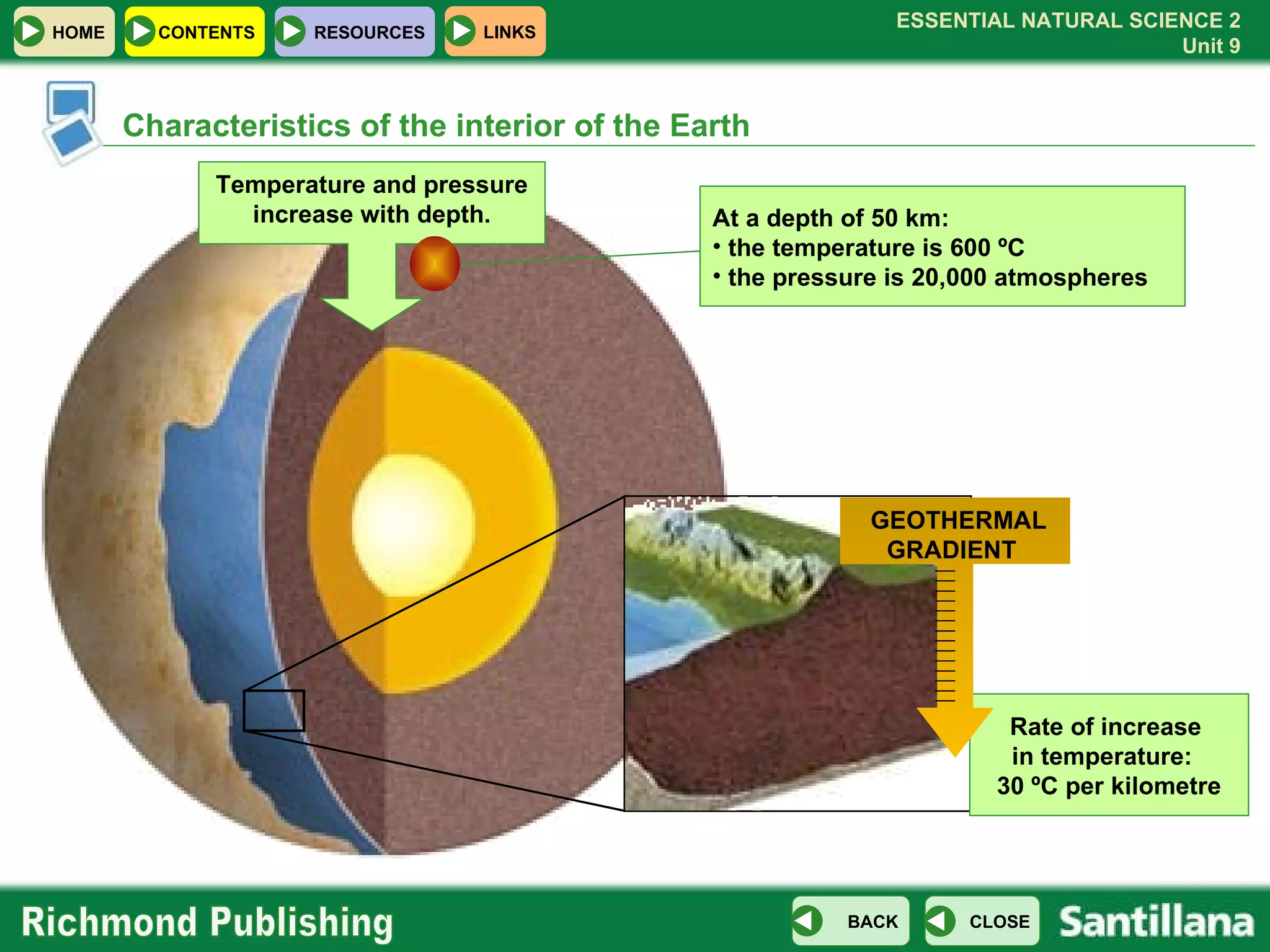
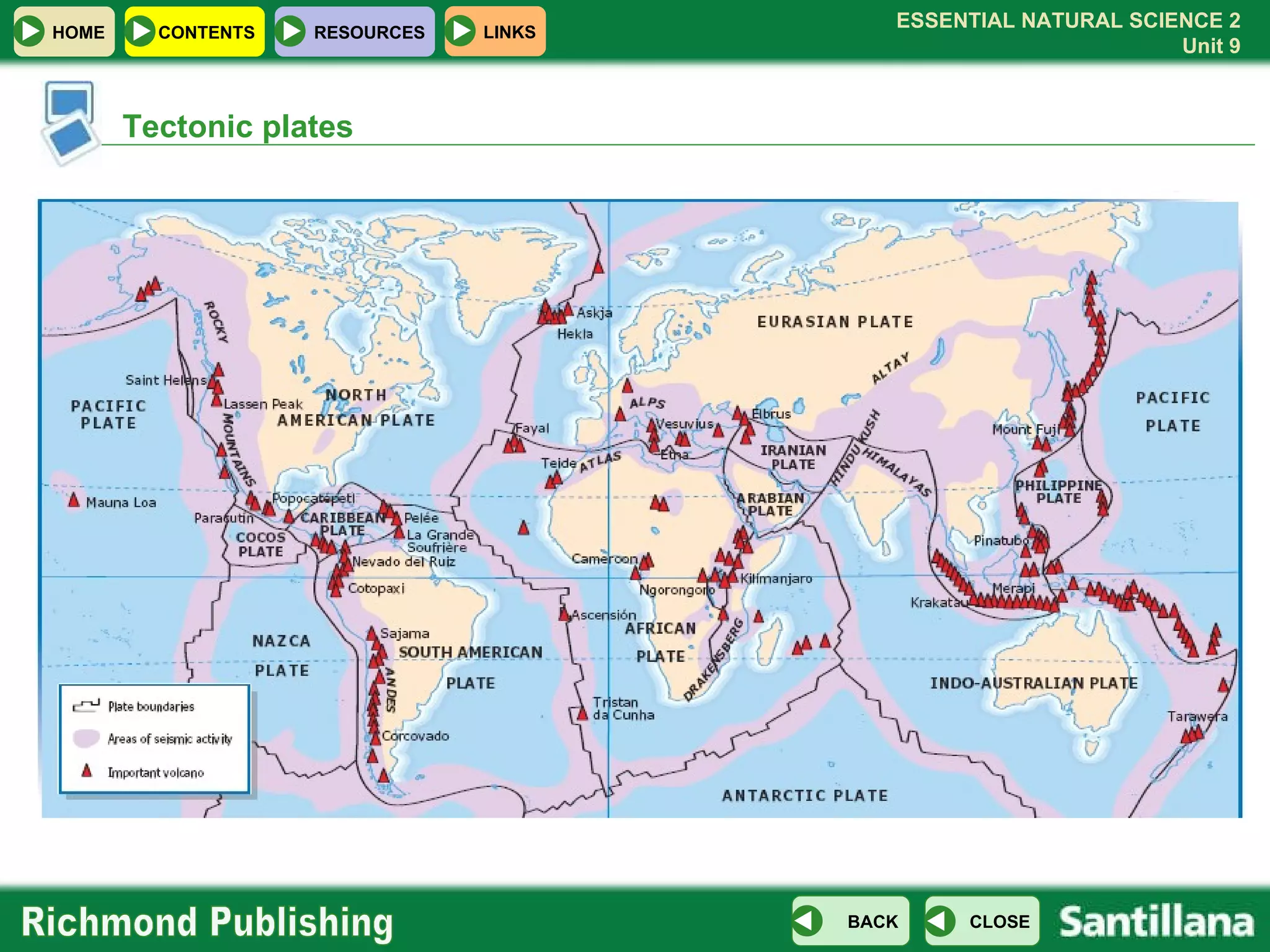
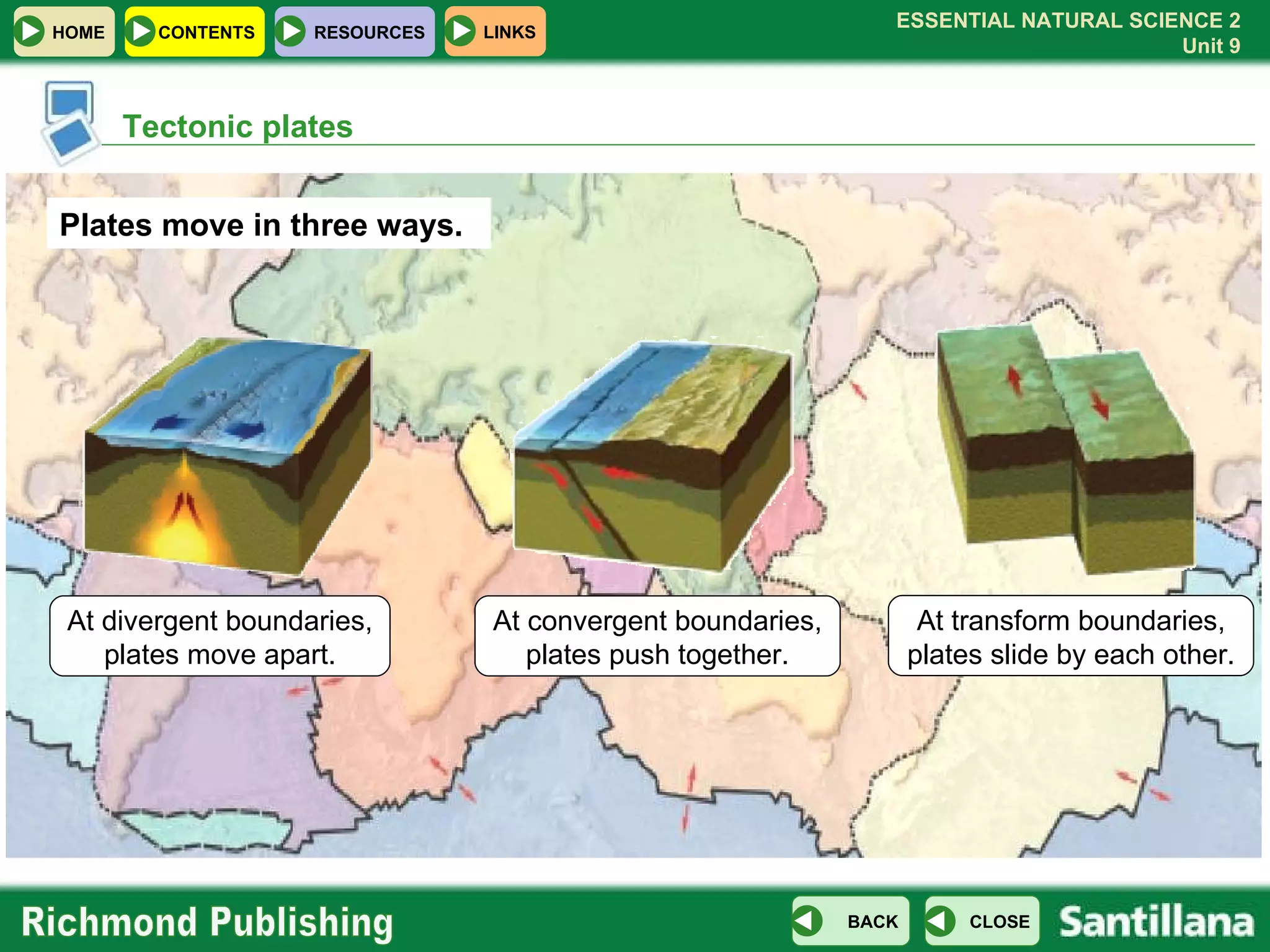
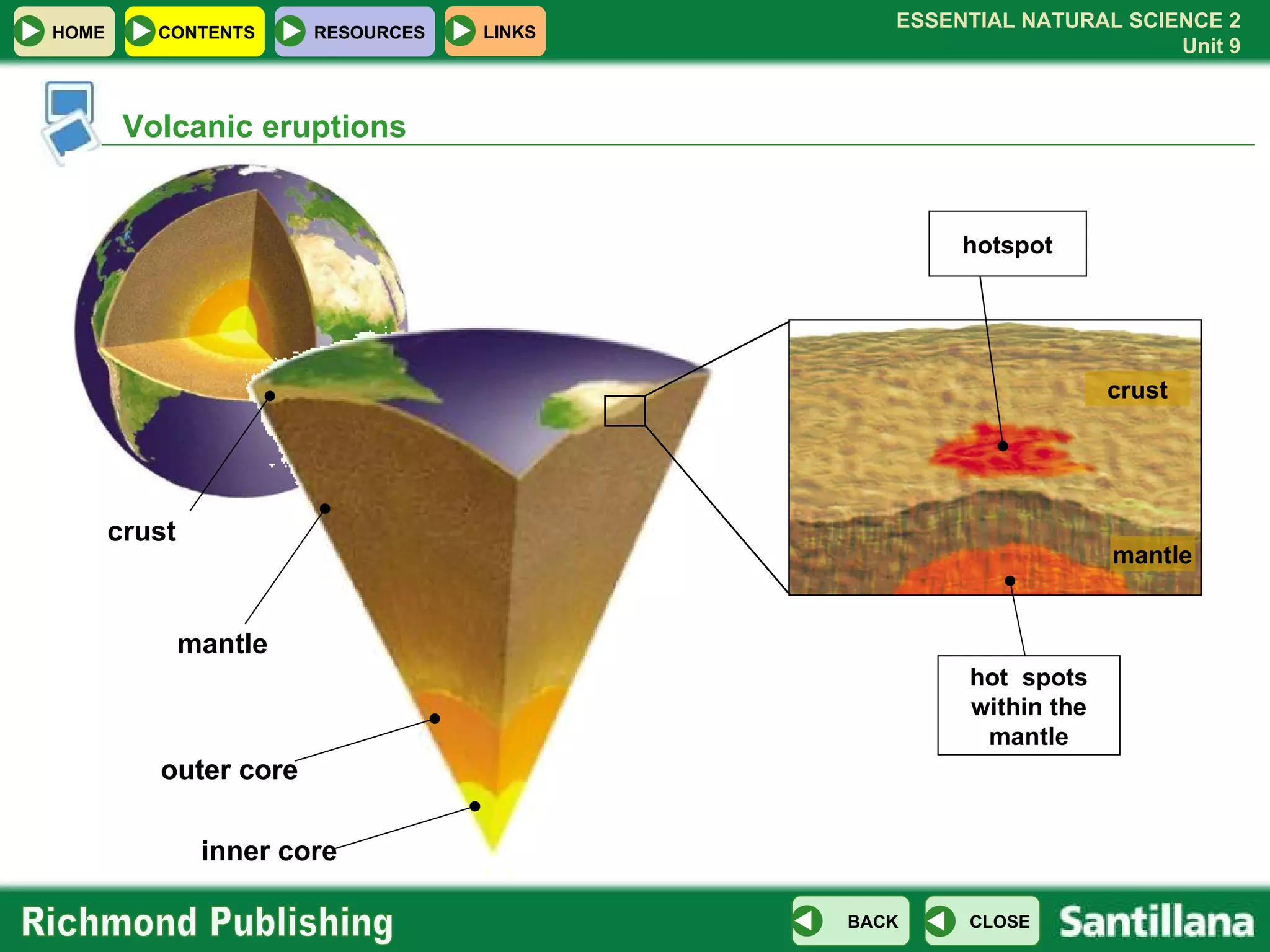
The document discusses the internal structure and dynamics of the Earth. It describes how the Earth's interior is very hot due to radioactive decay and gravitational settling. It explains plate tectonics and how the movement of tectonic plates results in volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. It also discusses different rock types, the rock cycle, and landform features related to tectonic activity.




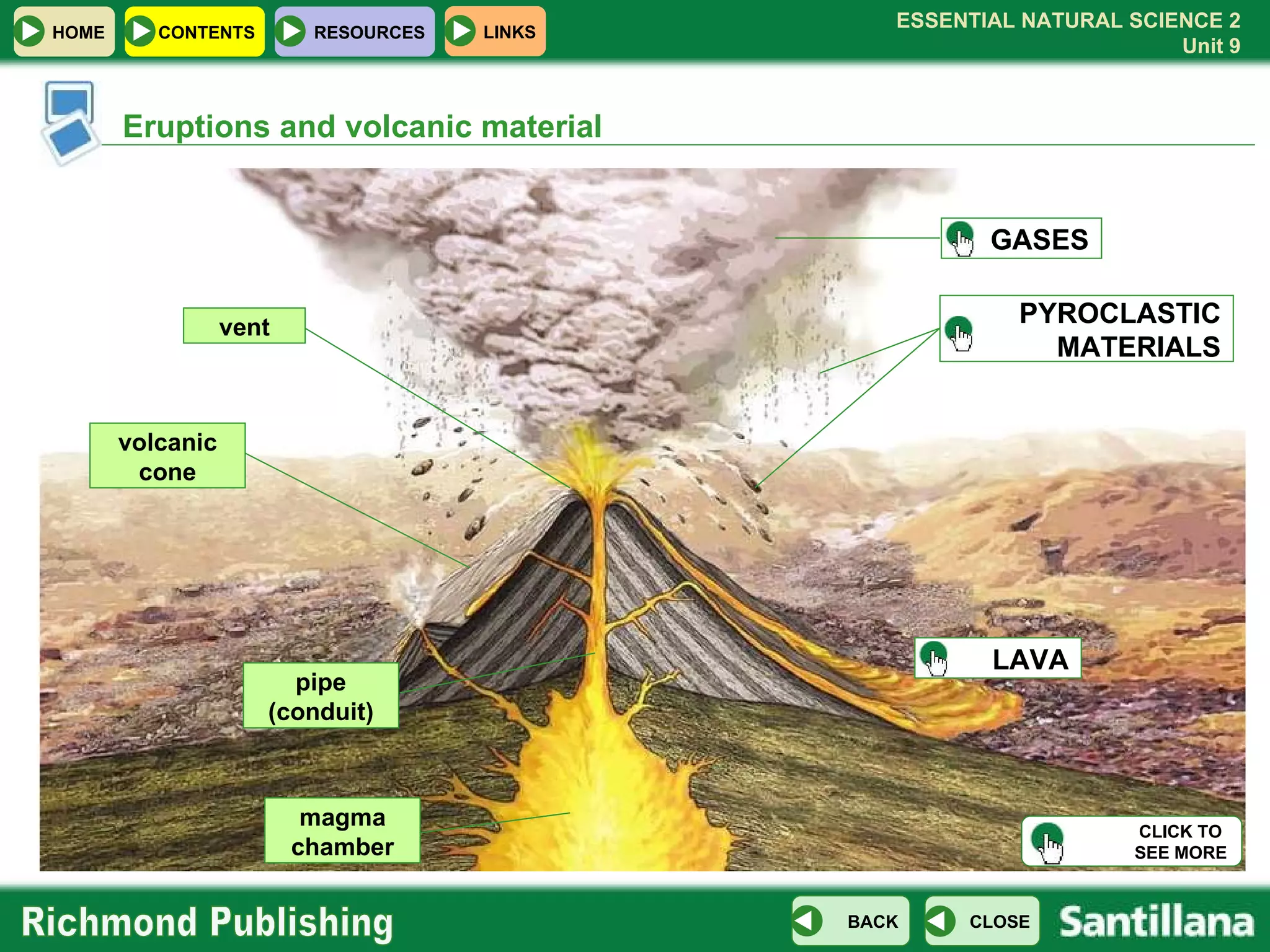
![Eruptions and volcanic material vent volcanic cone PYROCLASTIC MATERIALS GASES LAVA magma chamber pipe (conduit) CLICK TO SEE MORE GASES carbon dioxde water vapour sulphur gases carbon monoxide X [close]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u09internaldynamics-100104154127-phpapp01/75/U09-Internal-Dynamics-12-2048.jpg)
![Eruptions and volcanic material vent volcanic cone PYROCLASTIC MATERIALS GASES LAVA magma chamber pipe (conduit) CLICK TO SEE MORE PYROCLASTIC MATERIAL ash lapilli volcanic bombs X [close]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u09internaldynamics-100104154127-phpapp01/75/U09-Internal-Dynamics-13-2048.jpg)
![Eruptions and volcanic material Bubbles of gas escape gently. Bubbles of gas splatter and cause explosions. vent volcanic cone PYROCLASTIC MATERIALS GASES LAVA magma chamber pipe (conduit) CLICK TO SEE MORE HOME CONTENTS RESOURCES LAVA At more than 1,000 ºC, lava is very liquid and flows easily. At less than 700 ºC, lava is thick and flows slowly. X [close]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u09internaldynamics-100104154127-phpapp01/75/U09-Internal-Dynamics-14-2048.jpg)
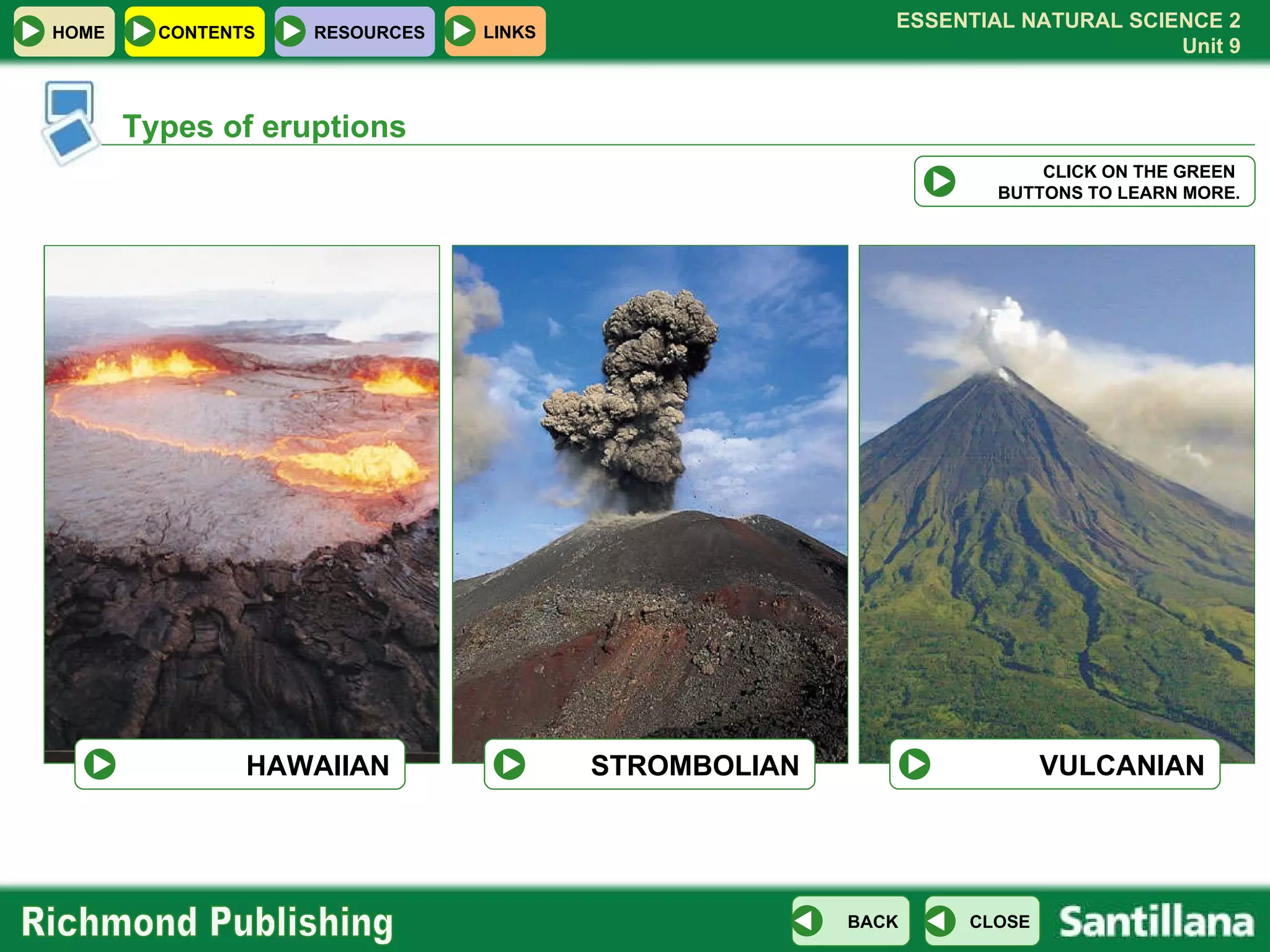
![Types of eruptions HAWAIIAN CLICK ON THE GREEN BUTTONS TO LEARN MORE. STROMBOLIAN VULCANIAN magma temperature: very high (over 1,000 ºC) very liquid lava not very destructive nor explosive Shield volcano magma chamber central vent pipe (conduit) X [close]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u09internaldynamics-100104154127-phpapp01/75/U09-Internal-Dynamics-16-2048.jpg)
![Types of eruptions CLICK ON THE GREEN BUTTONS TO LEARN MORE. HAWAIIAN STROMBOLIAN VULCANIAN STROMBOLIAN magma temperature: moderate (700 - 1,000 ºC) thick lava explosive pyroclastic material pipe (conduit) Stratovolcano (composite volcano) magma chamber volcanic cone central vent X [close]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u09internaldynamics-100104154127-phpapp01/75/U09-Internal-Dynamics-17-2048.jpg)
![Types of eruptions CLICK ON THE GREEN BUTTONS TO LEARN MORE. HAWAIIAN STROMBOLIAN VULCANIAN VULCANIAN magma temperature: low (less than 700 ºC) violent, destructive explosions generally gases and ash are expelled magma chamber Dome volcano volcanic pipe of solidified lava X [close]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u09internaldynamics-100104154127-phpapp01/75/U09-Internal-Dynamics-18-2048.jpg)