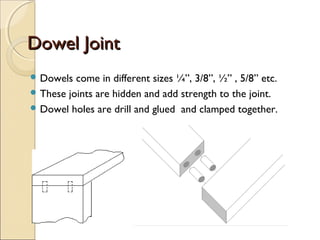
This document describes several common types of wood joints:
Dowel joints use dowels inserted into drilled holes for strength. Dado joints cut away wood to hold shelves without fasteners. Rabbet joints cut wood at specific lengths then glue them together. Lap joints overlap cut wood and glue or nail them together. Dovetail joints cut interlocking wood shapes to join drawers strongly. Mortise and tenon joints cut a tenon that inserts into a mortise for a very strong connection. Miter joints at corners can be strengthened with hidden wood splines. Tongue and groove joints insert a tongue into a groove to join flooring or panels edge to edge into a flat surface.