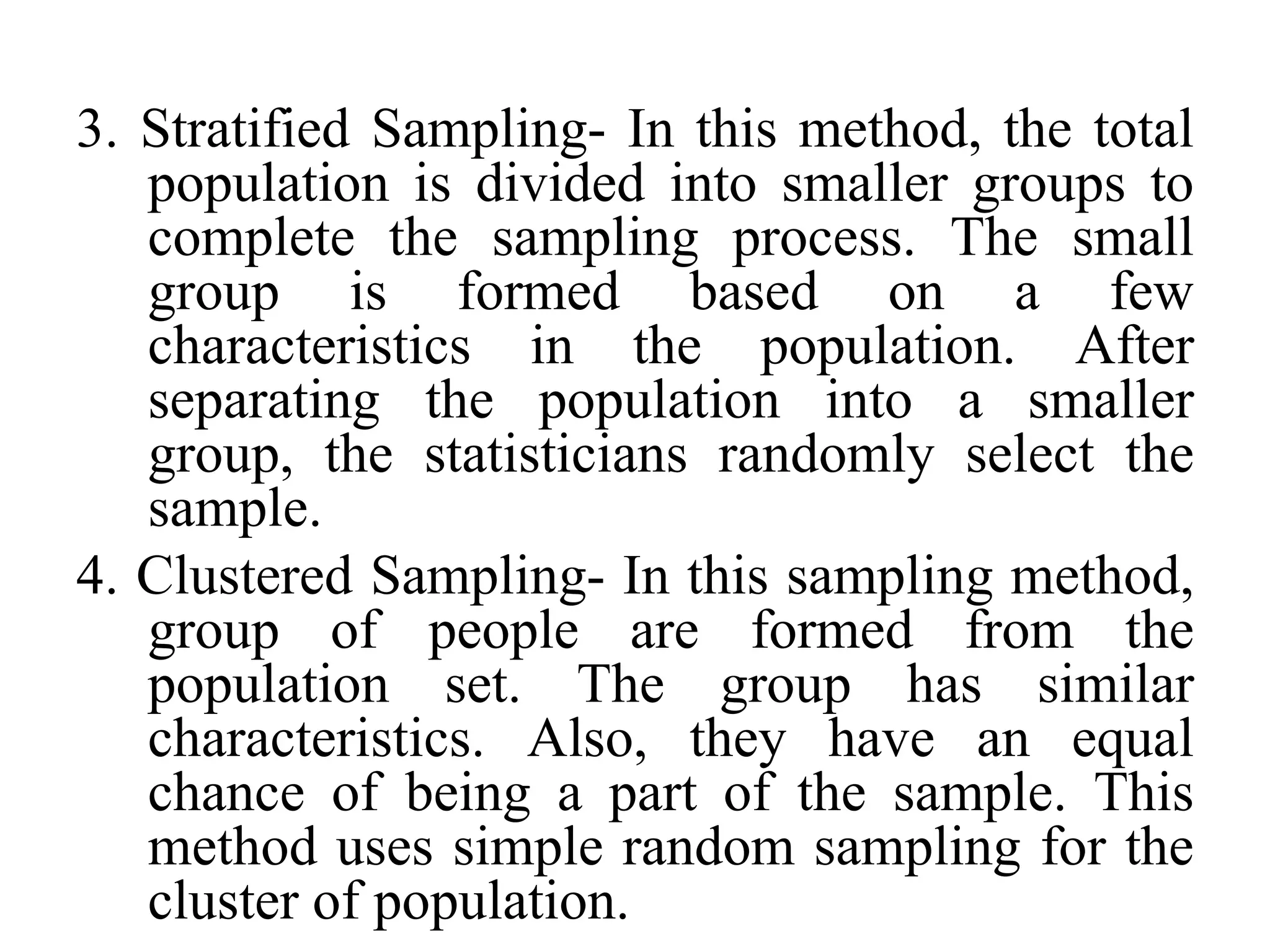
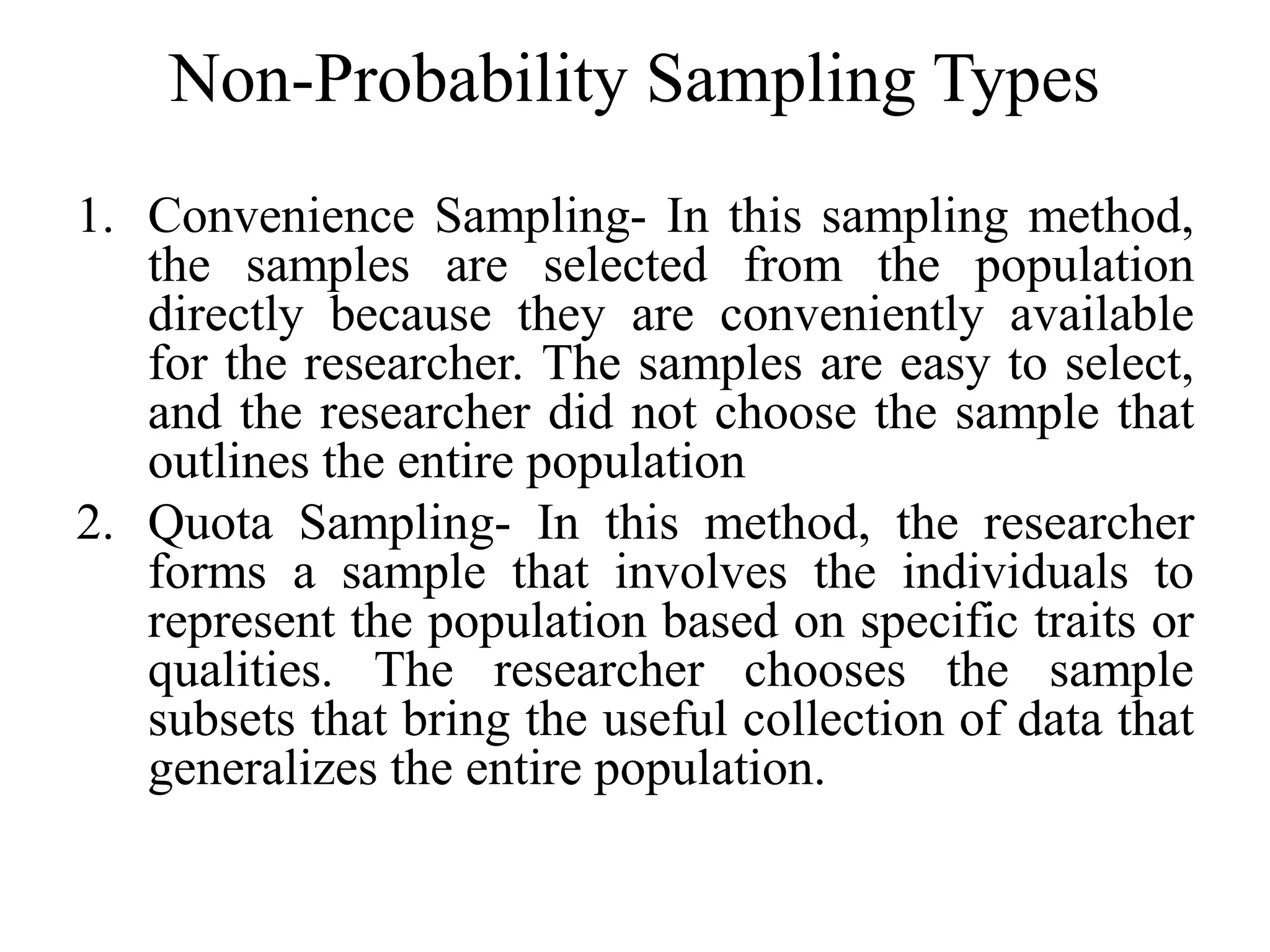
This document discusses different sampling methods used in statistics. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling uses random selection so every member of the population has a chance of being selected, including simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and clustered sampling. Non-probability sampling does not use random selection and includes convenience sampling, quota sampling, purposive sampling, and snowball sampling. The document provides details on each of these sampling techniques.