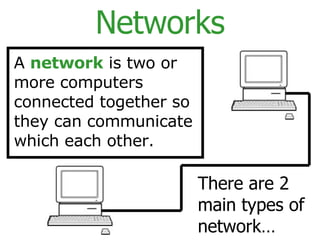
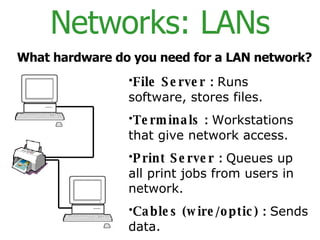
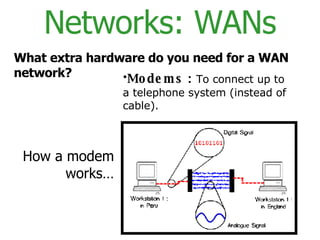
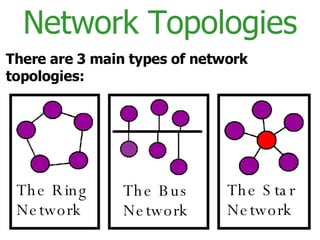
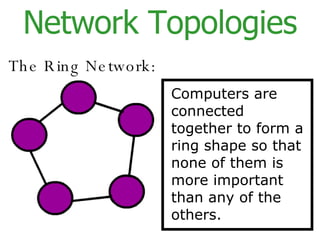
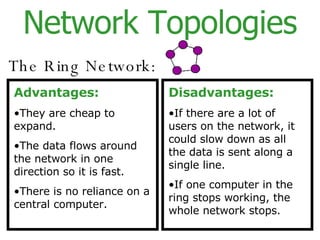
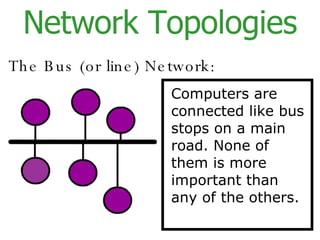
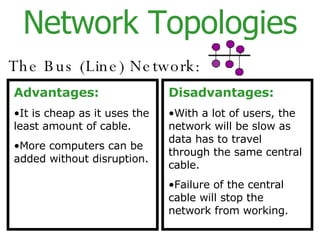
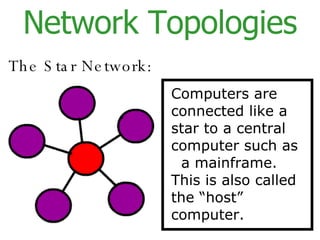
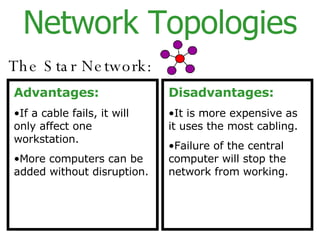
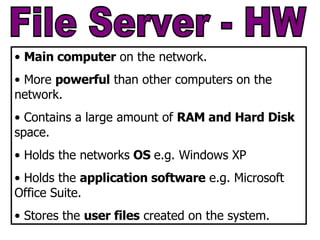
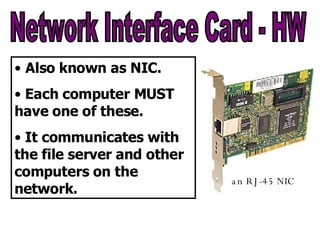
The document provides an overview of computer networks, including local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs). It defines LANs and WANs, describes the necessary hardware components for each including servers, cables, switches and modems. It also covers the advantages and disadvantages of networks, the three main network topologies - star, ring and bus - and aspects of network security.