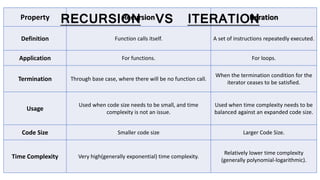
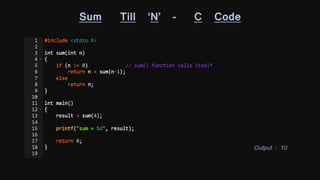
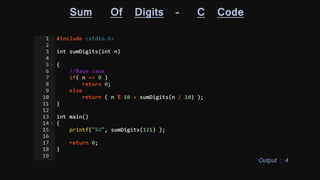
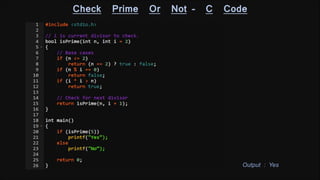
The document discusses recursion and provides examples of recursive algorithms and code implementations. It defines recursion as a function calling itself directly or indirectly. Examples given include computing factorials recursively and calculating the sum of digits of a number recursively. Algorithms are presented for checking if a number is prime recursively and calculating the sum of the first N natural numbers recursively. Code snippets are included to demonstrate recursive implementations in C.