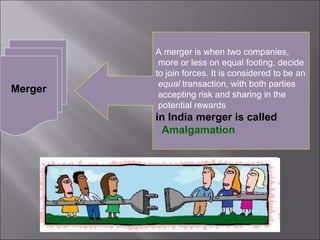
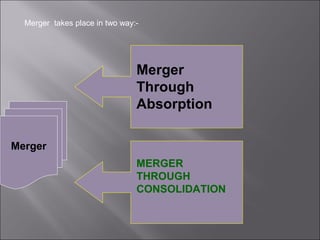
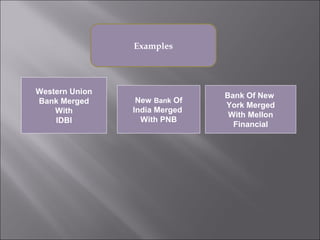
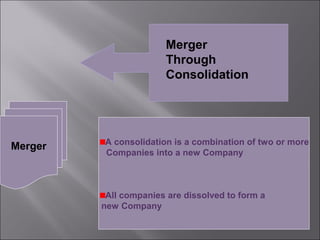
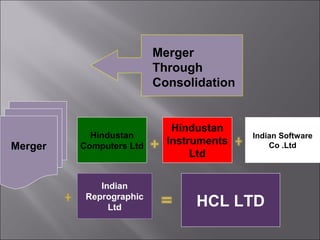
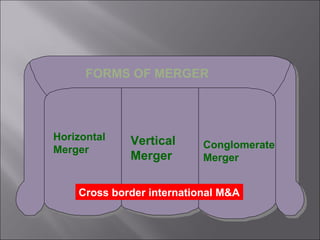
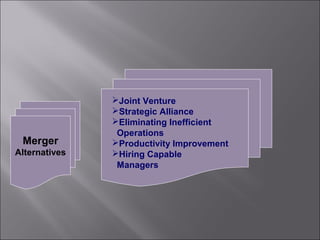
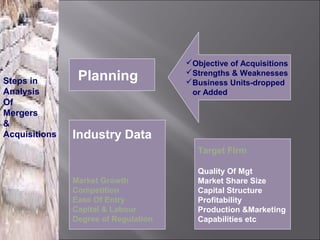
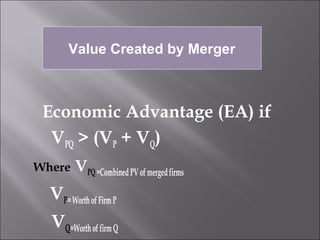
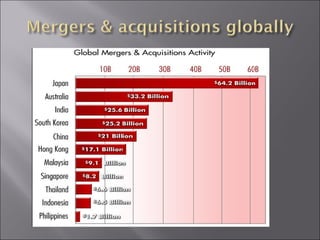
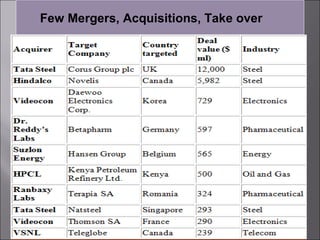
This presentation discusses mergers and acquisitions. There are several types of mergers, including horizontal mergers between companies in the same industry, vertical mergers between suppliers and customers, and conglomerate mergers between unrelated businesses. Mergers can occur through absorption, where one company acquires another, or through consolidation, where both companies dissolve to form a new entity. Acquisitions occur when one company takes control of another. Motives for mergers and acquisitions include growth, market power, diversification, economies of scale, and access to new resources or markets. The process of analyzing a potential merger or acquisition involves planning, searching for targets, financial evaluation, determining the acquisition method, negotiation, and post-merger integration.