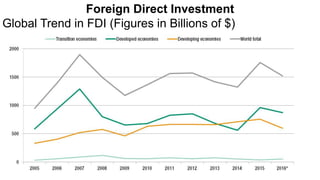
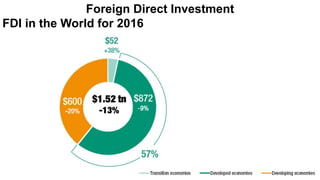
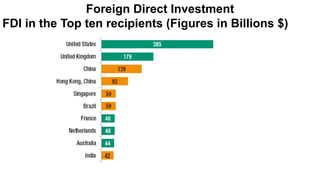
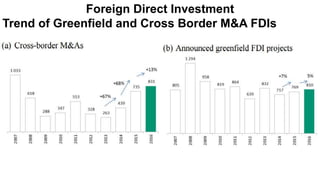
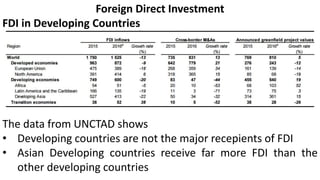
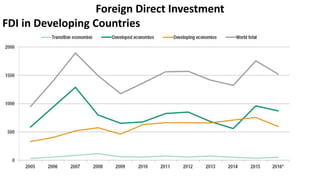
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country, in order to gain control or influence over them. There are three main types of FDI: greenfield investment which builds new facilities from scratch; mergers and acquisitions of existing foreign firms; and brownfield investment which upgrades facilities of acquired firms. Multinational firms engage in FDI for market seeking, resource seeking, strategic asset seeking, or efficiency seeking reasons. They establish foreign operations through franchising, branches, subsidiaries, or joint ventures with local firms. While developing countries receive FDI, Asian developing countries are the largest recipients among developing nations.