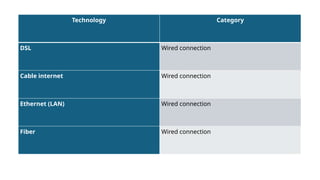
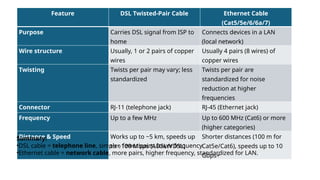
A connection is a link between two or more devices that allows them to communicate, share data, or access resources.
In simple words: It’s how devices “talk” to each other.
A link between two or more devices that allows them to communicate and exchange data.