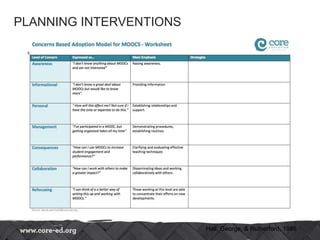
The document discusses using a concerns-based approach to professional development (PD) programming by identifying teachers' levels of concern about an innovation through open-ended questions and feedback, and then designing PD interventions focused on self, task, and impact that match the varying levels of concern, from raising awareness to collaboration and refinement of the innovation. Key aspects of the approach include the Concerns Based Adoption Model and focusing PD at each of the model's 7 levels of concern.




![OPEN-ENDED STATEMENT
“When you think about [innovation] what
concerns do you have? Please be frank, and
answer in complete sentences.”
Hall & Hord, p. 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbamoutline-140616192401-phpapp02/85/Cbam-outline-5-320.jpg)