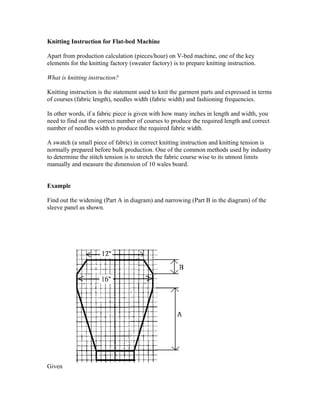
This document provides instructions for calculating production rates for circular and flat-bed knitting machines. It also provides an example of how to determine the knitting instructions needed to widen and narrow a sleeve panel on a flat-bed machine based on the given courses, wales, and dimensions. The key steps are outlined for calculating the number of needles and courses required to achieve the specified width and length changes over the height of the sleeve parts.