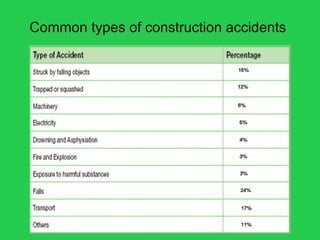
This document outlines major workplace hazards in construction such as falls, fires, chemicals, and vehicles. It discusses the importance of following health and safety guidelines to prevent long-term damage and diseases. Proper accident reporting procedures and emergency plans are also described, including notifying authorities of serious injuries or deaths. The roles and requirements for first aid personnel and equipment are explained as well.