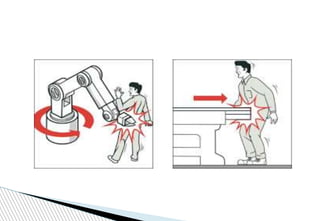
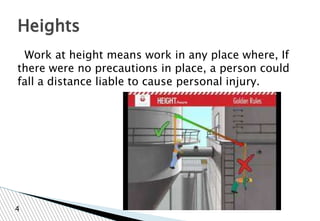
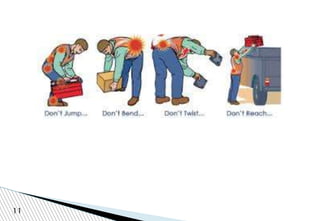
The document discusses various workplace hazards, emphasizing the importance of managing health and safety through moral, legal, and financial frameworks. It outlines common hazards including mechanical, physical, chemical, biological, environmental, and organizational risks, and highlights their potential impact on worker safety and health. Effective safety management strategies are proposed to recognize, control, and mitigate these hazards in order to reduce injuries and promote a healthier work environment.