Turbulence near the wall.pdf
•
2 likes•436 views
introduction to wall function in turbulence modeling
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
Interface delamination is the major failure mode of diamond-coated carbide tools in machining. On the other hand, coating cracking is possibly accompanied during a tribological process that induces the delamination phenomenon. However, such an influence between the two failure behaviors has not been investigated in a quantitative way to better understand and design diamond coating tools.
In this study, a three-dimensional (3D) indentation model combining cohesive interactions and extended finite element method (XFEM) was developed to investigate the diamond-coating, carbide-substrate interface behavior with the incorporation of coating cracking. The cohesive interaction was based on a cohesive zone model (CZM) with a bilinear traction-separation law. XFEM was applied to the coating domain to model cracking in the diamond coating with a damage criterion of the maximum principal stress. Deposition stresses were also included to investigate their effect on the coating delamination and fractures. The model was implemented in finite element (FE) codes to analyze the cone crack in brittle coatings, as well as the interface delamination of diamond coated carbide tools. The XFEM model was validated by the indentation testing data from literature in crack initiation and propagation in brittle materials. FE results from the indentation on diamond-coated tools show that the interface delamination size and loading force become smaller when coating fractures are incorporated in the model, and the deposition stresses will increase the initial crack radius and the critical load for delamination in diamond coatings.MSEC2013- Interface delamination of diamond-coated carbide tools considering ...

MSEC2013- Interface delamination of diamond-coated carbide tools considering ...The University of Alabama
While the computed transported turbulence dissipation rate, , works well as part of a differential
equation-based turbulence model in predicting turbulent flows, it doesn’t seem to work well when used to
determine the Kolmogorov length-scale (ℓ퐾표푙) which, like the other Kolmogorov scales, exists within the viscous
sublayer portion of the inner turbulent boundary layer zone. Using may lead to an increase in ℓ퐾표푙 as roughness
increases, the opposite of what should happen. It is proposed here to replace the computed (and its level at the
1
st point off the wall as dictated by wall functions) with the one resulting from basic law-of-the-wall sublayer
relationships which includes the Prandtl-Schlichting (P-S) roughness effect. This approach enables physically
correct prediction of ℓ퐾표푙, particularly a reliable decrease thereof with increasing roughness level.Rough Wall Kolmogorov Length-Scale Proposal

Rough Wall Kolmogorov Length-Scale ProposalInternational journal of scientific and technical research in engineering (IJSTRE)
More Related Content
What's hot
Interface delamination is the major failure mode of diamond-coated carbide tools in machining. On the other hand, coating cracking is possibly accompanied during a tribological process that induces the delamination phenomenon. However, such an influence between the two failure behaviors has not been investigated in a quantitative way to better understand and design diamond coating tools.
In this study, a three-dimensional (3D) indentation model combining cohesive interactions and extended finite element method (XFEM) was developed to investigate the diamond-coating, carbide-substrate interface behavior with the incorporation of coating cracking. The cohesive interaction was based on a cohesive zone model (CZM) with a bilinear traction-separation law. XFEM was applied to the coating domain to model cracking in the diamond coating with a damage criterion of the maximum principal stress. Deposition stresses were also included to investigate their effect on the coating delamination and fractures. The model was implemented in finite element (FE) codes to analyze the cone crack in brittle coatings, as well as the interface delamination of diamond coated carbide tools. The XFEM model was validated by the indentation testing data from literature in crack initiation and propagation in brittle materials. FE results from the indentation on diamond-coated tools show that the interface delamination size and loading force become smaller when coating fractures are incorporated in the model, and the deposition stresses will increase the initial crack radius and the critical load for delamination in diamond coatings.MSEC2013- Interface delamination of diamond-coated carbide tools considering ...

MSEC2013- Interface delamination of diamond-coated carbide tools considering ...The University of Alabama
What's hot (13)
Ppp3 Calculation Of Entropy And Theoretical Stress Strain Curve

Ppp3 Calculation Of Entropy And Theoretical Stress Strain Curve
MSEC2013- Interface delamination of diamond-coated carbide tools considering ...

MSEC2013- Interface delamination of diamond-coated carbide tools considering ...
Similar to Turbulence near the wall.pdf
While the computed transported turbulence dissipation rate, , works well as part of a differential
equation-based turbulence model in predicting turbulent flows, it doesn’t seem to work well when used to
determine the Kolmogorov length-scale (ℓ퐾표푙) which, like the other Kolmogorov scales, exists within the viscous
sublayer portion of the inner turbulent boundary layer zone. Using may lead to an increase in ℓ퐾표푙 as roughness
increases, the opposite of what should happen. It is proposed here to replace the computed (and its level at the
1
st point off the wall as dictated by wall functions) with the one resulting from basic law-of-the-wall sublayer
relationships which includes the Prandtl-Schlichting (P-S) roughness effect. This approach enables physically
correct prediction of ℓ퐾표푙, particularly a reliable decrease thereof with increasing roughness level.Rough Wall Kolmogorov Length-Scale Proposal

Rough Wall Kolmogorov Length-Scale ProposalInternational journal of scientific and technical research in engineering (IJSTRE)
Similar to Turbulence near the wall.pdf (20)
ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Theory Guide - 4.12.1 Overview.pdf

ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Theory Guide - 4.12.1 Overview.pdf
Turbulence Modeling – The k-ε Turbulence Model.pdf

Turbulence Modeling – The k-ε Turbulence Model.pdf
STRUCTURAL DAMAGE DETECTION USING WAVELET APPROACH

STRUCTURAL DAMAGE DETECTION USING WAVELET APPROACH
Retrofitting of Masonry Buildings by Base Isolation

Retrofitting of Masonry Buildings by Base Isolation
New-Fangled Approach to Predict the Behaviour of Composite Sandwich Pavements

New-Fangled Approach to Predict the Behaviour of Composite Sandwich Pavements
Sliding motion and adhesion control through magnetic domamins

Sliding motion and adhesion control through magnetic domamins
A Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Regular and Staggered Openings on the ...

A Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Regular and Staggered Openings on the ...
More from Mohammad Jadidi
More from Mohammad Jadidi (20)
01 reactive flows - governing equations favre averaging 

01 reactive flows - governing equations favre averaging
01 reactive flows - finite-rate formulation for reaction modeling

01 reactive flows - finite-rate formulation for reaction modeling
Recently uploaded
Differences between analog and digital communicationanalog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptx

analog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptxKarpagam Institute of Teechnology
Recently uploaded (20)
Filters for Electromagnetic Compatibility Applications

Filters for Electromagnetic Compatibility Applications
Involute of a circle,Square, pentagon,HexagonInvolute_Engineering Drawing.pdf

Involute of a circle,Square, pentagon,HexagonInvolute_Engineering Drawing.pdf
NO1 Best Powerful Vashikaran Specialist Baba Vashikaran Specialist For Love V...

NO1 Best Powerful Vashikaran Specialist Baba Vashikaran Specialist For Love V...
Seismic Hazard Assessment Software in Python by Prof. Dr. Costas Sachpazis

Seismic Hazard Assessment Software in Python by Prof. Dr. Costas Sachpazis
Research Methodolgy & Intellectual Property Rights Series 1

Research Methodolgy & Intellectual Property Rights Series 1
8th International Conference on Soft Computing, Mathematics and Control (SMC ...

8th International Conference on Soft Computing, Mathematics and Control (SMC ...
Theory of Time 2024 (Universal Theory for Everything)

Theory of Time 2024 (Universal Theory for Everything)
5G and 6G refer to generations of mobile network technology, each representin...

5G and 6G refer to generations of mobile network technology, each representin...
Interfacing Analog to Digital Data Converters ee3404.pdf

Interfacing Analog to Digital Data Converters ee3404.pdf
analog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptx

analog-vs-digital-communication (concept of analog and digital).pptx
Independent Solar-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Station

Independent Solar-Powered Electric Vehicle Charging Station
Working Principle of Echo Sounder and Doppler Effect.pdf

Working Principle of Echo Sounder and Doppler Effect.pdf
Turbulence near the wall.pdf
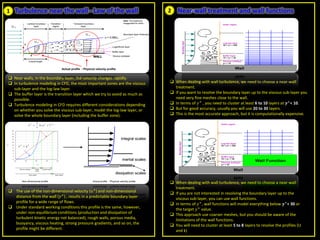
- 1. Turbulence near the wall - Law of the wall Near walls, in the boundary layer, the velocity changes rapidly. In turbulence modeling in CFD, the most important zones are the viscous sub-layer and the log-law layer. The buffer layer is the transition layer which we try to avoid as much as possible. Turbulence modeling in CFD requires different considerations depending on whether you solve the viscous sub-layer, model the log-law layer, or solve the whole boundary layer (including the buffer zone). The use of the non-dimensional velocity (𝑢+) and non-dimensional distance from the wall (𝑦+) , results in a predictable boundary layer profile for a wide range of flows. Under standard working conditions this profile is the same, however, under non-equilibrium conditions (production and dissipation of turbulent kinetic energy not balanced), rough walls, porous media, buoyancy, viscous heating, strong pressure gradients, and so on, the profile might be different. When dealing with wall turbulence, we need to choose a near-wall treatment. If you want to resolve the boundary layer up to the viscous sub-layer you need very fine meshes close to the wall. In terms of 𝑦+ , you need to cluster at least 6 to 10 layers at 𝒚+< 10. But for good accuracy, usually you will use 20 to 30 layers. This is the most accurate approach, but it is computationally expensive. Near-wall treatment and wall functions When dealing with wall turbulence, we need to choose a near-wall treatment. If you are not interested in resolving the boundary layer up to the viscous sub-layer, you can use wall functions. In terms of 𝑦+, wall functions will model everything below 𝒚+< 30 or the target 𝑦+ value. This approach use coarser meshes, but you should be aware of the limitations of the wall functions. You will need to cluster at least 5 to 8 layers to resolve the profiles (U and k) 1 2
