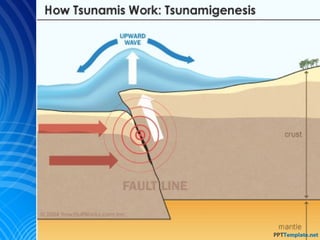
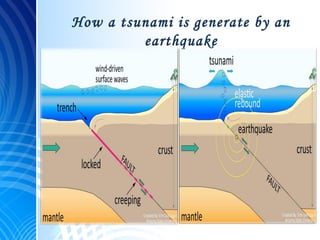
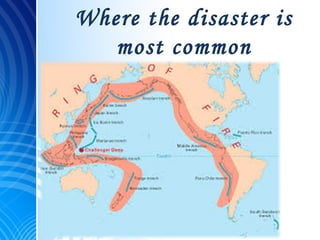
An earthquake at the edge of a tectonic plate can displace large amounts of water and generate a tsunami. When the ocean floor suddenly rises or drops, it throws the water above it into large waves that travel towards the shore. Most tsunamis occur in the Pacific Ocean, called the "Ring of Fire", where there is frequent seismic and volcanic activity. The Japanese word "tsunami" means "harbor wave" and describes the huge waves that can overwhelm coastal areas, as seen in the devastating 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami that killed over 280,000 people.