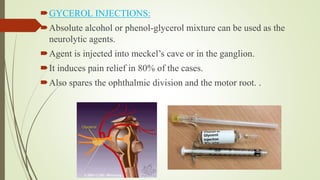
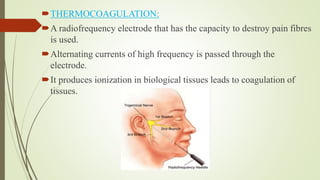
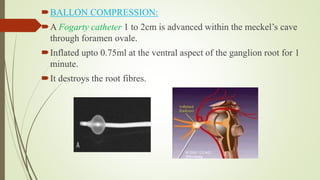
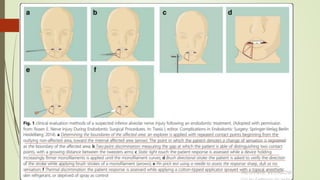
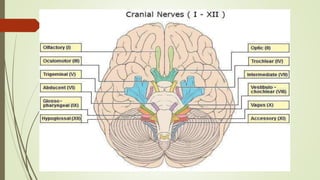
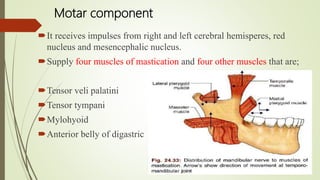
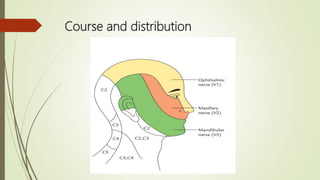
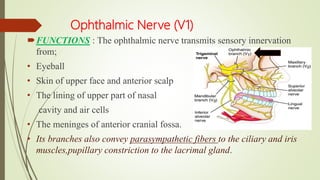
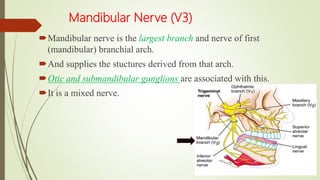
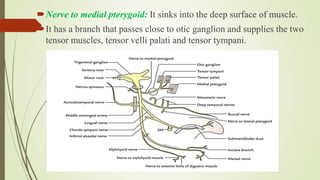
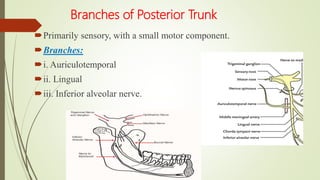
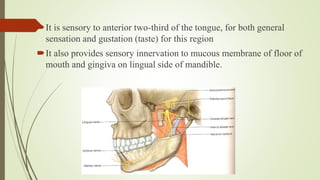
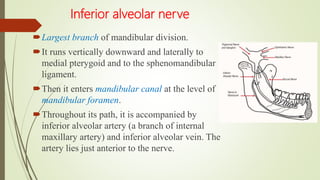
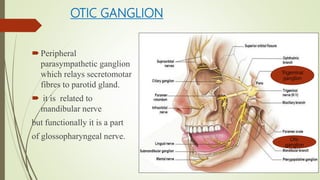
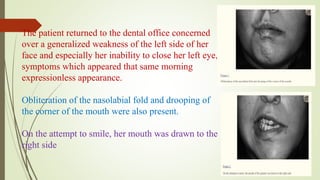
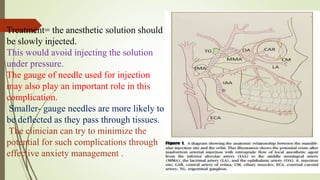
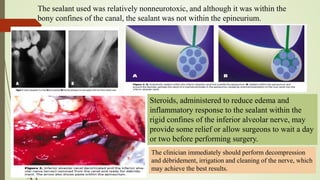
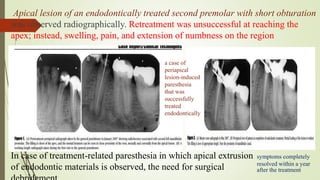
1. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves and has three main divisions - the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves. It provides sensory innervation to most of the face and motor innervation to the muscles of mastication.
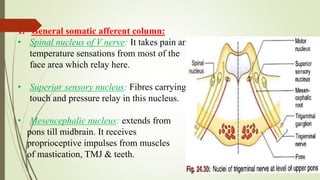
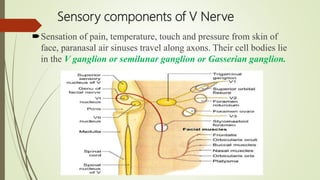
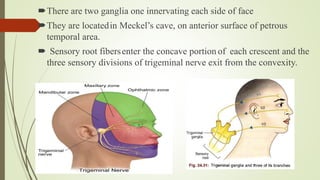
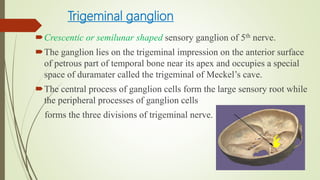
2. The trigeminal ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory fibers. It gives rise to the three divisions which have numerous branches that innervate the face, scalp, and oral cavity.
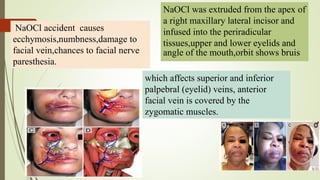
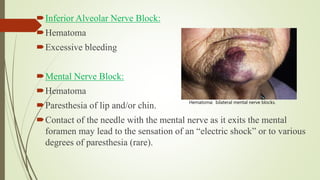
3. Clinical considerations for trigeminal nerve blocks and other procedures include risks of bleeding, infection, nerve injury, hematoma formation, and diplopia if local















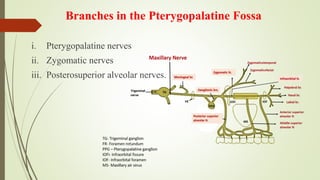


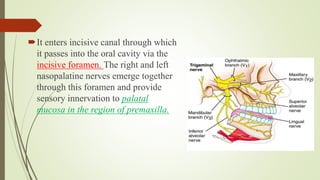









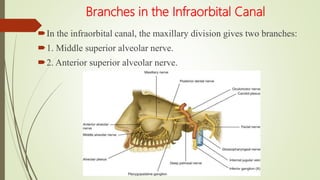


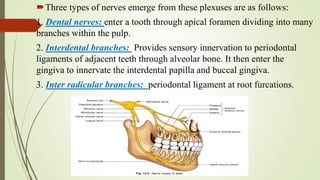
























![CLASSIFICATION:
International Headache Society (IHS);
A]Classical /idiopathic/typical B]Symptomatic
Classical trigeminal neuralgia=
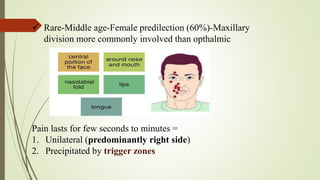
1. is a unilateral disorder characterized by brief
electric, shocklike pains.
2. Abrupt in onset and termination
3. limited to the distribution of one or more
divisions of the trigeminal nerve
Symptomatic trigeminal neuralgia =
1. Pain is similar to classical type But it is caused by a
demonstrable structural lesion other than vascular
compression.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-210331054004/85/Trigeminal-Nerve-And-Endodontics-83-320.jpg)