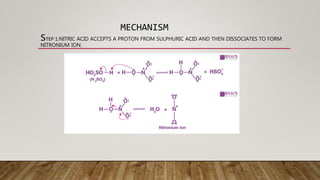
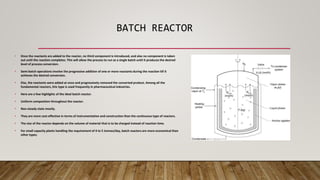
This document discusses the unit process of nitration. Nitration involves introducing nitro groups (-NO2) into a molecule through reaction with nitric acid. Common nitration reactions include those of benzene and other aromatic compounds. Nitration of benzene proceeds through a nitronium ion-mediated electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism. Batch and continuous stirred tank reactors are commonly used for nitration reactions. Proper selection of nitrating agents like nitric acid and sulfuric acid and equipment like nitrators are important for achieving high yields of nitro compounds. Nitro compounds find applications as solvents, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals and explosives.