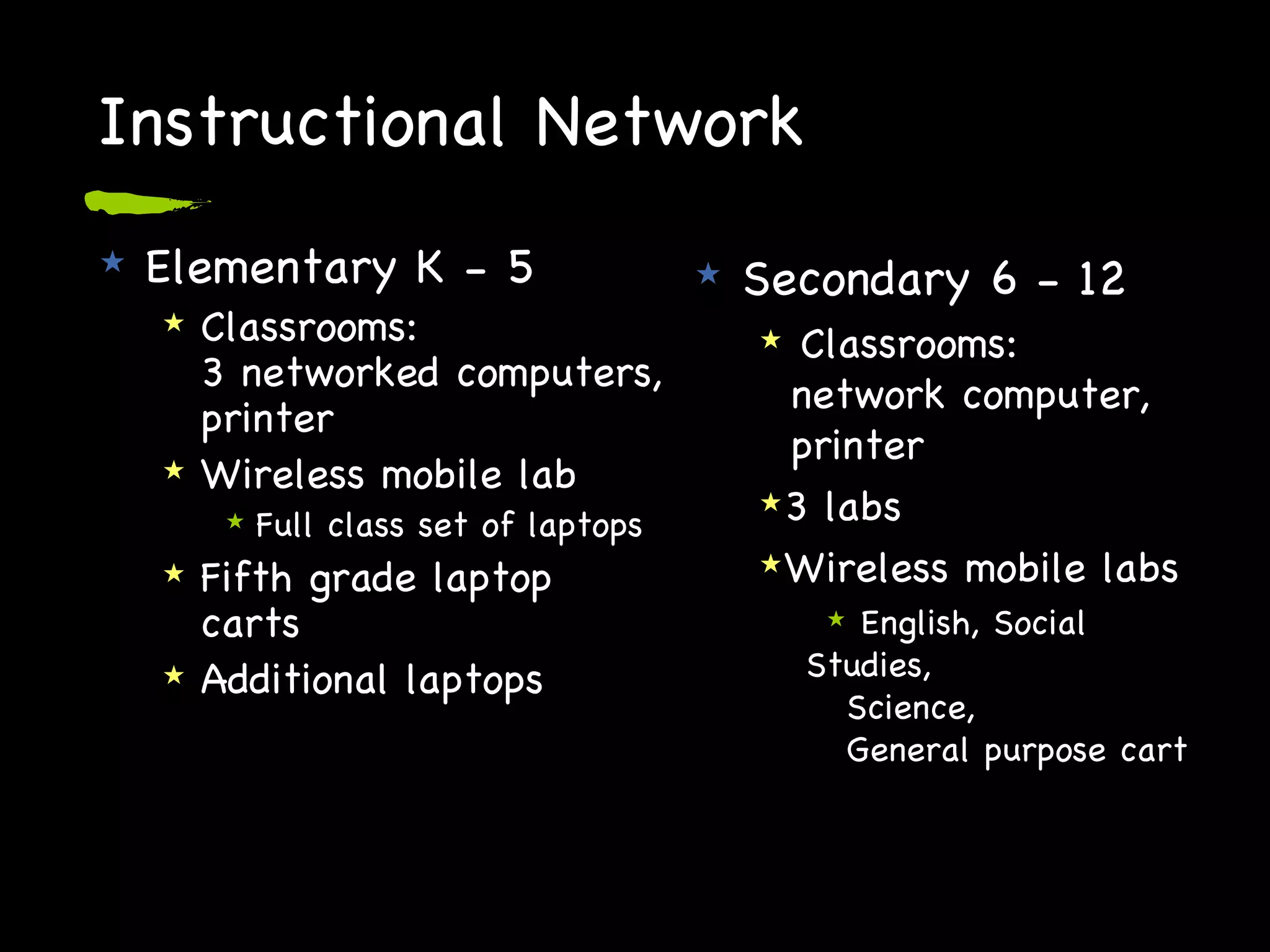
The document discusses trends in educational technology use in K-12 schools. It describes how digital native students use technology differently than digital immigrants. Schools aim to incorporate 21st century skills and tools into instruction while meeting student needs and increasing achievement. Technology is used as both an instructional and personal tool by teachers, administrators, and students. Challenges include maintaining infrastructure, providing access, and supporting professional development in technology integration.































![Who we are Corinne Carriero Director of Instructional Technology [email_address] Ellen Robertson Coordinator of Instructional Technology [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trends-in-k12-educational-technology-17660/75/Trends-in-K-12-Educational-Technology-32-2048.jpg)