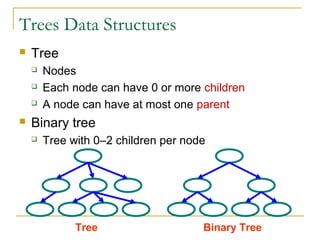
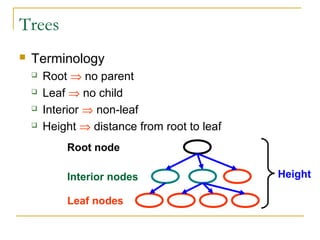
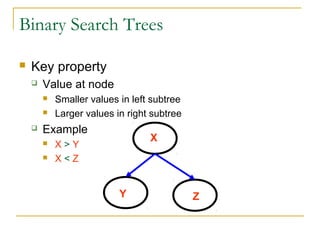
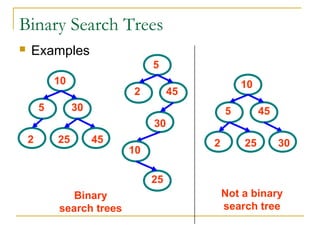
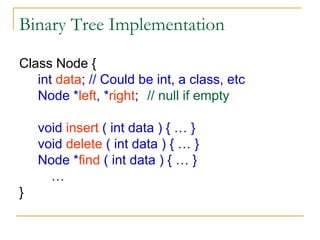
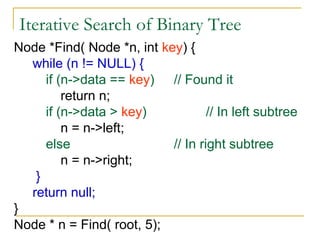
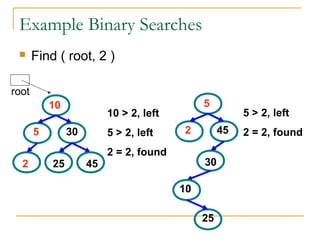
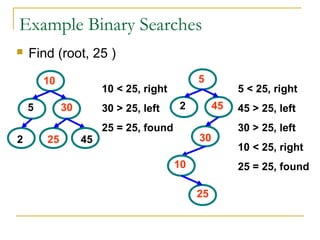
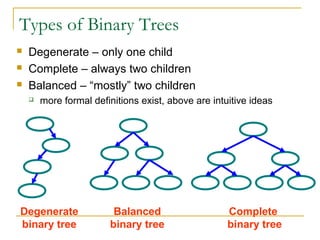
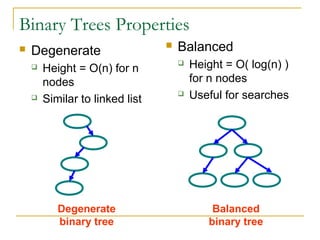
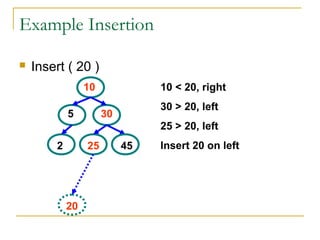
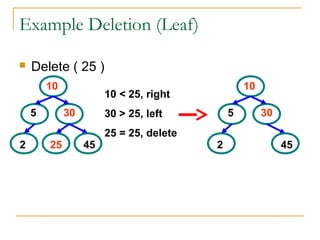
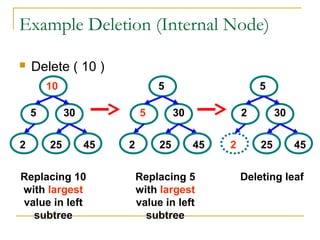
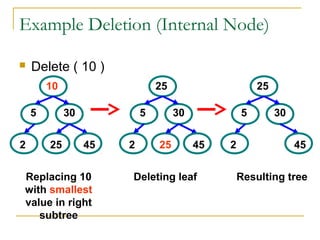
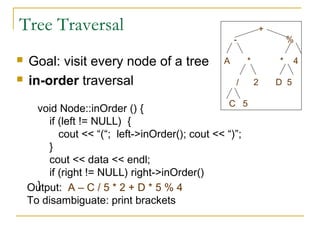
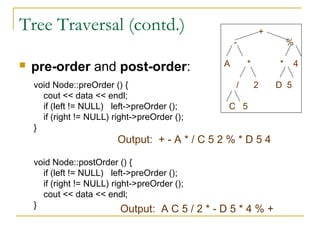
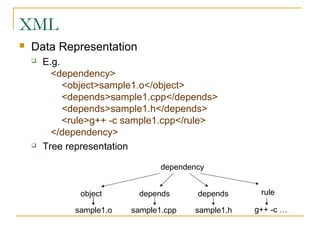
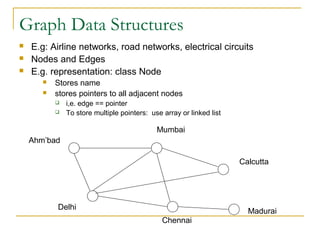
Tree data structures can be represented as nodes connected in a parent-child relationship. Binary trees restrict each node to having at most two children. Binary search trees organize nodes so that all left descendants of a node are less than the node and all right descendants are greater. They allow efficient lookup, insertion, and deletion operations that take O(log n) time on balanced trees. Other tree types include parse trees for representing code structure and XML trees for hierarchical data storage.