Embed presentation
Download to read offline


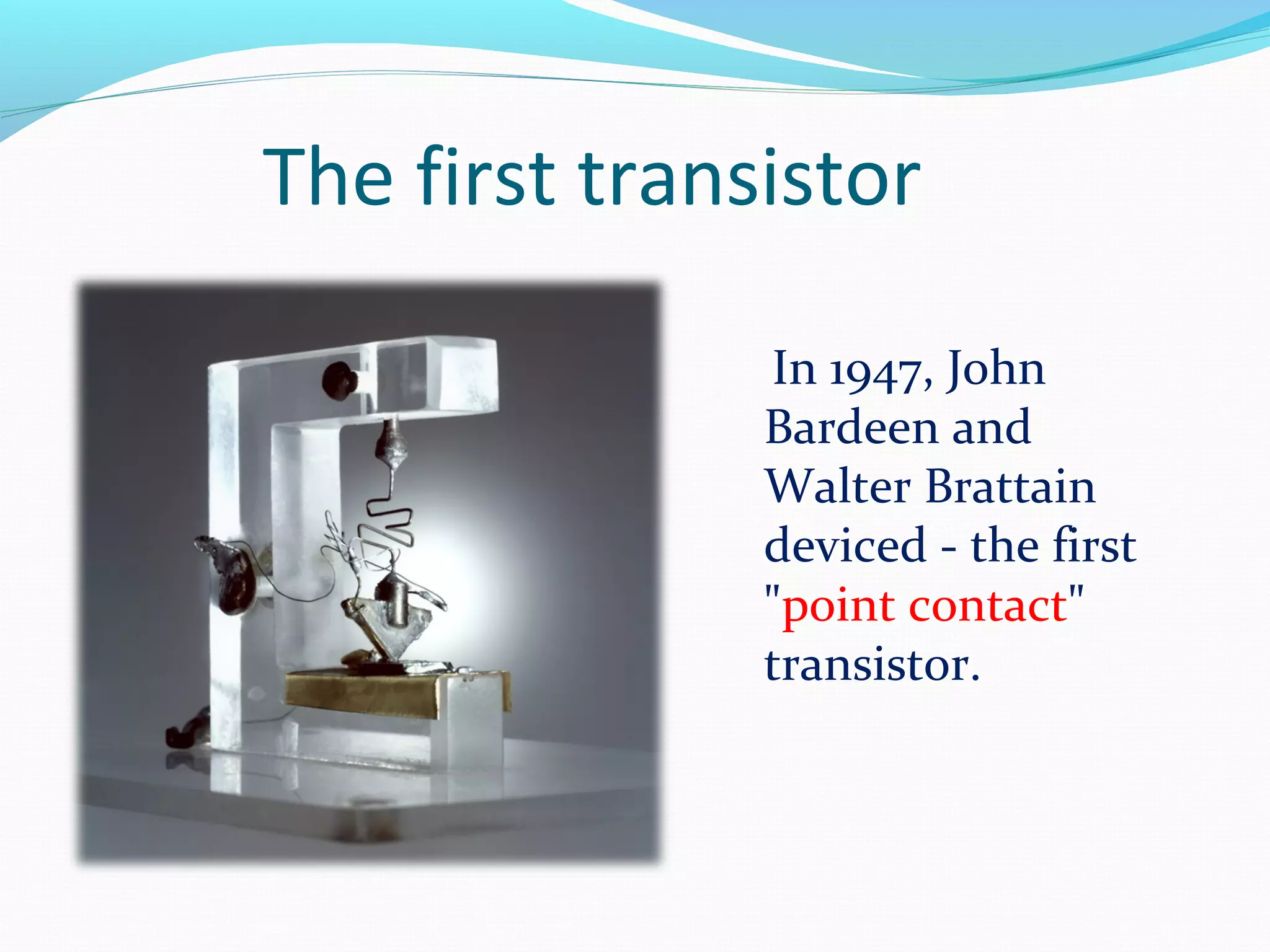


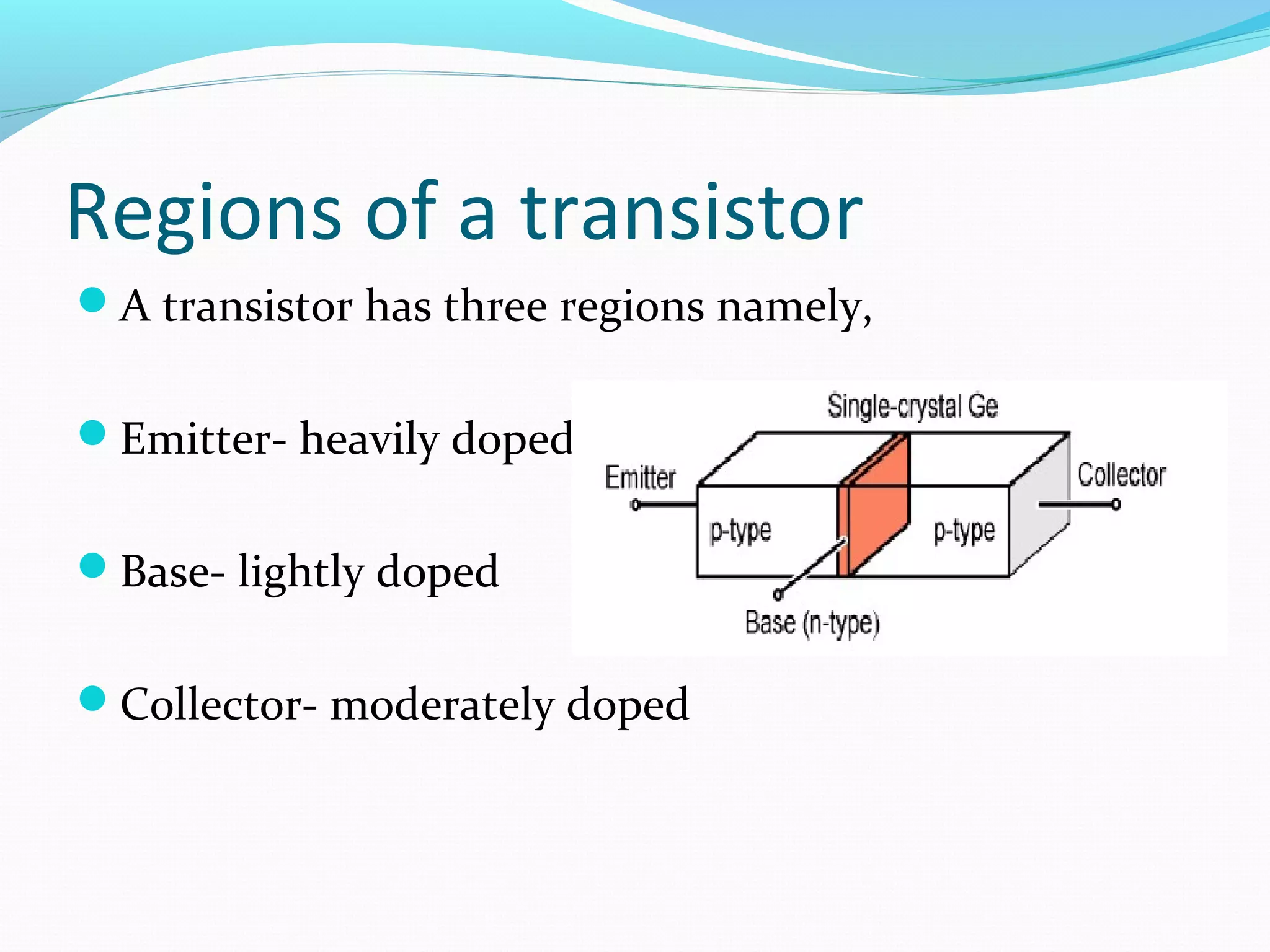


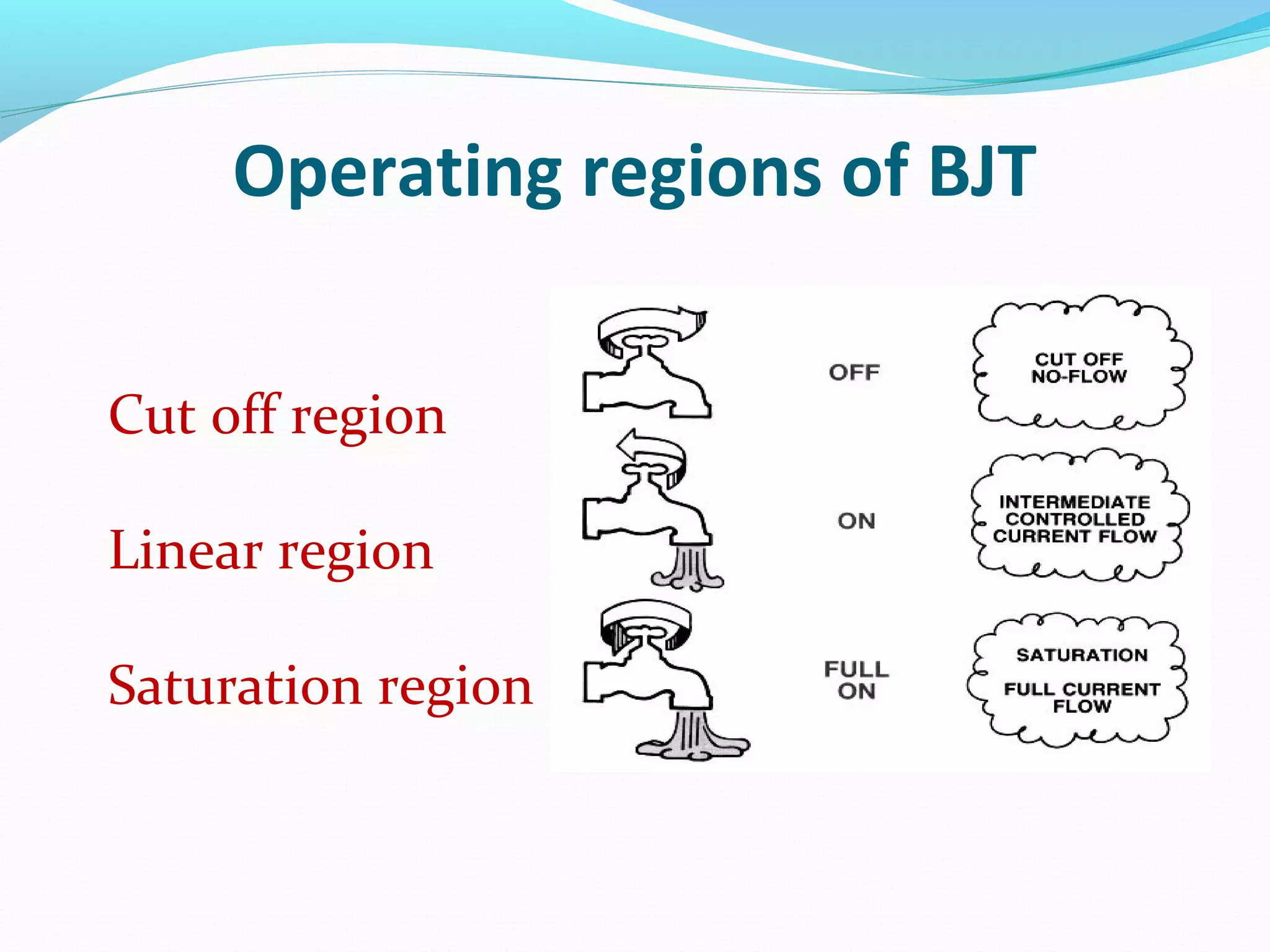



The document discusses the history and development of transistors. The vacuum tube triode was invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest and was used in early radios and computers. John Bardeen and Walter Brattain invented the first transistor in 1947 called the "point contact" transistor. A transistor is an electronic device made of semiconductor material that can act as an insulator or conductor, consisting of three layers known as a bipolar junction transistor. The transistor functions by using both holes and electrons as charge carriers and can operate in different regions including cutoff, linear, and saturation.











