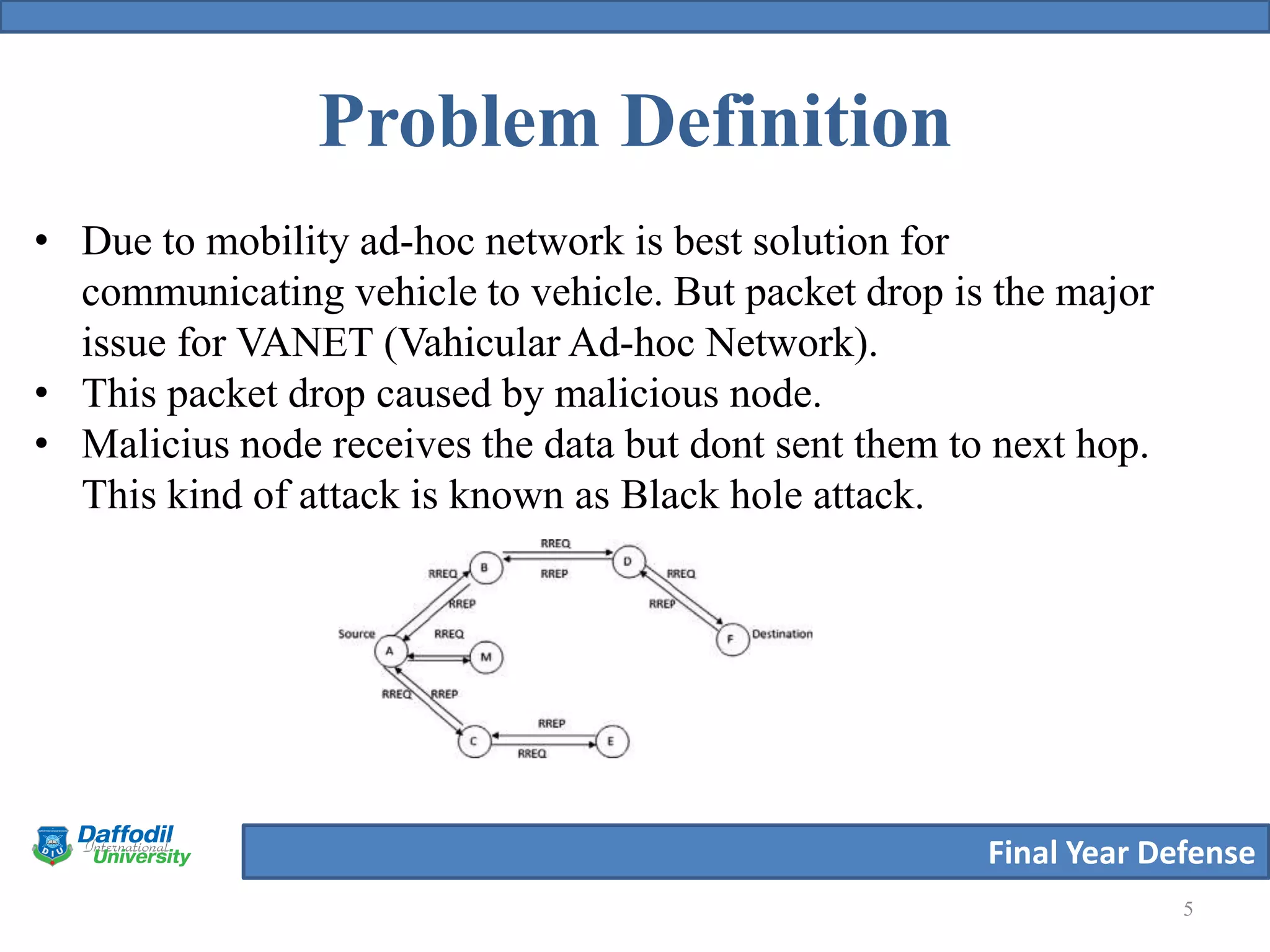
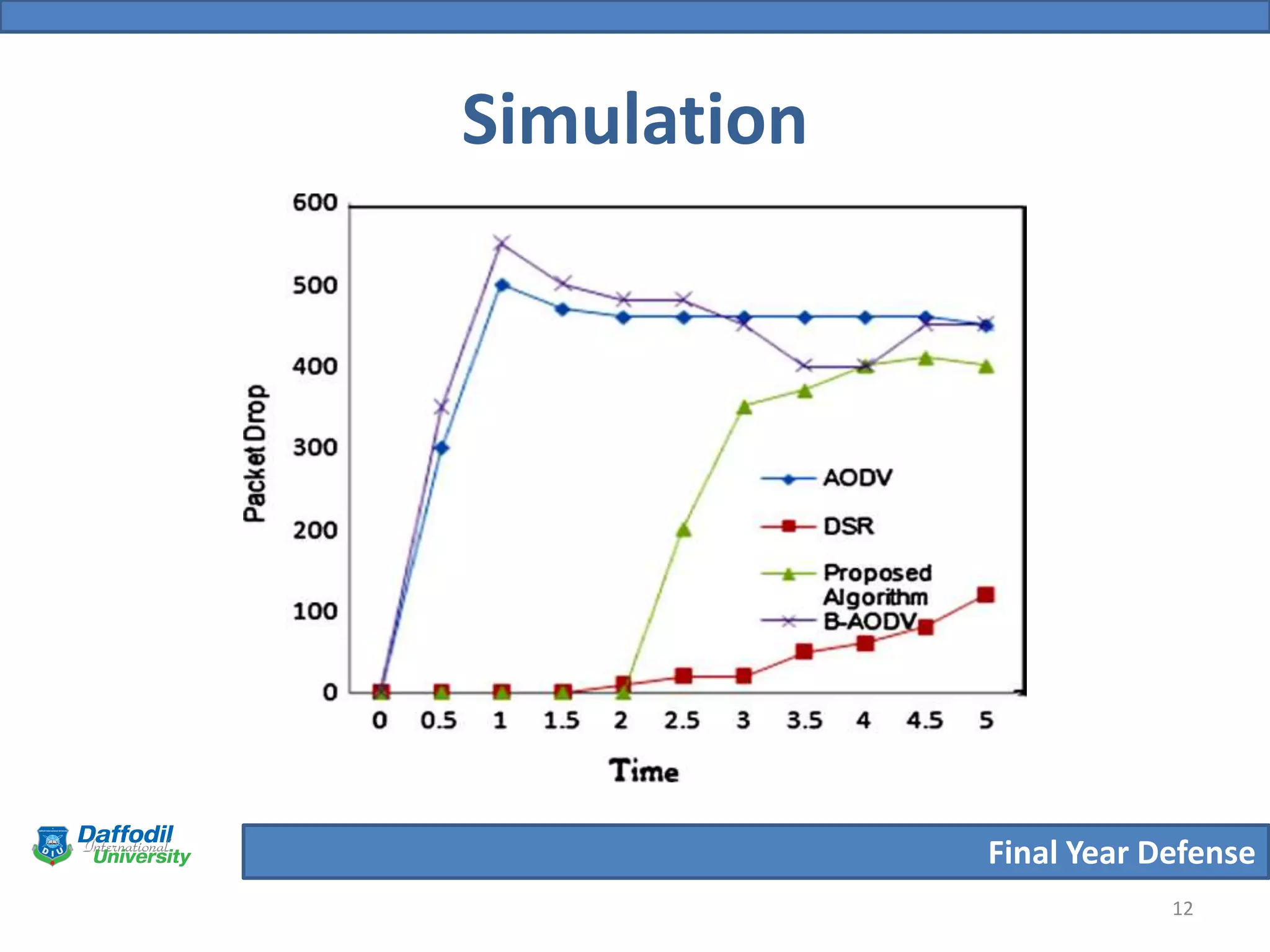
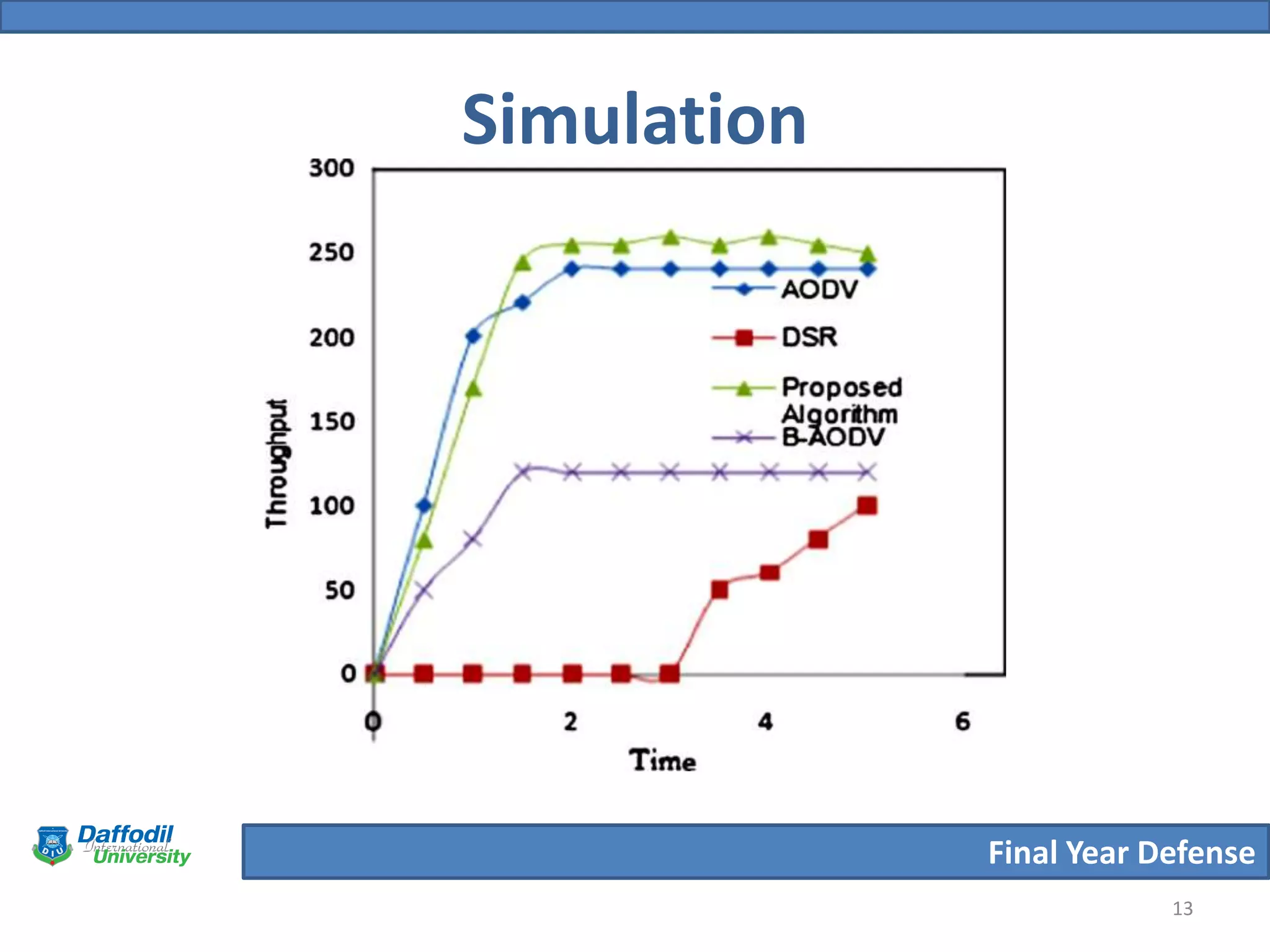
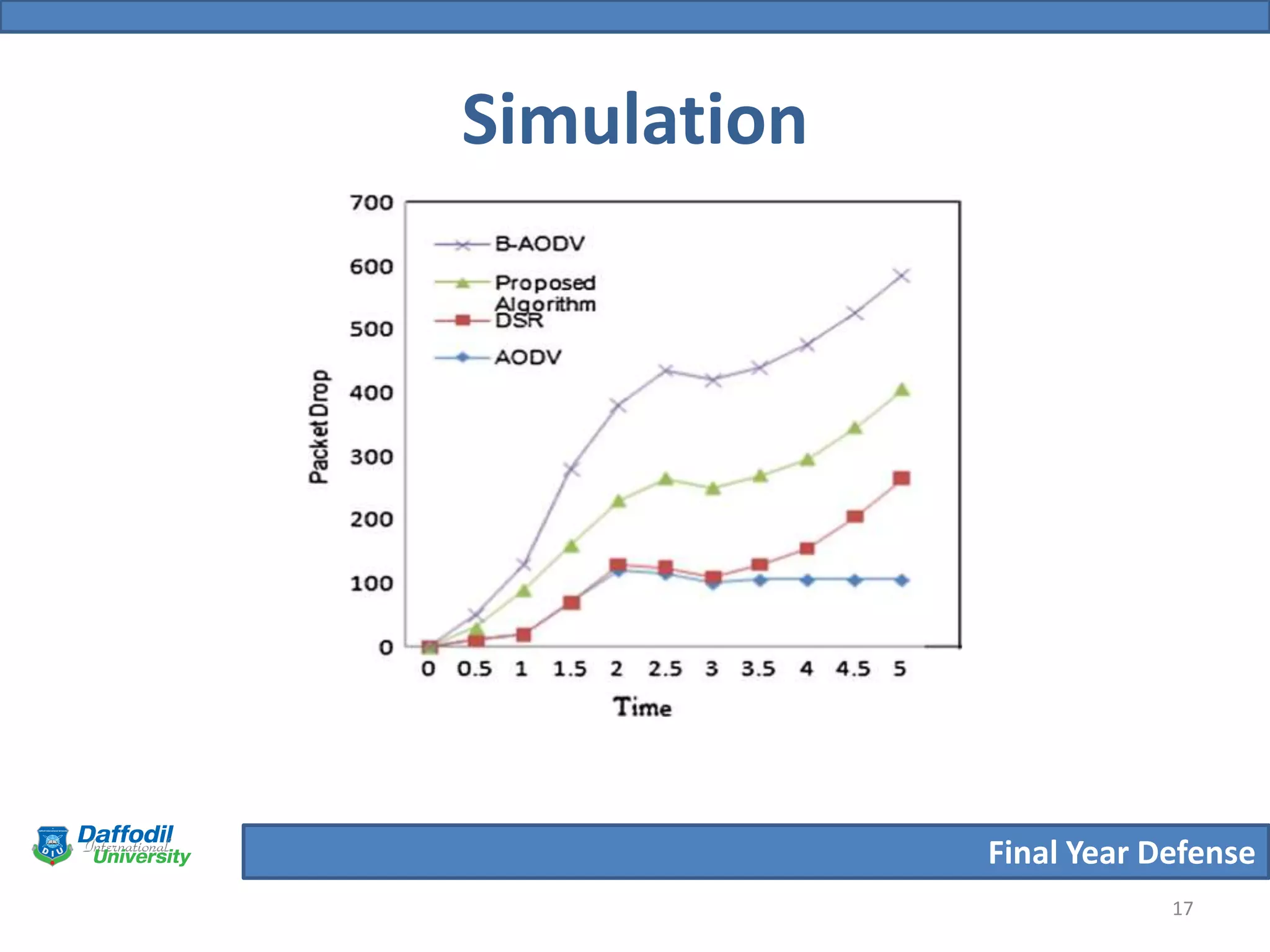
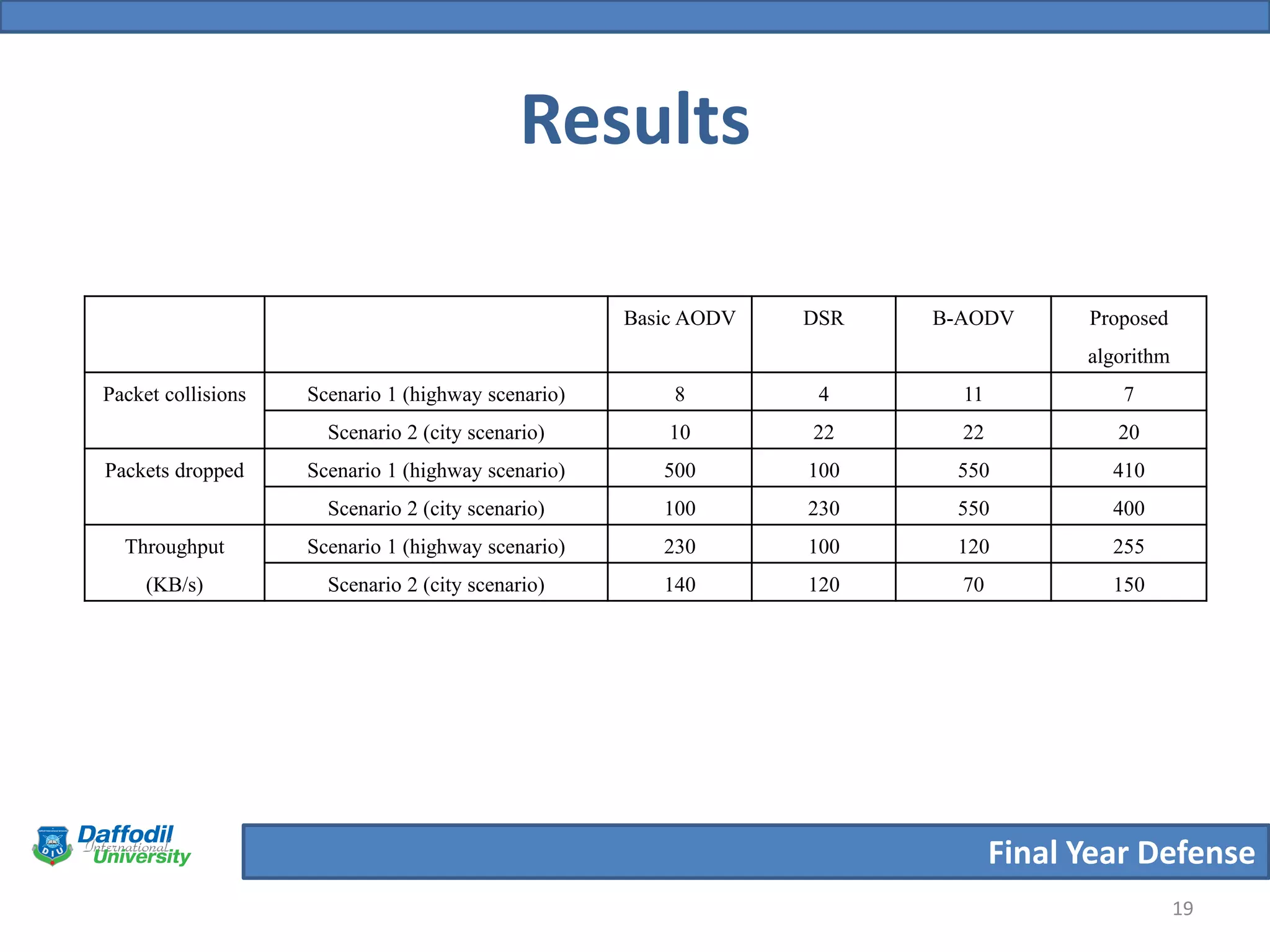
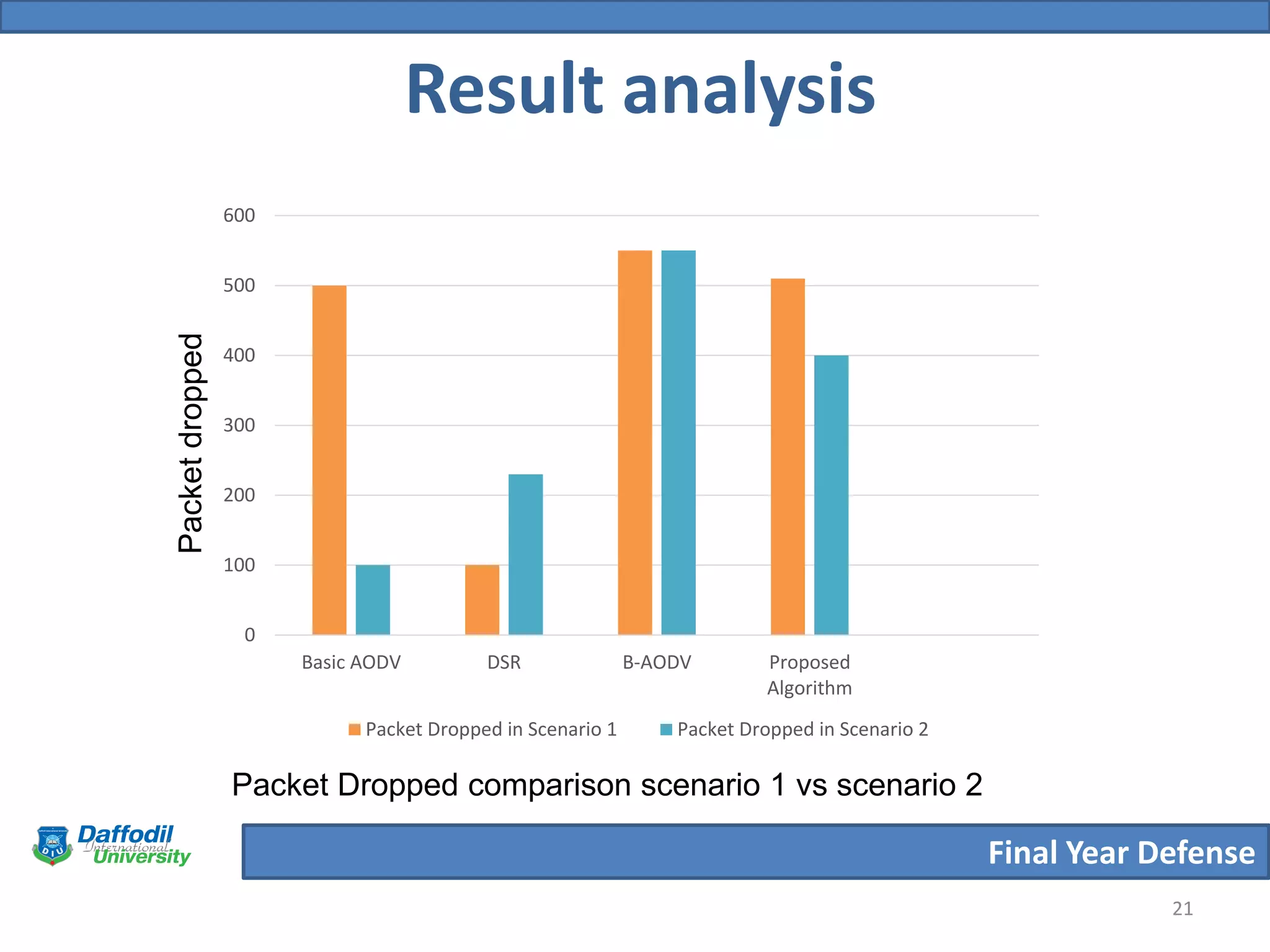
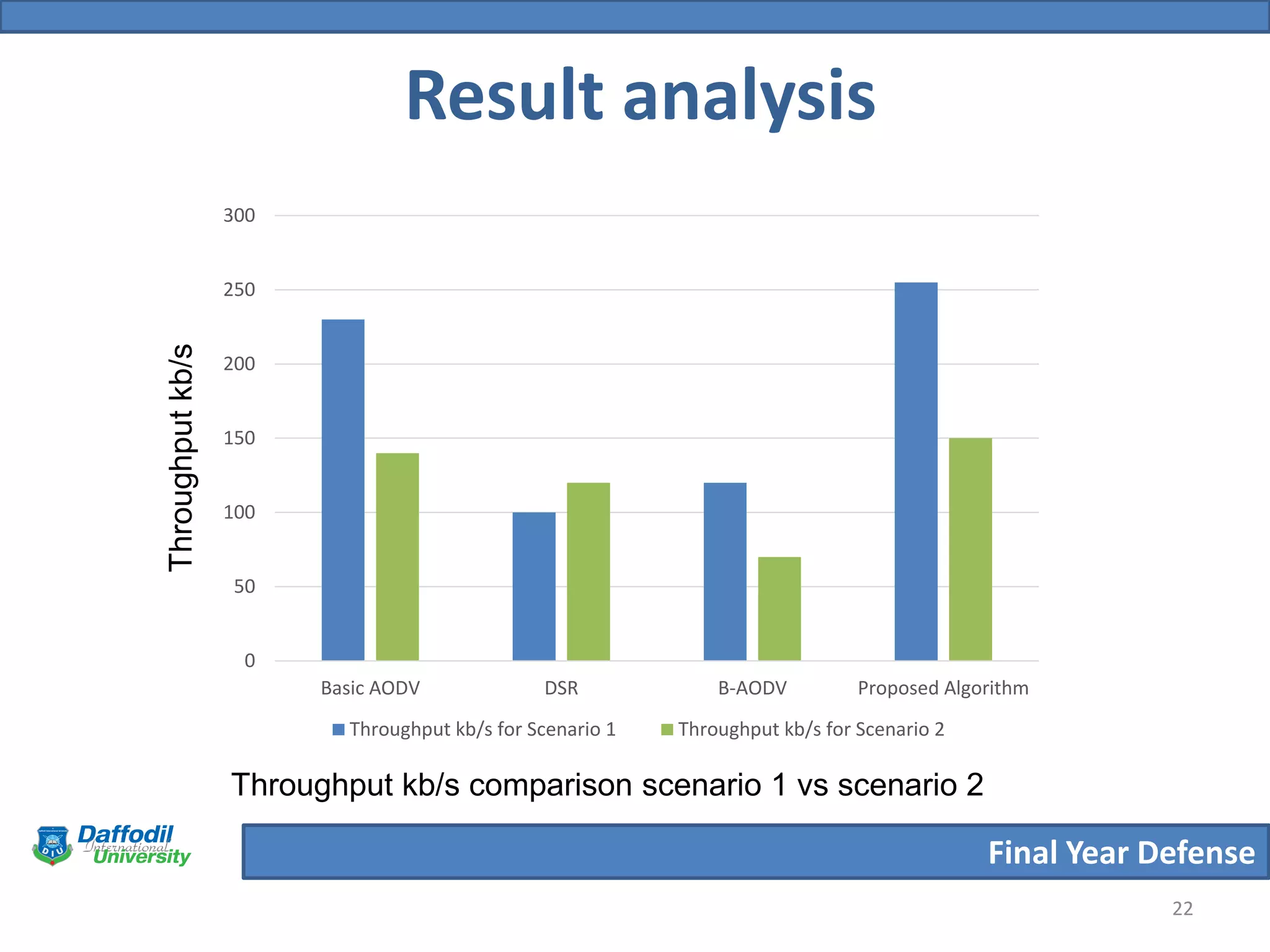
The document summarizes a student's final year defense presentation on analyzing and preventing security attacks in routing protocols for vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs). The presentation covers introducing VANETs and wireless ad-hoc networks, stating the aims to establish an algorithm and simulate scenarios to compare routing protocols. It describes simulating two highway scenarios using OMNeT++ and comparing the proposed algorithm to AODV, DSR and B-AODV based on packet collisions, packets dropped and throughput. The results show the proposed algorithm performs better, and future work could make the network immune to black hole attacks.