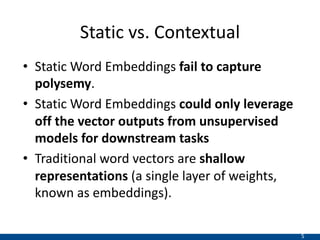
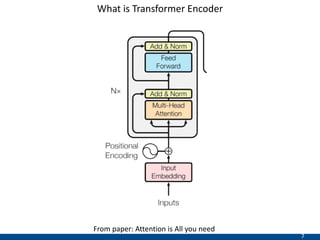
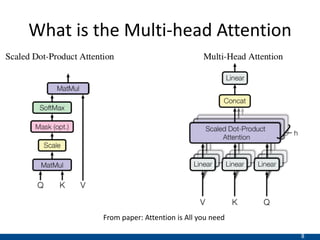
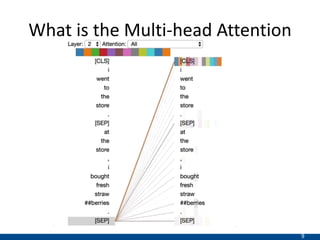
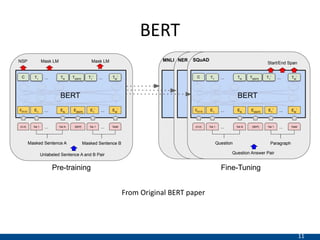
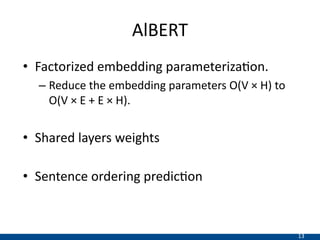
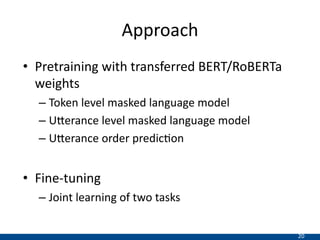
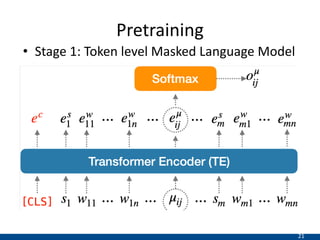
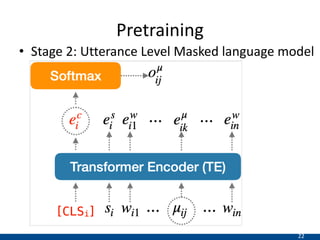
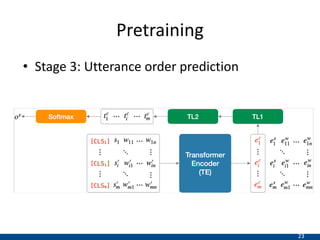
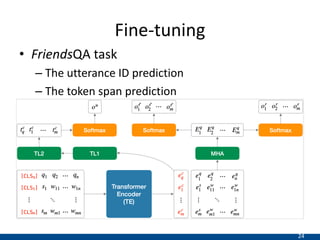
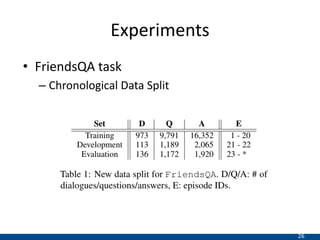
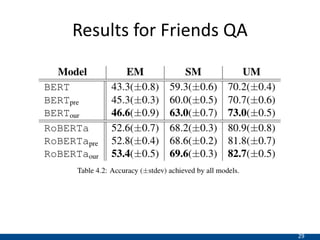
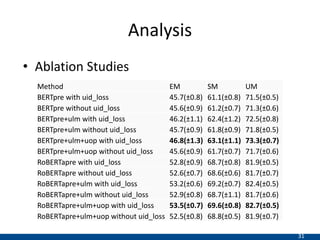
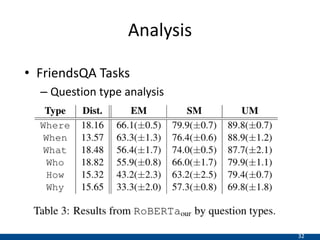
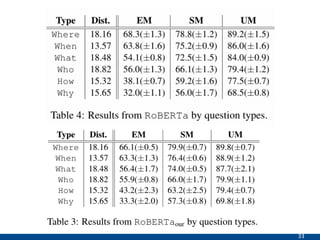
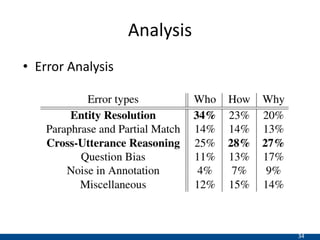
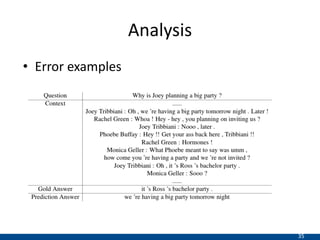
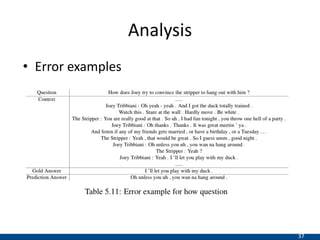
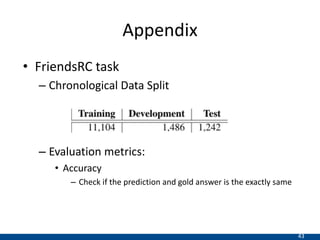
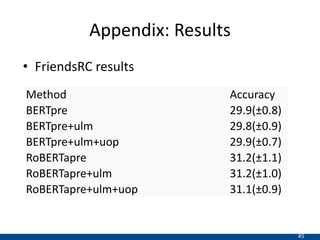
The document presents an approach using transformers to learn hierarchical contexts in multiparty dialogue. It proposes new pre-training tasks to improve token-level and utterance-level embeddings for handling dialogue contexts. A multi-task learning approach is introduced to fine-tune the language model for a Friends question answering (FriendsQA) task using dialogue evidence, outperforming BERT and RoBERTa. However, the approach shows no improvement on other character mining tasks from Friends. Future work is needed to better represent speakers and inferences in dialogue.