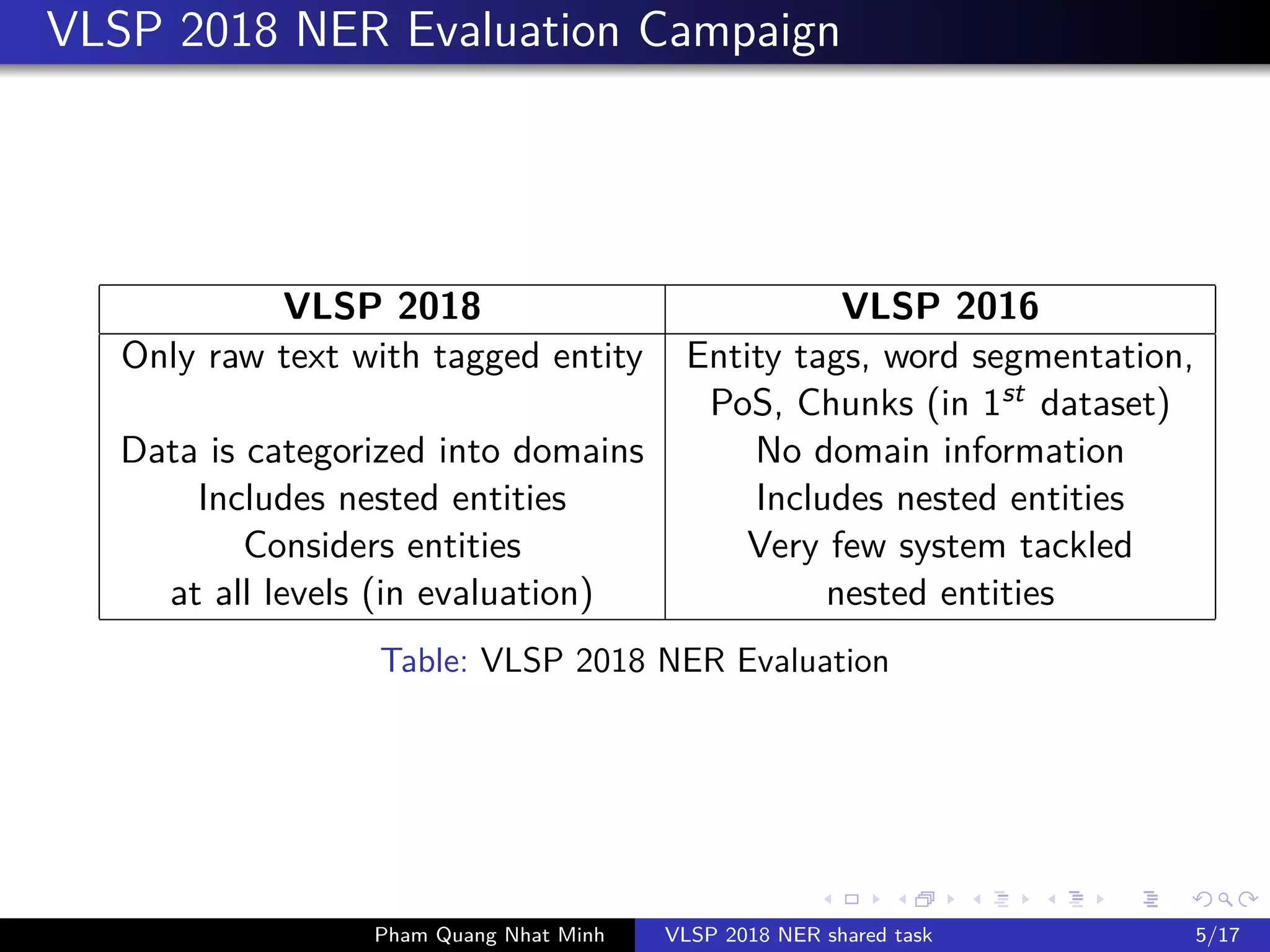
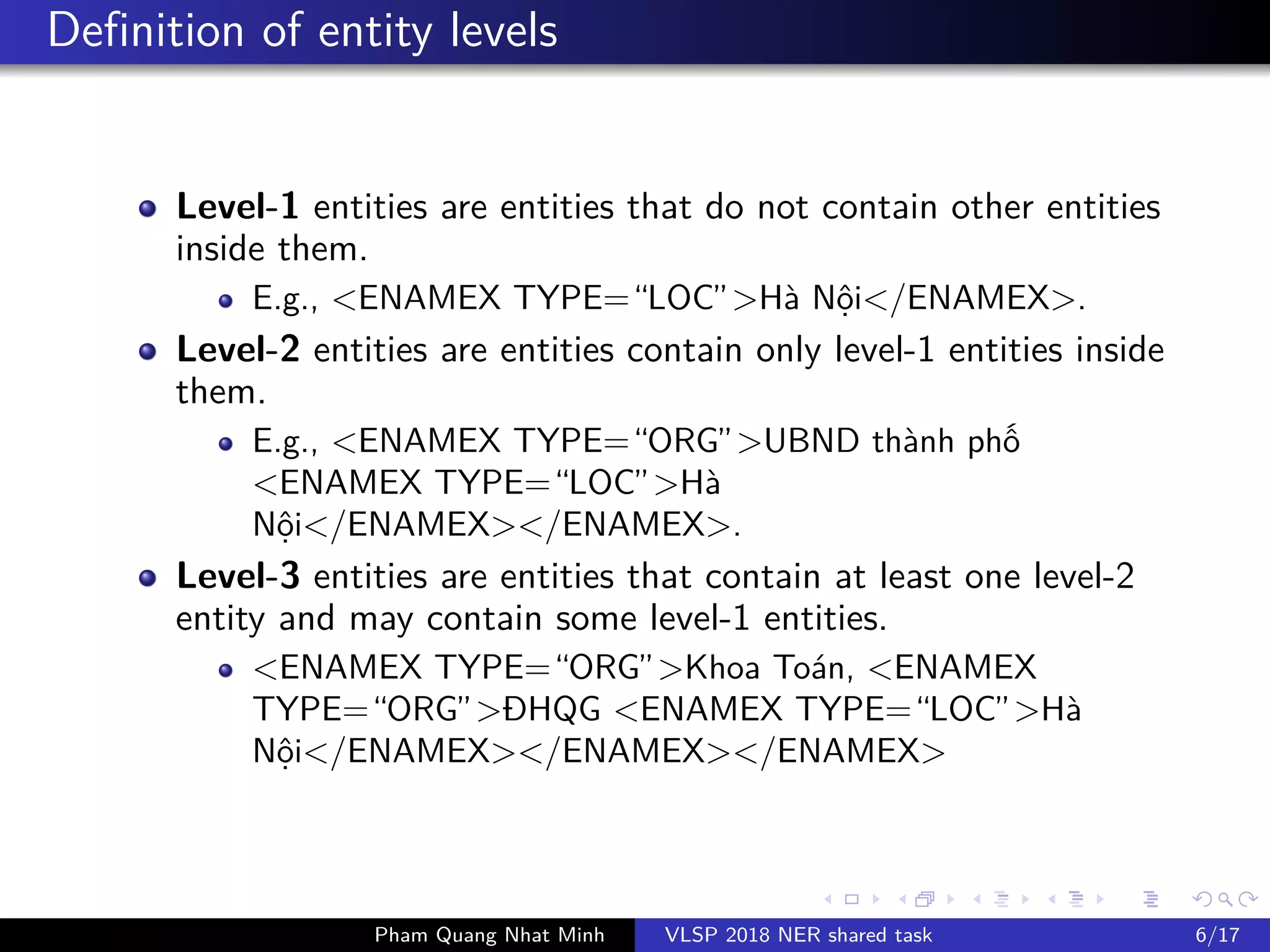
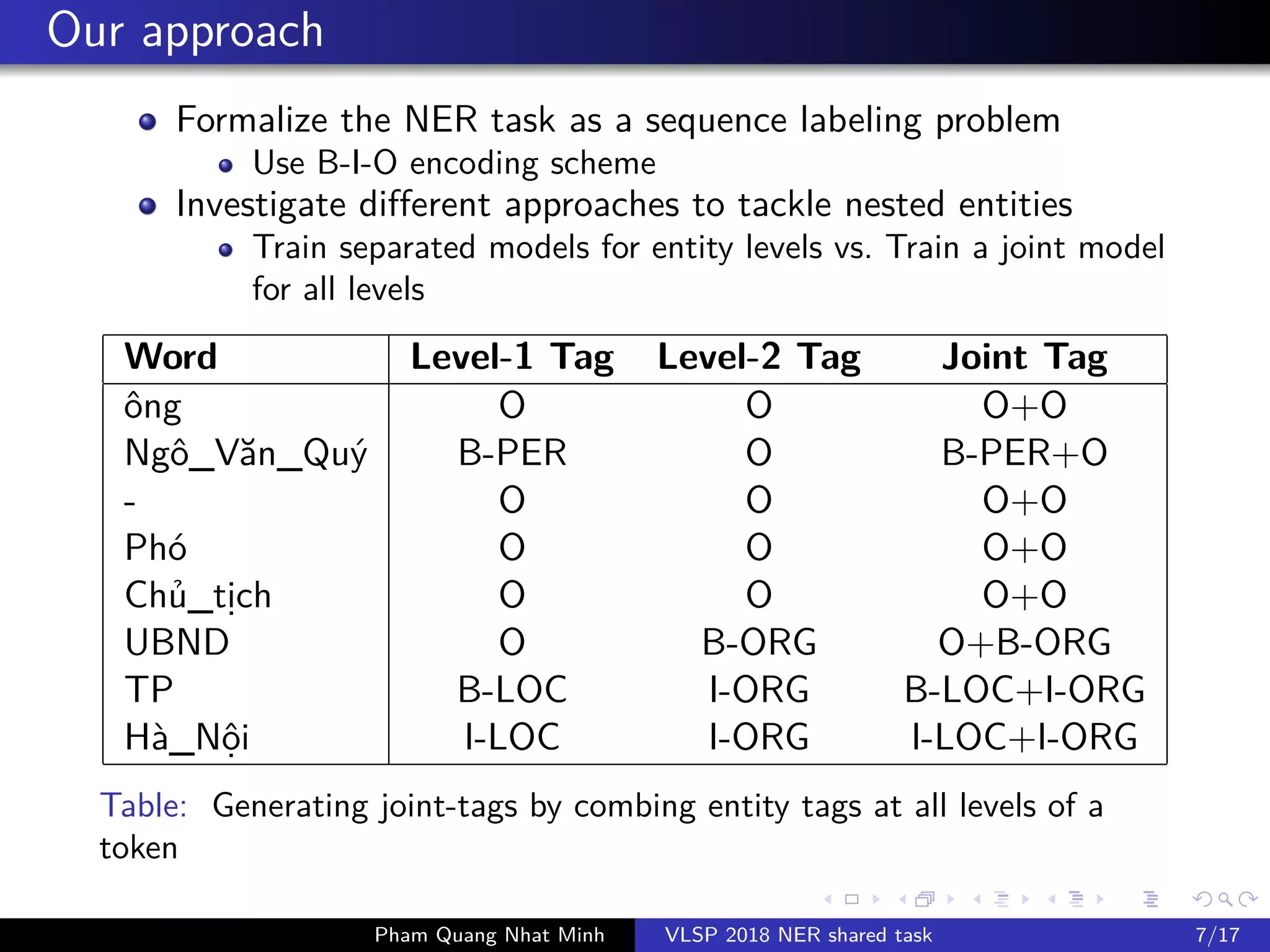
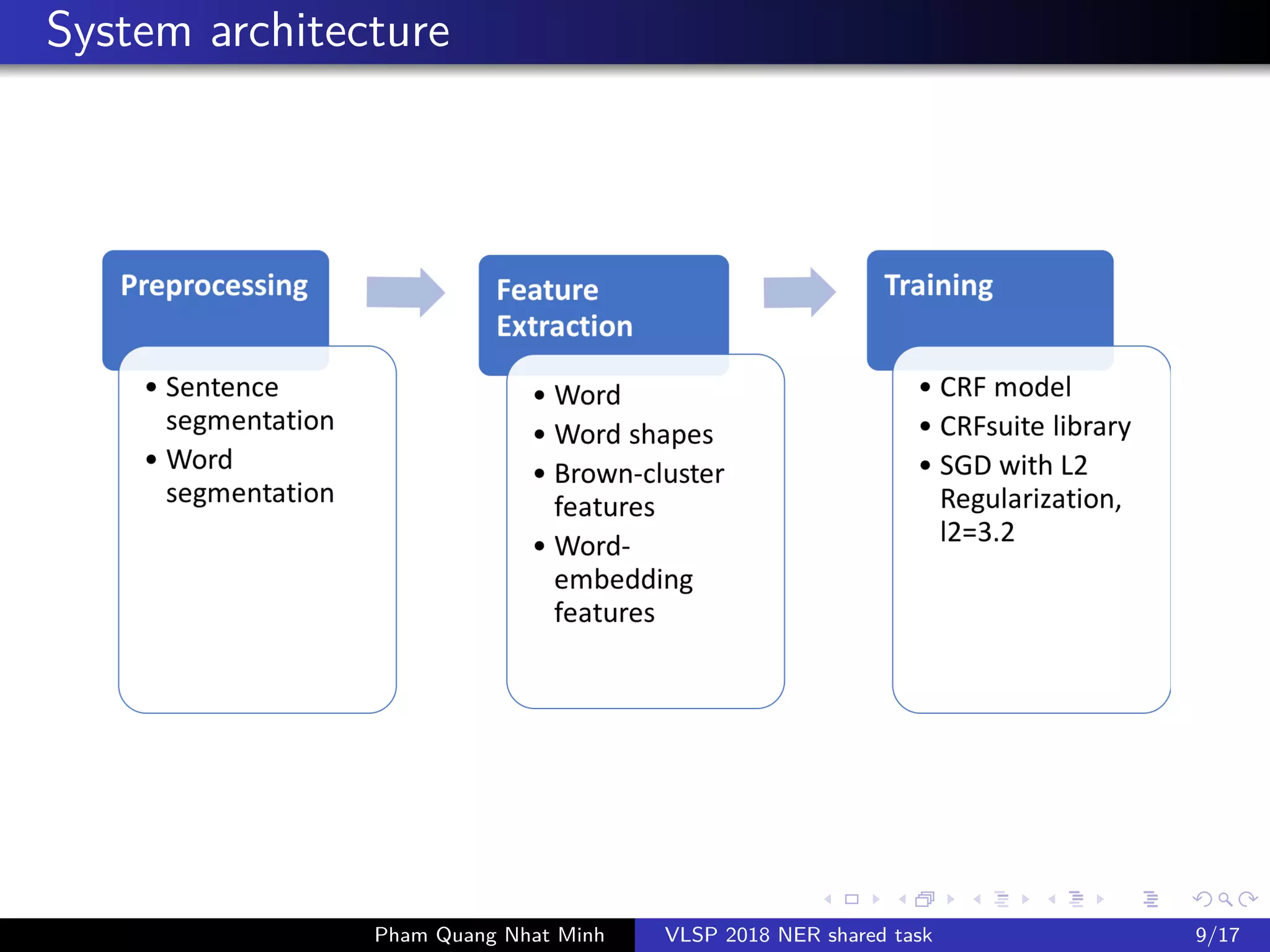
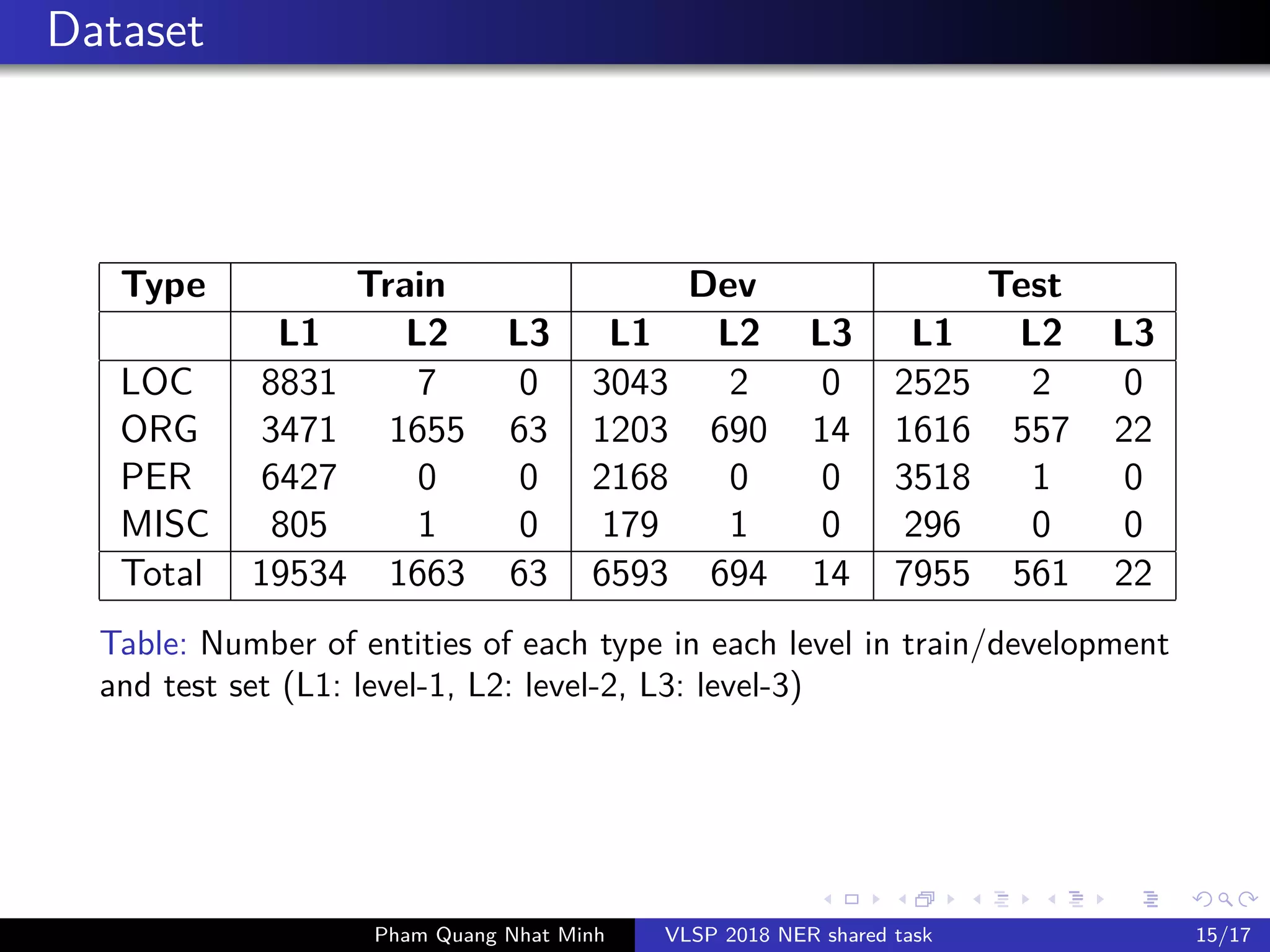
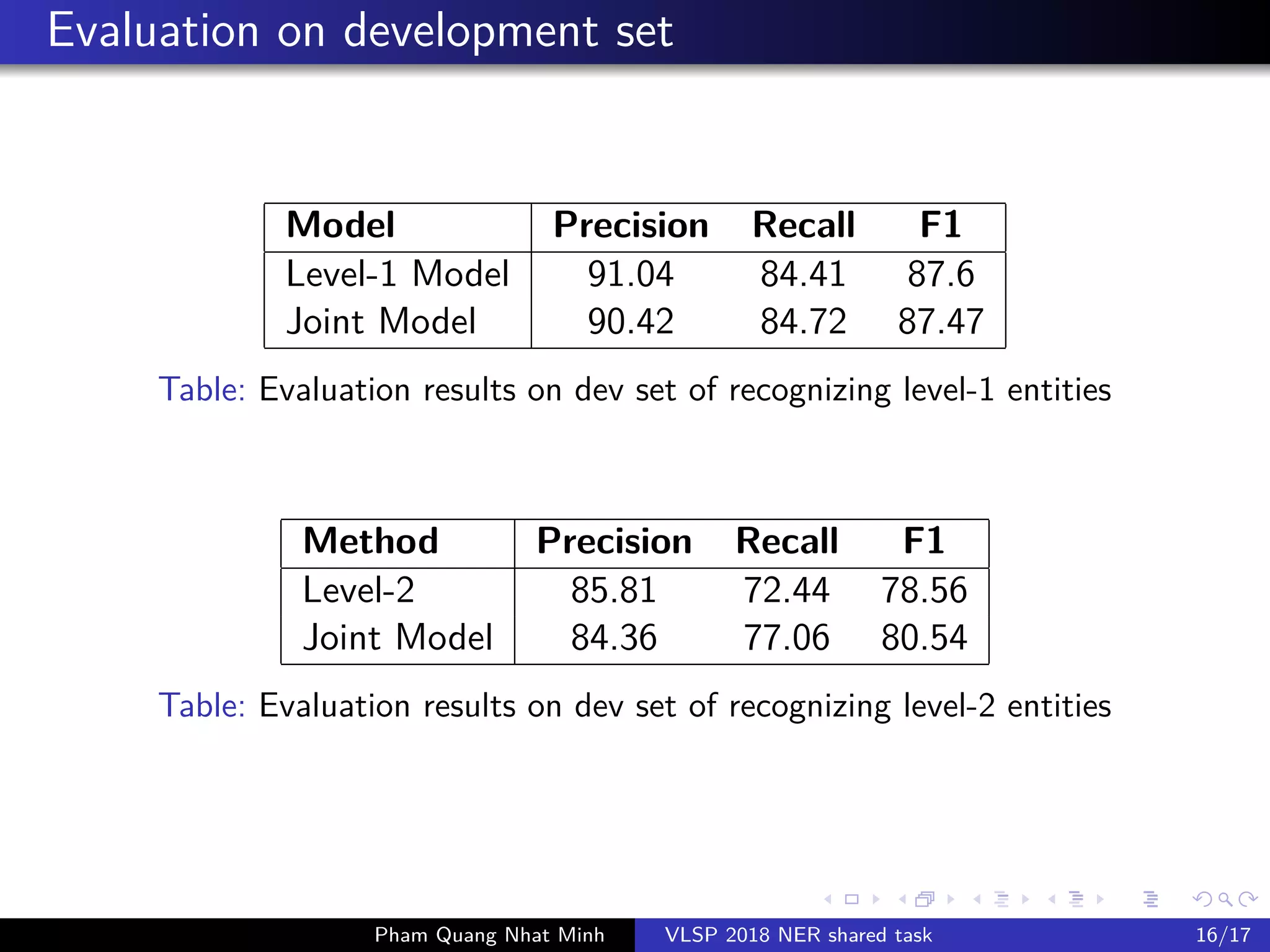
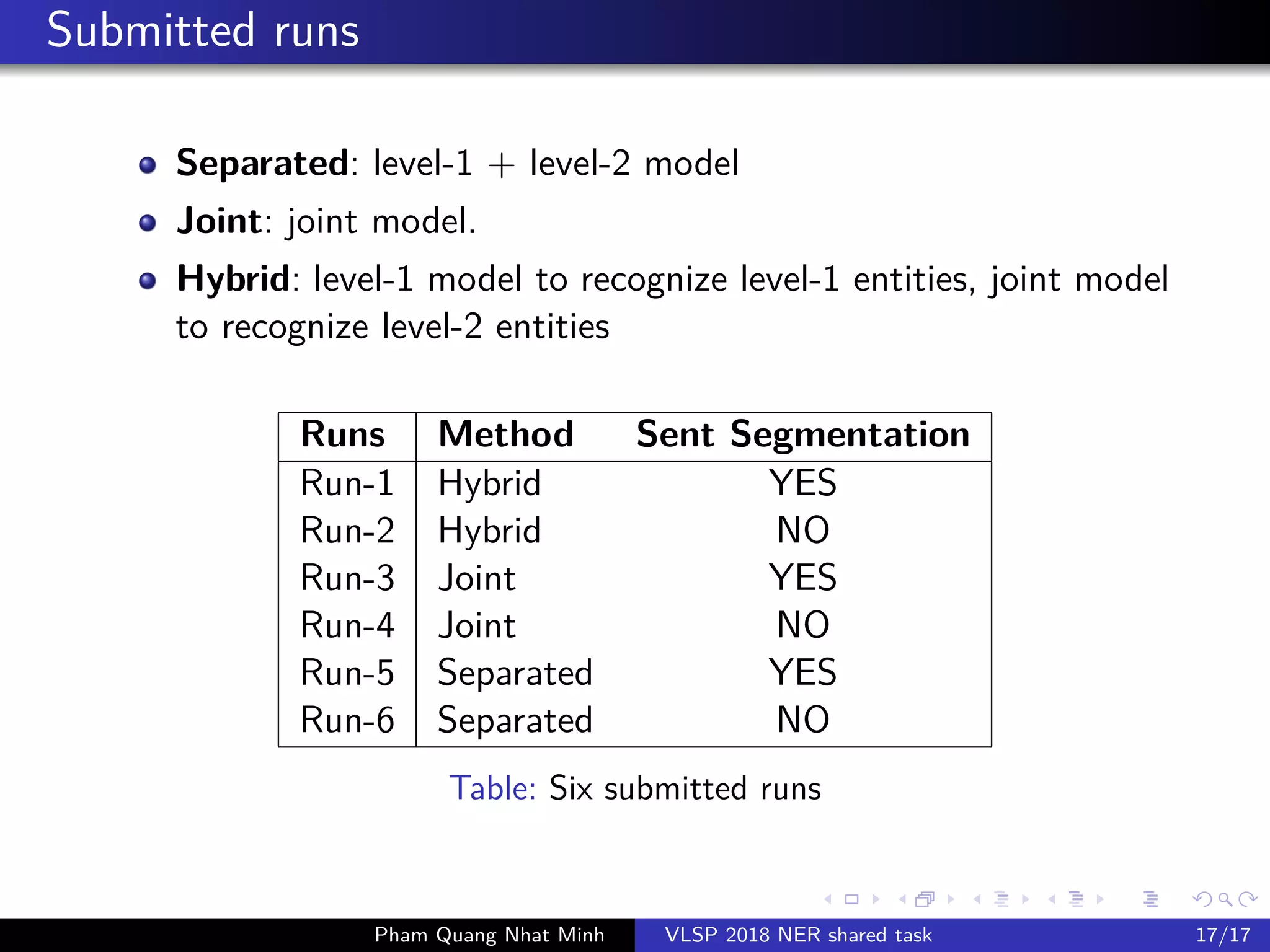
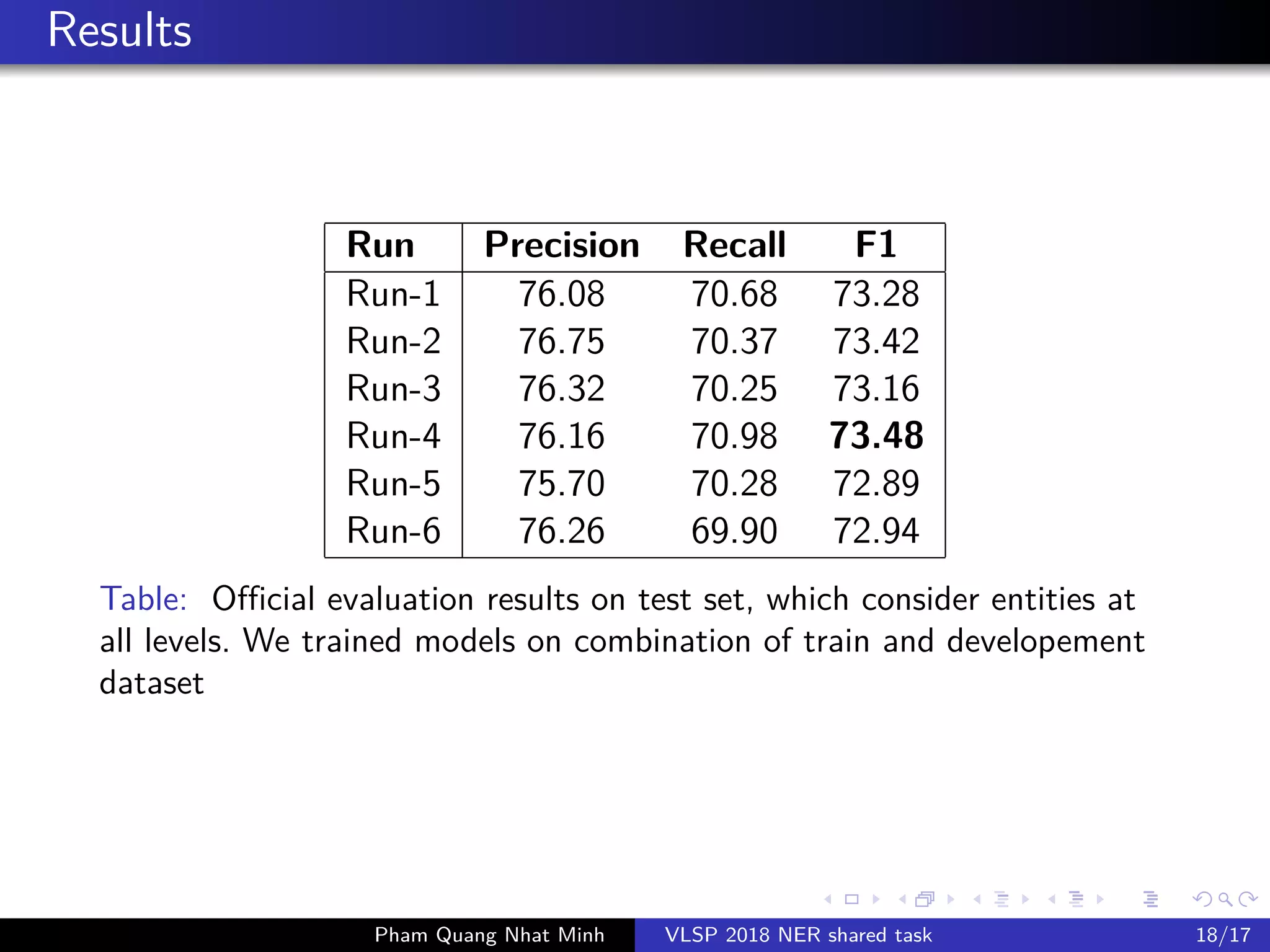
The document presents a feature-based model for nested named-entity recognition (NER) in the VLSP-2018 NER evaluation campaign. It details the system architecture, various entity levels, and evaluation results, demonstrating the effectiveness of a joint model that combines tags of all levels for improved accuracy. The findings suggest that while high accuracy was achieved on the development set, further domain adaptation techniques and enhancements, such as the use of dictionaries, are necessary to close the gap in performance on the test set.


![Named Entity Recognition
INPUT: V đ m tàu x y ra ngoài khơi th tr n Sabratha, phía B c
th đô Tripoli, v n là đi m t p k t và kh i hành c a nh ng ngư i
tìm cách di cư trái phép sang châu Âu.
OUTPUT: V đ m tàu x y ra ngoài khơi [Location th tr n
Sabratha], phía B c [Location th đô Tripoli], v n là đi m t p k t
và kh i hành c a nh ng ngư i tìm cách di cư trái phép sang
[Location châu Âu].
Pham Quang Nhat Minh VLSP 2018 NER shared task 4/17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vlsp2018nersharedtaskslide2018mar23-180323103906/75/A-Feature-Based-Model-for-Nested-Named-Entity-Recognition-at-VLSP-2018-NER-Evaluation-Campaign-4-2048.jpg)