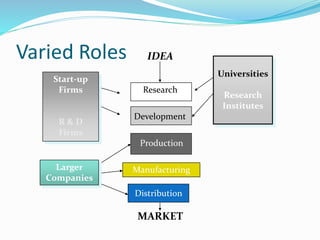
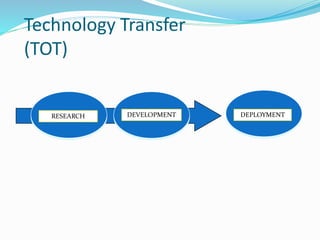
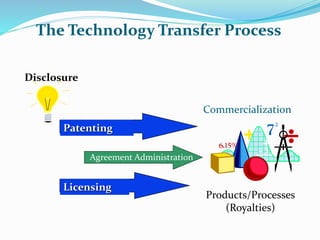
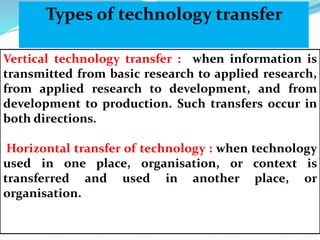
The document discusses technology transfer, defining it as the transfer of research results to develop new products and processes. It states technology transfer is a process that involves different stakeholders at various levels. The document outlines where technology transfer occurs, including universities, research institutes, start-ups, and larger companies. It describes the technology transfer process as moving from research to development to commercialization. The document also discusses different forms and types of technology transfer, as well as necessary conditions for successful technology transfer like direct people-to-people communication and ensuring all parties benefit.


![Definition of Technology Transfer
Technology transfer [and commercialization] is defined
as the transfer of results of basic and applied research to
the design, development, production, and
commercialization of new and improved products,
services or processes. That which is transferred is often
not really technology but rather a particular kind of
knowledge that is a precursor of technology.
The transfer process emphasizes the value and
protection of the intellectual product of the researchers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transferoftechnology-141231020134-conversion-gate01/85/Transfer-of-technology-3-320.jpg)