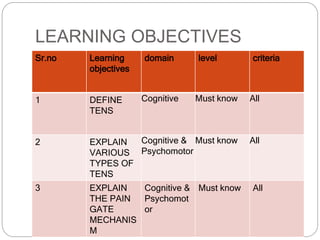
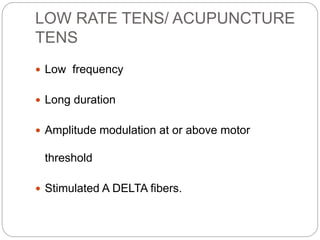
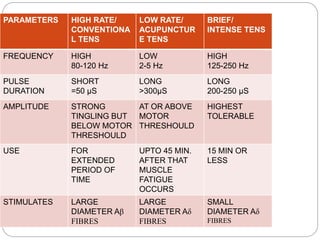
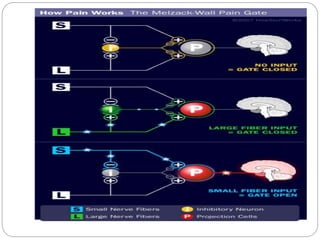
The lecture covers Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), including its definition, types, and the pain gate mechanism. TENS is a noninvasive analgesic technique that applies electrical current through the skin to manage pain, categorized into high rate, low rate, and brief intense TENS. The pain gate mechanism, proposed by Melzack and Wall, explains how pain is modulated in the spinal cord.