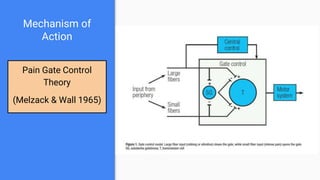
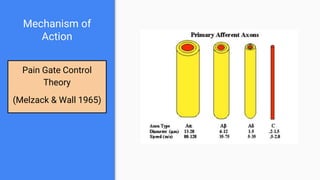
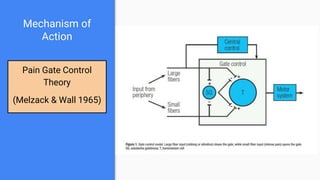
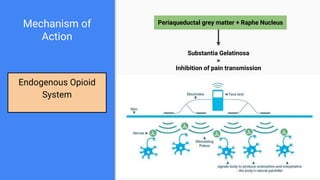
This lecture provides an overview of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy. TENS involves using electric currents to stimulate nerves for pain relief. It works by activating the body's pain gate mechanism or endogenous opioid system. There are different types of TENS machines and techniques depending on factors like frequency and pulse width. Proper electrode placement is also important for targeting specific nerves or areas. TENS is generally safe but should not be used by people with certain medical conditions or over some parts of the body.