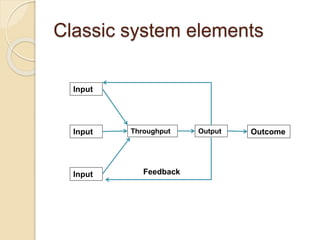
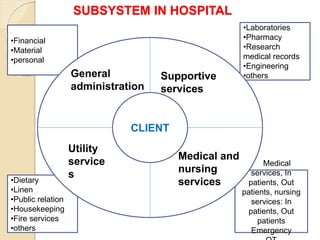
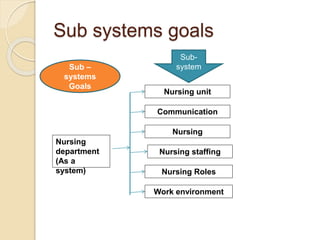
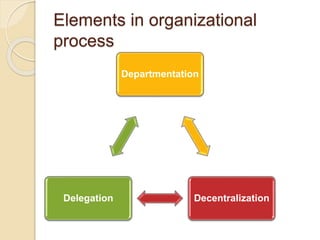
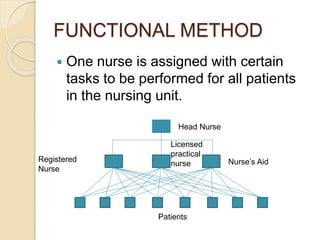
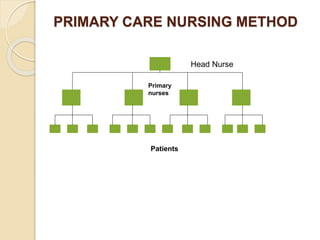
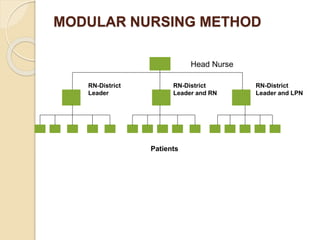
The document discusses various organizational concepts and nursing delivery systems. It defines organization and describes it as a system comprising interrelated subsystems. A hospital is presented as an open system with four major subsystems: general administration, clinical/nursing services, supportive services, and utility services. Various nursing delivery systems are also outlined, including total patient care, functional method, team nursing, primary nursing, and modular nursing. Each system is explained in terms of its approach to patient care assignments, advantages, and disadvantages.