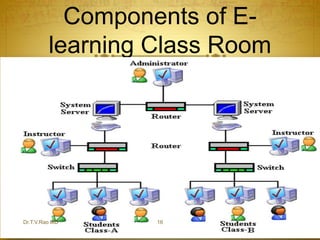
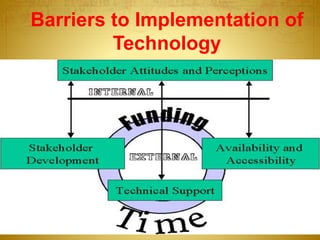
The document discusses the transition from traditional education to e-learning, emphasizing the need for interactive classrooms and the use of technology in education. It highlights the benefits of e-learning, such as flexible learning environments and the integration of medical informatics, while also addressing the challenges and necessary adaptations for educators and students. Ultimately, it underscores the importance of preparing students to be proficient in managing electronic information in their medical careers.